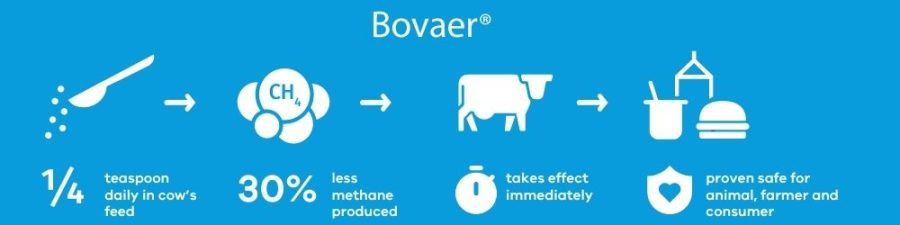
Learn how the FDA-approved Bovaer supplement can reduce methane emissions from dairy cattle by 30%. Are you prepared to transform your dairy farm into a model of sustainability and profitability?
“Bovaer’s approval signifies a pivotal shift for sustainable dairy farming, offering a viable solution to one of agriculture’s most pressing environmental challenges,” said Katie Cook, Vice President of livestock Sustainability and Farm Animal Marketing at Elanco.
By adding Bovaer to cattle feed, dairy farmers can reduce methane emissions, a key climate concern. This supplement supports the dairy industry’s sustainability goals. It helps farmers make more money by joining environmental programs and voluntary carbon markets.
Innovative Breakthrough: Bovaer Approved to Combat Methane Emissions in Dairy Farming
Bovaer, also called 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP), is a new feed additive made to cut down methane emissions from dairy cows. The development of Bovaer is a big step forward in agricultural science, aimed at solving a major environmental problem caused by livestock farming. Bovaer’s journey from idea to approval involved a lot of research and testing. Created by dsm-Firmenich, the project included cooperation with experts in animal nutrition and environmental science worldwide. Over the years, many trials showed Bovaer’s effectiveness and safety, leading to a multi-year review by the FDA. This detailed review ensured that Bovaer met all the strict safety and effectiveness standards, resulting in its recent approval for use in the US dairy industry. This approval is critical in pushing for more sustainable dairy farming practices. It highlights the potential of science-driven solutions in fighting climate change.
FDA’s Rigorous and Comprehensive Review Process for Bovaer Ensures Safety and Efficacy
The FDA’s review of Bovaer was comprehensive. It initially focused on preclinical trials to assess 3-NOP’s chemical properties and impacts on animal health and the environment. Detailed toxicology assessments confirmed the supplement’s safety at recommended dosages.
Subsequent controlled clinical trials on various dairy farms evaluated Bovaer’s efficacy in reducing methane emissions and its effects on cow health, milk production, and quality. These trials demonstrated a 30% reduction in methane emissions.
The FDA also reviewed dsm-firmenich’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures, ensuring the supplement’s consistency and purity. Environmental assessments confirmed no adverse impact on soil or water systems.
Having met these rigorous safety and effectiveness standards, Bovaer presents a viable methane-reducing solution for the dairy industry. The FDA’s approval marks a significant advancement, enabling broader adoption of this innovative technology in the United States.
Bovaer’s Biochemical Mechanism: A Closer Look at the Enzyme Inhibition in Ruminant Methane Production
Bovaer functions inside a cow’s rumen, focusing on a critical enzyme involved in methane production. The rumen is a unique part of the stomach in animals like cows, containing microorganisms that break down plant material. Methane, a byproduct of this process, is mainly produced by microorganisms called methanogens.
The compound 3-NOP, or Bovaer, stops the enzyme methyl-coenzyme M reductase (MCR), essential for making methane from carbon dioxide and hydrogen. By attaching to the active part of MCR, Bovaer blocks its regular activity, preventing the creation of methane.
As a result, the hydrogen that would have made methane is used differently, boosting the production of volatile fatty acids. These acids are then absorbed and used by the cow for energy. This reduces methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, and increases cows’ energy efficiency, making Bovaer a significant step forward for sustainable dairy farming.
The Environmental Imperative: Unlocking Climate Benefits Through Methane Reduction in Dairy Farming
Reducing methane emissions from dairy cattle holds significant environmental potential, especially in the fight against climate change. Methane is about 27 times more effective than carbon dioxide at trapping heat. Since methane has a short atmospheric lifespan of roughly a decade, cutting its emissions can yield rapid climate benefits.
Lowering methane emissions from dairy operations enhances agricultural sustainability. Fewer greenhouse gases mean less severe climate changes and more stable growing conditions, supporting food security.
Reducing methane also aligns with global climate initiatives, like the Paris Accord. Innovations such as Bovaer help nations meet these targets, promoting environmental stewardship and making the dairy industry a leader in sustainability.
Methane-reducing solutions like Bovaer are crucial for a more resilient and sustainable agricultural future. By tackling a major environmental issue, stakeholders contribute meaningfully to fighting global warming and benefit economically from new programs and carbon markets.
