Who’s better for dairy farmers: Harris, with her focus on sustainability, or Trump, with his deregulation and trade deals? Our expert analysis digs in.
The dairy business plays a significant role in the American agricultural economy and is strongly rooted in rural communities. With the 2024 presidential election approaching, dairy experts, ranging from farmers to business executives, are keenly monitoring the contenders and actively participating in the discourse. The stakes are high—decisions taken now about market stability, environmental laws, and trade policies will directly influence the lives and futures of individuals who support this critical business. Will it be Harris, with her emphasis on sustainability and worker rights, or Trump, with his history of deregulation and trade deals? The importance of making informed decisions cannot be emphasized.
| Issue | Kamala Harris | Donald Trump |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Regulations | Focus on stringent environmental regulations to reduce methane emissions and combat climate change. Supports the Green New Deal, which could increase operational costs for farmers. | Emphasis on deregulation, rolling back many environmental protections to lower costs for farmers. Prioritizes immediate economic concerns over long-term environmental impacts. |
| Labor Laws | Advocates for higher minimum wages and stronger labor protections, which could raise labor costs for dairy farmers but improve worker conditions. | Supports deregulation of labor laws to maintain lower costs for farmers. Focuses on reducing undocumented immigration, affecting labor availability for the dairy sector. |
| Trade Policies | Advocates fair trade practices with stringent labor and environmental standards. Emphasizes multilateral agreements, focusing on long-term stability. | Aggressively renegotiates trade deals to benefit American farmers, as seen with USMCA. Focuses on opening markets quickly, but at the risk of trade volatility. |
| Financial Support | Targeted subsidies for adopting sustainable practices. Promotes financial aid for organic farming and complying with environmental regulations. | Broad financial relief measures like the Market Facilitation Program to offset trade impacts. Advocates tax cuts and reduced regulatory burdens. |
| Rural Support | Supports infrastructure improvements and sustainable development programs in rural areas. Focuses on long-term investment in rural resilience. | Emphasizes immediate support through programs like the Farmers to Families Food Box Program. Advocates for expanding broadband and rural development funding. |
Dairy Strongholds: Critical Swing States in 2024’s High-Stakes Election
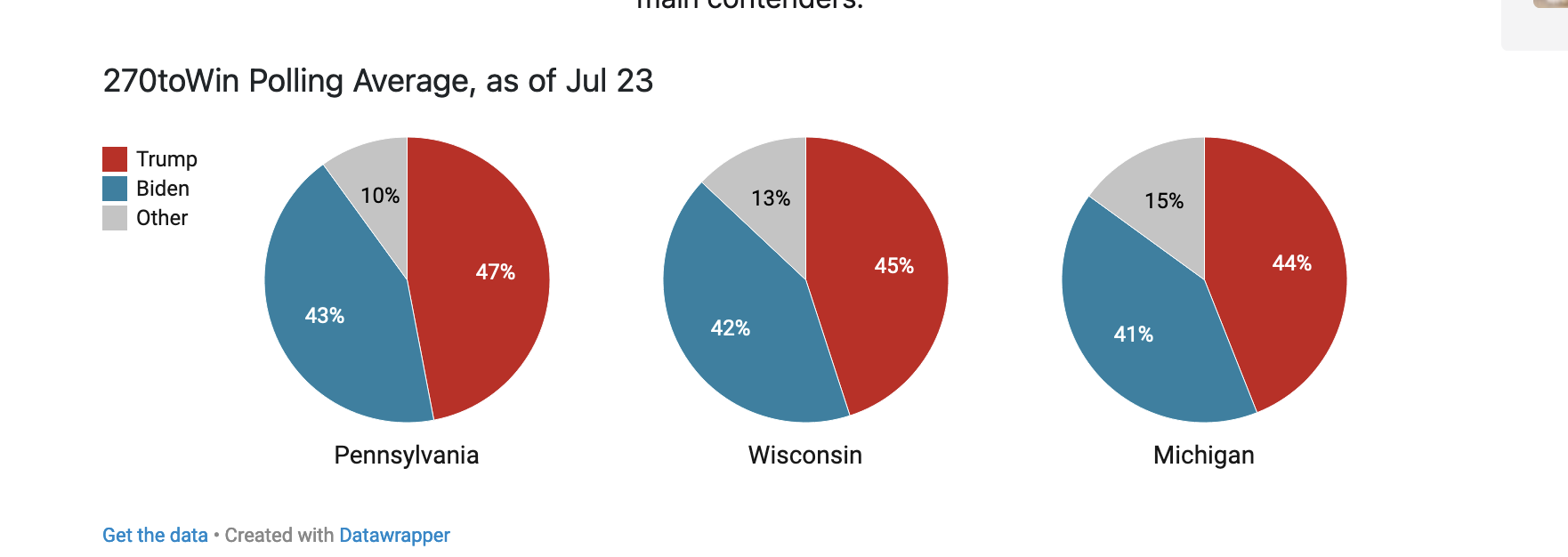
As we approach the approaching election, it is critical to understand the strategic value of dairy farm communities in swing states. States such as Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, and Michigan are not just political battlegrounds but also home to large dairy farms. Wisconsin, frequently termed “America’s Dairyland,” significantly impacts local and national markets, producing more than 30 billion pounds of milk annually. Pennsylvania and Michigan have sizable dairy industries, contributing billions to their respective economies and sustaining thousands of employment.
