Find out why ignoring the June DMC margin could hurt your profits. Ready to maximize your premiums? Learn how to secure your earnings.
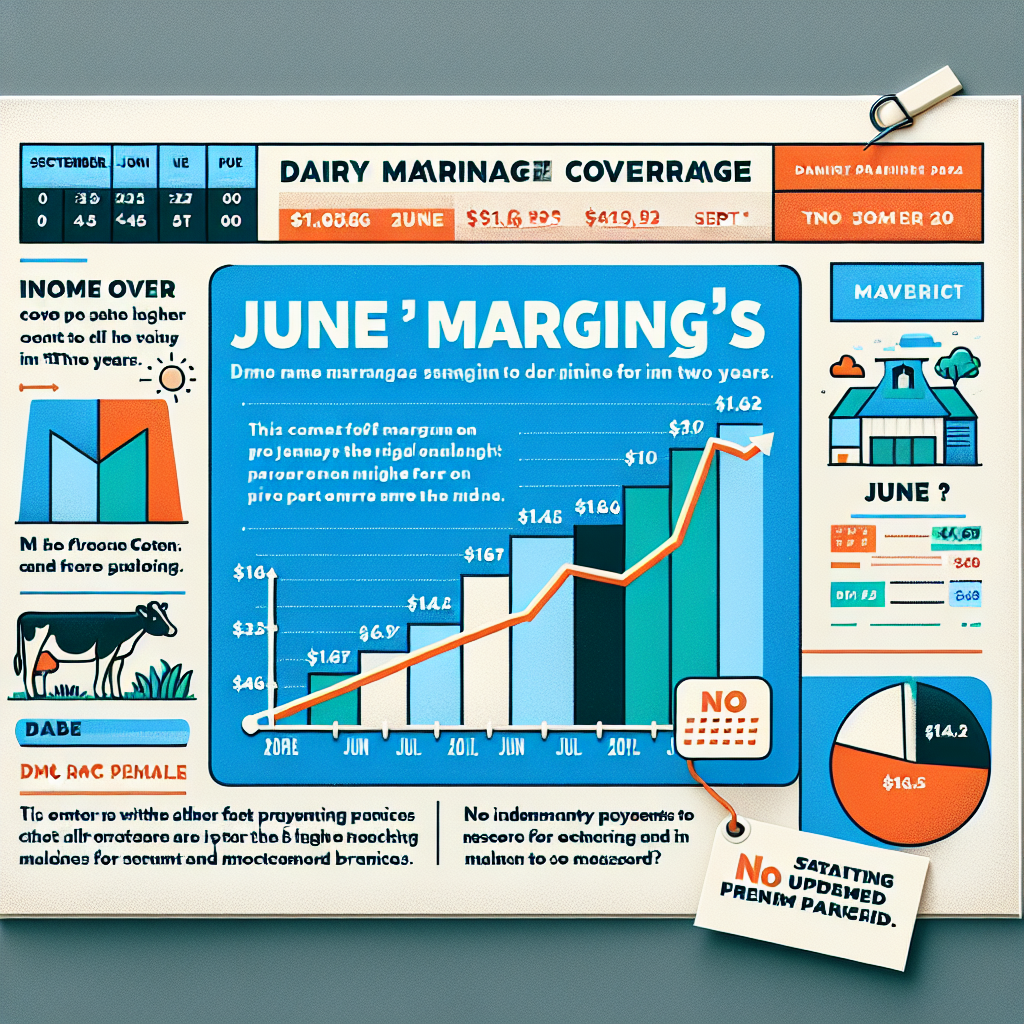
Summary: With June’s Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC) margin surpassing $11.66 per hundredweight (cwt), dairy farmers are witnessing some of the most favorable conditions in recent years. Predictions indicate record-breaking DMC margins peaking at $14.52 per cwt in October 2024. While the income over feed cost was the highest in two years, no indemnity payments were necessary for June. Farmers should mark their calendars: all outstanding DMC premium balances must be settled by September 1. Finally, it’s imperative to stay updated with these trends to maximize the benefits of the DMC program and ensure timely payments.
- June’s margin of $11.66 per cwt is the most favorable in two years, eliminating the need for indemnity payments for the month.
- Predicted margins are set to peak at a record-breaking $14.52 per cwt in October 2024.
- Dairy farmers must clear all outstanding DMC premium balances by September 1.
- Farmers should stay informed about the DMC program trends to optimize their benefits and ensure timely payments.
If you’re in the dairy industry, you understand that margins are as important as feeding and milking your cows. June’s Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC) margin reached $11.66 per cwt, which is critical to your bottom line. But how does this affect your farm?
The Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC) program, established in the 2018 Farm Bill, protects you from fluctuating milk and feed costs. It bridges the difference between the all-milk price and the average feed cost, allowing your farm to stay profitable despite market changes. The DMC program is similar to an insurance policy for your paycheck; it will not make you wealthy but will keep you from going bankrupt.
- A June margin of $11.66 per cwt provides better cushioning against feed price hikes.
- The DMC payouts can offset lower milk prices, keeping your farm afloat.
- Understanding these margins lets you strategize better for the rest of the year.