Strategic Alliances and Market Readiness: Preparing for Bovaer’s Landmark Launch in Late 2024
As a result of years of hard work and review, Bovaer will launch commercially in late 2024. This important initiative will bring together expertise from dsm-Firmenich and Elanco Animal Health Inc. The goal is to make the methane-reducing supplement sustainably produced and widely available. DSM-Firmenich, which created Bovaer, uses its advanced biochemical knowledge to manufacture the supplement to the highest standards. On the other hand, Elanco Animal Health Inc. will use its vast distribution network and market presence across North America, making Bovaer accessible to dairy farmers who want to adopt sustainable practices. This collaboration between these industry leaders aims to drive a significant move towards more environmentally friendly dairy farming.
Practical Implementation and Efficacy: Maximizing Bovaer’s Climate Impact in Dairy Farming
Understanding how to use Bovaer and its effectiveness is essential for dairy farmers considering this new option. To put it into practice, farmers must give one tablespoon per lactating cow daily. This small change in daily feeding can reduce methane emissions by about 30%. In simpler terms, this means each cow would produce 1.2 metric tons less CO2e each year, showing the significant positive impact of this supplement on the climate when used widely.
Turning Point in Dairy Farming: Bovaer’s Role in Environmental Stewardship and Economic Sustainability
The approval and impending launch of Bovaer mark a transformative shift in dairy farming. Bovaer offers a powerful tool to reduce the industry’s environmental footprint. For producers, integrating Bovaer into daily operations is not just about meeting stringent ecological regulations; it’s a tangible step toward sustainability.
Governments worldwide are tightening regulations on greenhouse gas emissions, and dairy farmers face increasing pressure to demonstrate their environmental stewardship. By significantly reducing methane emissions—a key contributor to global warming—Bovaer provides a direct path for farmers to meet and exceed these requirements, thereby avoiding penalties and enhancing the sector’s reputation as a proactive climate leader.
Financial incentives tied to environmental performance are significant. Using Bovaer allows farmers to tap into voluntary carbon markets, where methane reductions can be sold as carbon credits. This offers both additional revenue and promotes wider adoption of climate-smart practices. Earning up to $20 or more per lactating cow annually adds a compelling economic benefit to the environmental gains.
Beyond immediate financial returns, Bovaer’s broader adoption will likely inspire innovation and investment in sustainable farming technologies. By setting a new standard for methane reduction, Bovaer can catalyze further advancements in eco-friendly solutions, contributing to a more resilient agricultural sector.
Ultimately, Bovaer’s approval and US market introduction symbolize a pivotal moment for the dairy industry, highlighting the crucial intersection of environmental responsibility and economic viability. As farmers adopt this groundbreaking supplement, ripple effects will be felt across regulatory frameworks, market dynamics, and the global effort to mitigate climate change.
Financial Incentives and Economic Viability: Unlocking New Revenue Streams with Bovaer for Dairy Producers
From a financial perspective, the introduction of Bovaer presents compelling opportunities for dairy producers. The supplement is cost-effective, with an extra cost of only a few cents per gallon of milk per day. Significant environmental and economic returns balance this small investment. By adding Bovaer to their feed, dairy farmers can achieve an annual return of $20 or more per lactating cow. This return comes from benefits like joining voluntary carbon markets and working with USDA and state conservation programs, which can promote sustainability and create more revenue streams.
Expert Commentary: Katie Cook Sheds Light on Bovaer’s Crucial Impact on Sustainable Dairy Farming
Katie Cook, Vice President of Livestock Sustainability and Farm Animal Marketing at Elanco, emphasizes the critical role Bovaer plays in promoting sustainable dairy farming. She states, “For just a few cents more per gallon of milk, Bovaer provides a practical solution for dairy producers to cut methane emissions and meet the climate goals of food companies and consumer demands for eco-friendly products.”
Cook adds, “By joining voluntary carbon markets and using USDA and state conservation programs, dairy farmers can make sustainability practices profitable. Using Bovaer not only helps the environment but can also bring in an annual return of $20 or more per lactating cow, showing its economic and environmental value.” Introducing Bovaer is a significant step forward, creating a self-sustaining carbon market for American agriculture.
The Bottom Line
The FDA approval of Bovaer is a big step for the dairy industry and the environment. Bovaer can significantly cut methane emissions, tackle a major environmental issue, and help fight climate change. The FDA’s thorough review ensures this new solution is safe and effective, with Elanco set to launch it in late 2024. By using Bovaer in dairy farming practices, farmers can reduce methane emissions and gain economic benefits from environmental programs and carbon markets. This dual advantage shows Bovaer’s potential to revolutionize the dairy sector, moving towards a more sustainable and economically sound future.
Key Takeaways:
- Regulatory Milestone: Bovaer, also known as 3-NOP, receives FDA approval after an extensive multi-year review.
- Environmental Impact: One tablespoon per lactating cow per day can reduce methane emissions by 30%, equivalent to 1.2 metric tons of CO2e annually.
- Biochemical Mechanism: The supplement works by inhibiting an enzyme in the cow’s rumen responsible for methane formation.
- Economic Benefits: Potential annual return of $20 or more per lactating cow through engagement in carbon markets and environmental programs.
- Market Readiness: Bovaer is slated for a commercial launch in North America by Elanco during Q3 2024.