Dairy producers in these states are at a crossroads regarding policy consequences from both candidates. Given their dire economic situation, their voting decisions have the potential to tip the balance in this close election. Historically, rural and agricultural populations have played critical roles in swing states, with their participation often reflecting the overall state result. The interests and preferences of dairy farmers in these areas surely increase their political relevance, making them crucial campaign targets as both candidates compete for their support.
Navigating the Milk Price Roller Coaster and Trade Turbulence: Challenges in Dairy Farming
The dairy sector, a pillar of the American agricultural economy, confronts several severe difficulties that jeopardize its road to stability and expansion. Despite these challenges, the industry has shown remarkable resilience, instilling hope and optimism. Market volatility, a significant problem, is driven by shifting milk prices and uncertain demand. According to the USDA, dairy producers have seen substantial price fluctuations. Class III milk prices have shifted considerably in recent years, resulting in a roller-coaster impact on farm profits (USDA Report).
Trade disruptions worsen the problem. Tariffs and international trade agreements significantly impact the fortunes of dairy producers. For example, the reworking of NAFTA into the USMCA provided some respite, but persistent trade conflicts, notably with China, continue to create uncertainty. According to the International Dairy Foods Association, export tariffs may reduce US dairy exports by up to 15%, directly affecting farmers’ bottom lines (IDFA Study).
Labor shortages exacerbate the issues. Dairy production is labor-intensive, and many farms struggle to find enough workers, a challenge exacerbated by tighter immigration rules. According to the American Dairy Coalition, foreign workers account for more than half of all dairy labor, and workforce shortages threaten to reduce production efficiency and raise operating costs.
These challenges often create a ripple effect across the sector. For instance, market volatility may strain financial resources, making it harder to retain employees. Conversely, restrictive trade policies may limit market prospects, increasing economic stress and complicating labor management. In the face of these issues, dairy farmers and industry stakeholders must take the lead in strategic planning and proactive solutions. By assuming control and preparing proactively, the industry can overcome these problems and emerge stronger.
Kamala Harris’s Multidimensional Policy Impact on Dairy Farming: An In-Depth Look
Kamala Harris’ dairy-related policies are complex, emphasizing environmental objectives, labor legislation, and trade policy. Let us break them down to understand how they could affect dairy producers.
Environmental Goals: Striking a Tough Balance
Harris is dedicated to robust climate action, campaigning for steps that would drastically cut greenhouse gas emissions. Her support for ideas like the Green New Deal aims to enact broad environmental improvements. This means stricter methane emissions, water consumption, and waste management restrictions for dairy farms.
While such actions may enhance long-term sustainability, they provide immediate financial concerns. Compliance with these requirements is likely to raise operating expenses. Farmers may need to invest in new technology or change existing processes, which may be expensive and time-consuming. However, there are potential benefits: these regulations may create new income sources via government incentives for adopting green technology or sustainable agricultural techniques, instilling a sense of optimism about the future.