Now is the time to study these statistics and prepare to make educated choices that will affect your profitability. Stay tuned as we break down the details and provide practical insights.
| Month | DMC Margin ($ per CWT) | Milk Price ($ per CWT) | Feed Cost ($ per CWT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 9.87 | 18.96 | 9.09 |
| February | 10.56 | 19.45 | 8.89 |
| March | 11.34 | 20.21 | 8.87 |
| April | 10.78 | 19.74 | 8.96 |
| May | 11.45 | 20.63 | 9.18 |
| June | 11.66 | 21.09 | 9.43 |
June’s DMC Margin Surpasses $11.66 per CWT.
With June’s Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC) margin of $11.66 per hundredweight (cwt), farmers are seeing the most significant income over feed costs (IOFC) in two years. IOFC measures your farm’s profitability by subtracting the feed cost from the revenue generated by selling milk. This data suggests a relatively robust situation for dairy farms, with a $1.14 gain per cwt since May.
Several variables led to the positive margin. First, the milk price increased to $22.80 per cwt, increasing margins. Furthermore, the USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) Agricultural Prices report, issued on July 31, offered vital information on feed prices, which are critical in estimating DMC margins.
For dairy producers, this margin results in a temporary stoppage of indemnity payments in June since the revenue above feed cost exceeded the payout threshold. While the lack of indemnity payments may seem alarming, it is a good indicator showing strong market conditions and profitability without further assistance.
Favorable margins like this stabilize the dairy business, encouraging sustained output and supporting farm upgrades and development investments. However, dairy producers must be cautious since market circumstances change quickly, demanding continual milk prices and feed costs monitoring. As usual, paying premium amounts by the September 1 deadline is critical for continued participation in the DMC program, which provides a safety net against potential market turbulence.
Don’t Miss Out on These Record-Breaking DMC Margins!
Ignoring the substantial June DMC margin may have a severe financial impact. With the DMC margin over $11.66 per cwt and milk prices approaching $22.80 per cwt, ignoring these figures means losing significant profit opportunities. The income over feed cost (IOFC) has reached a two-year high, wiping out the June indemnity payments and indicating a prosperous time.
Consider this: a typical dairy company in the DMC program expects to receive around $2,383 in payments this year. Please capitalize on higher milk prices in June to avoid a loss of profits. A farm producing 250,000 pounds of milk per month may increase income by $2,000 by strategically selling during high-margin times. Overlooking these margins might cost you a lot of money at the end of the year.
And, with margins expected to peak at $14.52 per cwt in October, planning around these figures is critical. The 72% of dairy enterprises in the DMC program demonstrate the significance of ensuring financial stability and generating revenues. Enrolling in and actively participating in these programs allows you to maximize every financial advantage, reduce losses, and capitalize on profit chances.
Don’t Miss The Critical DMC Premium Payment Deadline!
Making timely payments for the Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC) program is essential to maintain your coverage and financial stability. You must complete the September 1 deadline to avoid suspending your benefits and affecting your income, especially during these high-margin periods.
Here are some practical tips to ensure timely premium payments:
- Set Reminders: Mark your calendar and set phone alerts for the premium due dates to avoid last-minute stress.
- Budget Wisely: Dedicate a portion of your monthly income to covering premiums. With today’s high margins, the investment is worth it.
- Financial Advisor: Talk to a professional to help you manage your DMC obligations effectively.
- Keep Records: Maintain detailed payment records to prevent disputes or misunderstandings.
By paying your premiums on time, you secure your benefits. Throughout 2024, you can fully take advantage of these record-breaking DMC margins.
If You’re Not Yet Acquainted with Dairy Margin Coverage (DMC), Now is the Time to Get in the Loop
Designed to safeguard dairy farmers against volatile market forces, the DMC program steps in when the margin—the difference between the milk price and feed costs—shrinks below a predetermined level. Think of it as a financial safety net explicitly aimed at reducing the risks associated with unpredictable feed costs and fluctuating milk prices.
“Essentially, DMC acts as a buffer. You pay a premium to ensure that if your margins drop below a certain threshold, you receive a payment to help cover the shortfall,” says Joe Horner, an agricultural economist.
The program, launched under the 2018 Farm Bill, allows dairy producers to select a coverage level ranging from $4.00 to $9.50 per hundredweight (cwt) in 50-cent increments. In practice, this means:
- Producers can obtain financial assistance when feed costs spike or milk prices drop, stabilizing income.
- Different coverage levels can be chosen based on risk tolerance and financial strategy.
- Premiums for the program are scale-based, ensuring that smaller operations can also afford a basic level of coverage.
Participating in DMC is a strategic move that could mean the difference between weathering a tough market and facing substantial economic hardship. As any seasoned dairy farmer will tell you, it’s all about managing risk effectively.
The Bottom Line
Record-breaking DMC margins present a golden opportunity for dairy producers to boost their profits. Ignoring these margins could mean missing out on significant financial rewards, especially given the promising outlook for the rest of 2024. With feed costs decreasing and milk prices rising, the time to act is now.
June’s remarkable $11.66 per hundredweight (cwt) margin and October’s forecast of $14.52 per cwt underline the significance of participating in the DMC program. With a projected payout of $2,383 and a critical premium payment date of September 1, proactive management is required.
What’s the best strategy? Pay any outstanding premiums by September 1. Monitor feed costs and milk prices closely and seek advice when needed. Remember, ‘Failing to plan is planning to fail.’ Are you leveraging the DMC program to maximize your dairy operation’s profitability? Your decisions today can make all the difference.