Labor Laws: A Double-Edged Sword
Harris favors stricter labor legislation, such as increasing the federal minimum wage and guaranteeing safer working conditions. This position may benefit farm workers, who comprise a sizable chunk of the dairy farm workforce. However, dairy producers face a double-edged sword.
Improved labor regulations may force farmers to pay higher salaries and provide more extensive benefits. While this might result in a more steady and committed staff, it also raises operating expenses. These additional costs may pressure profit margins, particularly for small—to mid-sized dairy enterprises that rely primarily on human labor. As a result, farm owners would need to weigh these expenditures against possible increases in production and labor pleasure.
Trade Policies: Navigating New Waters
Harris promotes fair trade policies, which include strict labor and environmental requirements. Her strategy is to expand markets for American goods while safeguarding domestic interests. This might boost the dairy business by leveling the playing field with overseas rivals who may face fewer regulations.
However, renegotiating trade treaties to integrate these norms may result in times of uncertainty. Transitional periods may restrict market access until new agreements are firmly in place, temporarily reducing export volumes. However, if appropriately implemented, Harris’s fair trade proposals might stabilize and grow market prospects for American dairy producers long-term, instilling hope about future market prospects.
To summarize, Kamala Harris’ ideas bring immediate obstacles and possible long-term advantages. Dairy producers must carefully balance the effects of higher regulatory and labor expenses with the potential for long-term sustainability and fairer trading practices. As we approach this election, we must analyze how her ideas may connect with your operations and future objectives.
The Dairy Industry Under Trump: Trade Triumphs, Deregulation, and Rural Support
Donald Trump’s experience with the dairy business provides a powerful case study on the effects of trade agreements, deregulation, and rural support. Let’s examine how these rules have influenced the sector and what they signify for dairy producers.
First and foremost, Trump’s most significant major victory in trade agreements has been reworking NAFTA into the USMCA. This deal improved market access to Canada, previously a bone of contention for American dairy producers. The revised conditions were described as a “massive win” for the sector, promising stability and new export potential [Reuters]. The Dairy Farmers of America hailed this decision, citing the much-needed market stability it provided [Dairy Farmers of America].
Deregulation has been another defining feature of Trump’s presidency. Rolling down environmental rules has been a two-edged sword. On the one hand, cutting red tape has provided dairy producers with more operational freedom and cheaper expenses. However, some opponents contend that these changes may jeopardize long-term viability. Tom Vilsack, CEO of the United States Dairy Export Council, underlined that lower rules enable farmers to innovate while remaining internationally competitive [U.S. Dairy Export Council].
Support for rural areas has also been a priority. Trump hoped to stimulate rural economies by extending internet access and boosting agricultural R&D investment. The Farmers to Household Food Box Program, a COVID-19 relief tool, helped farmers and vulnerable households by redistributing unsold dairy products. While not without practical obstacles, many saw this campaign as a vital lifeline during the epidemic.
Trump’s initiatives immediately affected dairy farmers, creating a business-friendly climate suited to their specific needs and interests. Reduced restrictions and freshly negotiated trade agreements helped to calm turbulent markets, providing much-needed respite. However, the long-term implications raise concerns about sustainability and environmental health. Balancing economic viability and sustainability practices remains difficult as farmers adopt fewer regulatory restraints.
Overall, Trump’s policies have matched dairy farmers’ immediate demands well, prioritizing profitability, market access, and lower operating costs. These actions have created a favorable climate, but the consequences for long-term sustainability must be carefully considered as the sector progresses.
Understanding Historical Context: Harris vs. Trump on Agriculture and Dairy Farming
Understanding the historical background of Harris’ and Trump’s previous acts and policies in agriculture and dairy farming is critical for projecting their future influence on the sector. Let us review their records to get a better idea.
While Kamala Harris has no direct experience with agriculture, she has been outspoken about her environmental attitude. During her term in the Senate, she co-sponsored the Green New Deal, which seeks to combat climate change via broad economic and ecological changes (Congress.gov). This emphasis on sustainability may cause tension with conventional farming techniques, which depend significantly on present environmental rules. Her support for these initiatives shows that she may emphasize ecological issues, which might lead to harsher dairy sector regulations.
In contrast, Donald Trump has a well-documented track record of promoting agriculture via deregulation and trade policies. His government repealed various environmental restrictions, stating they were costly to farmers (WhiteHouse.gov). Trump’s renegotiation of NAFTA, now known as USMCA, featured dairy measures that benefited American farmers and expanded export potential (USTR.gov). These policies reflect a more industry-friendly approach, focusing on profitability and less government intrusion.
We can see how each contender could oversee the dairy industry by examining their backgrounds. Harris’ support for environmental changes creates both chances and hazards, while Trump’s past term constantly emphasizes deregulation and trade gains. These circumstances pave the way for a tight and effective campaign on behalf of dairy producers. Remember these concepts as we look at how they could affect your livelihood and the dairy business as a whole.
Policy Showdown: Harris’s Environmental Ambitions vs. Trump’s Farmer-Friendly Regulations
When we examine Kamala Harris and Donald Trump’s ideas, we see significant discrepancies, notably in dairy farming. Harris has often highlighted environmental sustainability, which aligns with larger climate aims. However, her emphasis on strict ecological standards may result in additional expenditures for dairy producers. Her support for the Green New Deal, for example, promises to cut greenhouse gas emissions while potentially increasing farmers’ operating expenses due to rising energy prices and compliance costs.
On the other hand, Trump’s policies have been more beneficial to farmers. His administration’s attempts to reduce regulatory barriers have benefitted the agriculture industry, namely dairy farming. The repeal of WOTUS (Waters of the United States) is a classic example of lowering compliance costs while providing farmers more control over their property. Furthermore, his trade policies, notably the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement), have expanded dairy producers’ market access. This is critical for bolstering dairy exports, which have grown dramatically during Trump’s leadership.
Furthermore, Harris’ dedication to shifting away from fossil fuels may put transition costs on farmers, who depend significantly on fuel for machines. In contrast, Trump’s policy to preserve low energy prices has benefited these farmers by assuring reduced operating expenses.
In short, whereas Harris’ environmental emphasis reflects long-term sustainability aims, Trump’s plans meet dairy farmers’ urgent economic demands. Trump aligns with the industry’s present requirements by lowering restrictions and promoting trade, making him a more appealing choice for dairy producers seeking quick relief and expansion potential.
Trump’s Legacy vs. Harris’s Vision: Navigating Dairy’s Complex Future
Under Trump’s administration, the dairy business saw both obstacles and development. The USDA reported a 1.3% yearly growth in milk output from 2017 to 2020 [USDA]. During this period, the Dairy Margin Protection Program was reorganized, which helped many farmers by providing improved risk management tools. Furthermore, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) opened up new markets, notably in Canada, which was a massive success for dairy producers, resulting in almost 25% more exports in 2020 [International Dairy Foods Association].
In contrast, Harris’ suggested policies emphasize serious climate action, which might substantially affect the dairy business. For example, according to the Dairy Producers of America, her ideas for severe methane emission laws might raise operating expenses for dairy producers, possibly increasing production costs by 5-10%. Her focus on plant-based alternatives can potentially reduce dairy consumption by 3-5% in the next decade (USDA forecasts).
These numbers present a clear picture: although Trump’s term had mixed outcomes, with significant benefits from trade deals and policy restructuring, Harris’s plans may face significant hurdles due to increased environmental restrictions and market upheavals. The issue for dairy producers ultimately comes down to evaluating immediate rewards against long-term sustainability implications.
The Regulatory Crossroads: Navigating Harris’s Sustainability and Trump’s Deregulation
Understanding each candidate’s attitude on regulation allows us to forecast how they will impact the dairy industry’s future. Environmental restrictions are a significant problem.
Kamala Harris promotes environmental sustainability, which might lead to harsher dairy farm regulations. Increased controls on greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, and waste management may result in more extraordinary operating expenses. While these efforts promote environmental friendliness, they may burden already low business margins. However, adopting sustainable methods may result in incentives and subsidies to encourage green technology, placing wise farmers for long-term success.
Donald Trump’s strategy relies primarily on deregulation. Trump hopes to minimize compliance costs by reducing environmental regulations, giving dairy producers greater operational freedom. Critics fear this strategy might cause long-term ecological damage, reducing agricultural yield. Nonetheless, reducing red tape in the near term implies cheaper expenses and perhaps increased profitability.
Harris favors stricter labor rules, including increasing the federal minimum wage. While this approach benefits workers, it may entail more significant labor costs for dairy producers, further reducing margins. However, improved working conditions may result in a more dependable and productive staff.
Trump’s track record demonstrates a willingness to ease labor restrictions, which may help lower expenses. However, his strict immigration policies may restrict the supply of migrant labor, on which the dairy sector is strongly reliant. As a consequence, manpower shortages may arise, reducing manufacturing efficiency.
Trade agreements are another critical area of regulatory effect. Harris promotes fair trade policies, which may open new markets and include transitional risks to exporters. Her diplomatic strategy promotes global accords prioritizing labor and environmental norms, perhaps leading to more steady, if slower, market development.
Trump’s aggressive trade renegotiations, represented by the USMCA, are intended to improve American dairy export conditions. His administration’s emphasis on bilateral agreements seeks instant rewards but often results in volatility and retaliatory levies that disrupt markets. Nonetheless, his prompt measures may immediately improve market access in essential areas.
The regulatory climate under each candidate confronts dairy producers with a trade-off between immediate assistance and long-term stability. As the election approaches, choosing which course best meets your farm’s requirements and ideals is critical.
Financial Uplift: Harris’s Sustainability Focus vs. Trump’s Immediate Relief
Both candidates have distinct perspectives on subsidies and financial assistance. Kamala Harris’ strategy focuses on targeted incentives for sustainable practices and encouraging smaller, more diverse farms. Her programs include financial assistance for farmers transitioning to organic techniques or installing environmentally friendly measures and tax breaks for those that follow more rigid environmental rules. This is consistent with her overall environmental and climatic aims, but it may face opposition from larger-scale dairy operations who want more immediate and comprehensive help.
In contrast, Donald Trump has consistently supported more excellent financial relief and deregulation. During his presidency, he increased help for dairy producers harmed by tariffs and trade disputes via programs like the Market Facilitation Program (MFP), which gave direct financial aid. In addition, Trump’s administration argued for considerable tax cuts to help larger tax-sensitive enterprises. There is also a strong emphasis on removing regulatory barriers, which supposedly reduces expenses and operational overhead for dairy producers.
Which strategy seems to be more robust? If you’re a dairy farmer who prefers rapid financial relief over regulatory action, Trump’s program is most likely in your best interests. His record of direct subsidy programs and tax breaks protects against market volatility and operating expenses. While Harris’ policies are forward-thinking and sustainability-focused, they may be more helpful in the long term but need a change in operating techniques and likely higher upfront expenses.
Trade Tactics: Trump’s Aggression vs. Harris’s Diplomacy
International trade policies are critical to the dairy business. They may make the difference between the sector’s success and failure. So, how do Trump’s trade agreements compare to Harris’ approach to international relations?
During his administration, Trump made substantial changes to international commerce. He renegotiated NAFTA to create the USMCA, which improved circumstances for American dairy farmers by expanding Canadian markets and strengthening connections with Mexico. His firm position in China paid off, with China agreeing to buy more U.S. dairy goods under trade accords [Agriculture.com]. However, these trade conflicts introduced unpredictability and retribution, occasionally harming farmers.
Harris, on the other hand, views international affairs through the lens of diplomacy and multilateral accords. Think about how this affects dairy exports. While less aggressive, this method may result in gradual, more consistent earnings rather than sudden, high-stakes victories and losses. For example, a Harris administration may concentrate on forming coalitions to eliminate minor trade obstacles, sometimes taking time and significant international effort.
Dairy producers may prefer Trump’s bold, high-risk, high-reward techniques to Harris’s steady diplomatic approach. Which method will best benefit your farm in the long run?
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, both Kamala Harris and Donald Trump provide unique benefits and difficulties for the dairy business. Harris stresses environmental sustainability via initiatives that may result in long-term advantages but may have current costs. Her position on labor rights seeks to enhance working conditions while perhaps increasing farmers’ operating costs. In contrast, Trump’s track record includes deregulation and trade deals such as the USMCA, which have offered immediate relief and expanded market prospects for dairy exporters. His initiatives have aimed to decrease regulatory burdens and provide financial assistance closely aligned with dairy producers’ urgent needs.
Dairy producers face a vital decision: temporary alleviation against long-term viability. Harris provides a forward-looking vision that necessitates changes and investments in green technology and labor standards but promises long-term advantages. Conversely, Trump takes a more realistic and business-friendly approach, addressing farmers’ short-term financial and regulatory concerns.
As the election approaches, dairy producers must carefully evaluate these issues. Consider your present problems and future goals. Which candidate’s policies are most aligned with your values and goals? Your choice will affect not just your livelihood but also the future of the dairy sector.
Key Takeaways:
- Dairy farmers face complex challenges, including market volatility, trade disruptions, and labor shortages.
- Harris’s policies focus on environmental sustainability, which could lead to stricter regulations and higher operational costs.
- Harris’s support for stronger labor protections might increase labor costs but could improve worker conditions and retention.
- Trump’s trade negotiations, such as USMCA, have provided dairy exports better market access and stability.
- Trump’s deregulation efforts aim to reduce costs and boost operational flexibility for dairy farmers.
- The historical context shows that Harris prioritizes environmental reforms while Trump focuses on deregulation and trade benefits.
- Subsidies and financial support differ significantly, with Harris promoting sustainable practices and Trump offering more immediate monetary relief.
- International trade strategies vary, with Trump’s aggressive and high-risk approach, while Harris’s emphasizes diplomatic diplomacy.
- The decision for dairy farmers hinges on balancing immediate economic viability with long-term sustainability.
Summary:
The 2024 presidential election presents a crucial decision for dairy farmers as they weigh the immediate economic relief promised by Donald Trump’s deregulation and aggressive trade policies against Kamala Harris’s long-term vision for sustainability and environmental responsibility. While Trump offers a track record of quick, impactful changes benefiting rural communities and dairy exports, Harris’s approach insists on balancing economic viability with stringent climate action and fair labor practices. Each path carries distinct implications for the dairy industry’s future, demanding careful consideration from professionals as they navigate these complex and heavily consequential choices.
Learn more:
- Trump vs Biden: Who is the Best Presidential Choice for Dairy Farmers?
- How the 2024 Presidential Election Could Reshape Agricultural Marketing Strategies
- American Dairy Farmers Grapple with Trade War and Immigration Policies: The Fight to Stay Afloat
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Bullvine Daily is your essential e-zine for staying ahead in the dairy industry. With over 30,000 subscribers, we bring you the week’s top news, helping you manage tasks efficiently. Stay informed about milk production, tech adoption, and more, so you can concentrate on your dairy operations.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!













 David Brown, like all of us, had his flaws. Endowed with remarkable skills as a breeder, showman, and promoter, he was often hailed as the finest cattleman of his era. Growing up on Browndale Farms in Paris, Ontario, he had towering expectations to meet. His father, R.F. Brown, was a luminary in the dairy world, winning the esteemed Curtis Clark Achievement Award in 1988 and the Klussendorf Trophy at the 1993 World Dairy Expo. As one of Canada’s most successful breeders, R.F. clinched Premier Breeder and Exhibitor honors at the World Dairy Expo and the Royal Winter Fair. His accolades included five Grand Champions at the Royal Winter Fair: Green Elms Echo Christina (1972 and dam of Browndale Commissioner), Vanlea Nugget Joyce (1974), Marfield Marquis Molly (1978), and Du-Ma-Ti Valiant Boots Jewel (1988). David certainly had big shoes to fill. And fill them he did. His list of accomplishments was extensive: He led Ontario’s top herd in production in 1991, bred two All-Canadian Breeder’s Herd groups, and produced the All-American Best Three Females in 1998. He was twice crowned Premier Breeder at the International Holstein Show and accumulated 92 awards in All-Canadian and All-American contests from 1986 through 2004. Yet, despite two auction sales in 1991 and 1996 aimed at reducing his debts, financial relief was elusive. Over time, his wife left him, his children moved away, and his prized cattle were sold off. Eventually, David relocated to Colombia, where he passed away. Views on Brown are mixed—some saw him as a charming inspiration, while others regarded him as a rule-bending showman or an irresponsible debtor. Nonetheless, his rapid ascent and remarkable achievements in his lifetime are indisputable. Many wealthy individuals have invested vast sums of money into the cattle industry, chasing the same recognition, only to leave empty-handed. What distinguished David Brown was his nearly mystical talent for preparing animals for the show ring and transforming them into champions.
David Brown, like all of us, had his flaws. Endowed with remarkable skills as a breeder, showman, and promoter, he was often hailed as the finest cattleman of his era. Growing up on Browndale Farms in Paris, Ontario, he had towering expectations to meet. His father, R.F. Brown, was a luminary in the dairy world, winning the esteemed Curtis Clark Achievement Award in 1988 and the Klussendorf Trophy at the 1993 World Dairy Expo. As one of Canada’s most successful breeders, R.F. clinched Premier Breeder and Exhibitor honors at the World Dairy Expo and the Royal Winter Fair. His accolades included five Grand Champions at the Royal Winter Fair: Green Elms Echo Christina (1972 and dam of Browndale Commissioner), Vanlea Nugget Joyce (1974), Marfield Marquis Molly (1978), and Du-Ma-Ti Valiant Boots Jewel (1988). David certainly had big shoes to fill. And fill them he did. His list of accomplishments was extensive: He led Ontario’s top herd in production in 1991, bred two All-Canadian Breeder’s Herd groups, and produced the All-American Best Three Females in 1998. He was twice crowned Premier Breeder at the International Holstein Show and accumulated 92 awards in All-Canadian and All-American contests from 1986 through 2004. Yet, despite two auction sales in 1991 and 1996 aimed at reducing his debts, financial relief was elusive. Over time, his wife left him, his children moved away, and his prized cattle were sold off. Eventually, David relocated to Colombia, where he passed away. Views on Brown are mixed—some saw him as a charming inspiration, while others regarded him as a rule-bending showman or an irresponsible debtor. Nonetheless, his rapid ascent and remarkable achievements in his lifetime are indisputable. Many wealthy individuals have invested vast sums of money into the cattle industry, chasing the same recognition, only to leave empty-handed. What distinguished David Brown was his nearly mystical talent for preparing animals for the show ring and transforming them into champions. Edward Young Morwick, a distinguished author, cattle breeder, and lawyer, was born in 1945 on the Holstein dairy farm owned by his father, Hugh G. Morwick. His early memories of his mother carrying him through the cow aisles profoundly shaped his trajectory. Although Edward pursued a career in law, excelling immediately by finishing second out of 306 in his first year, he harbored a deep-seated passion for journalism. This led to his later work chronicling Holstein’s cow history. His seminal work, “The Chosen Breed and The Holstein History,” stands as a cornerstone for those delving into the evolution of the North American Holstein breed. In it, he compellingly argues that the most influential bulls were those of the early historical period. (Read more:
Edward Young Morwick, a distinguished author, cattle breeder, and lawyer, was born in 1945 on the Holstein dairy farm owned by his father, Hugh G. Morwick. His early memories of his mother carrying him through the cow aisles profoundly shaped his trajectory. Although Edward pursued a career in law, excelling immediately by finishing second out of 306 in his first year, he harbored a deep-seated passion for journalism. This led to his later work chronicling Holstein’s cow history. His seminal work, “The Chosen Breed and The Holstein History,” stands as a cornerstone for those delving into the evolution of the North American Holstein breed. In it, he compellingly argues that the most influential bulls were those of the early historical period. (Read more: 









