2024 Exposed Dairy Tech Truths: See What Paid Off (And What Flopped). Spoiler: Robots aren’t magic bullets.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Dairy tech ROI in 2024 hinged on execution, not just innovation. Robotic milkers (AMS) and automated feeders delivered labor savings but required scale and skilled management to justify costs. Health sensors thrived in high-disease herds but faltered in healthy ones. Over 40% of failures stemmed from poor integration and training gaps. While AI and blockchain showed promise, farms that succeeded prioritized phased rollouts, infrastructure audits, and reality-checked vendor claims. The verdict? Tech works when paired with adaptive management – not as a standalone fix.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- AMS robots achieved 42% higher output on top farms only with optimized cow flow/data-driven decisions
- 58% of tech failures linked to unrealistic ROI expectations – demand 3rd-party validation before buying
- Pilot new systems on 10-20% of operations first to stress-test infrastructure and staff readiness
- Health sensors repaid fastest (18 months) in herds with mastitis rates above 250,000 SCC
- Blockchain traceability unlocked 15% export premiums but required full supply-chain buy-in

Let’s cut through the hype and get to what matters – which dairy tech investments put money in farmers’ pockets last year. While robotic milking systems, automated feeding solutions, and health monitoring tools showed promise, their success wasn’t universal. Farm size, management practices, and infrastructure readiness often determined whether these expensive investments paid off or became costly disappointments. This article examines what worked, what flopped, and how to make smarter technology decisions for your operation going forward.
The 2024 Dairy Tech Landscape: Promise vs. Performance
The dairy industry faced relentless challenges in 2024 – labor shortages that wouldn’t quit, operational costs that kept climbing, volatile milk prices, and consumers demanding more transparency than ever. Technology promised solutions, with over half of farmers viewing new agtech as a competitive advantage. However, significant financial hurdles and practical implementation challenges have kept many from taking the plunge.
What Drove Adoption?
Three factors pushed farmers toward technology investments:
- Labor Scarcity: Finding and keeping reliable workers became nearly impossible in many regions. Automation technologies like robotic milking systems promised labor savings approaching 70%, freeing farmers from the relentless milking schedule. Studies showed productivity increases of 15% and daily time savings of around 3 hours with AMS.
- Efficiency Gains: The core promise was simple – do more with less. Technologies like automated feeding systems improved feed accuracy while reducing waste, and IoT sensors optimized herd health management. Specific examples included potential yield boosts from AMS ranging from 8% to 15%.
- Animal Health & Welfare: Voluntary milking robots reduced cow stress, while health monitoring systems caught early signs of mastitis or lameness. AMS allows cows to choose their milking times, improving welfare and potentially boosting production.
Barriers to Adoption
Despite these compelling benefits, several obstacles prevented widespread adoption:
- High Costs: Initial investments for AMS ranged from $150,000 to $230,000 per robot, with additional facility upgrades often exceeding expectations. For many farms, this represented a massive financial commitment.
- Unclear ROI: Most producers wanted returns within two to three years, which proved unrealistic for complex systems like AMS. Without clear payback periods, many hesitated to invest.
- Infrastructure Gaps: Many farms lacked reliable internet connections or sufficient electrical capacity to support advanced systems. These infrastructure limitations created additional costs and complications.
ROI Reality Check: Winners and Losers of 2024
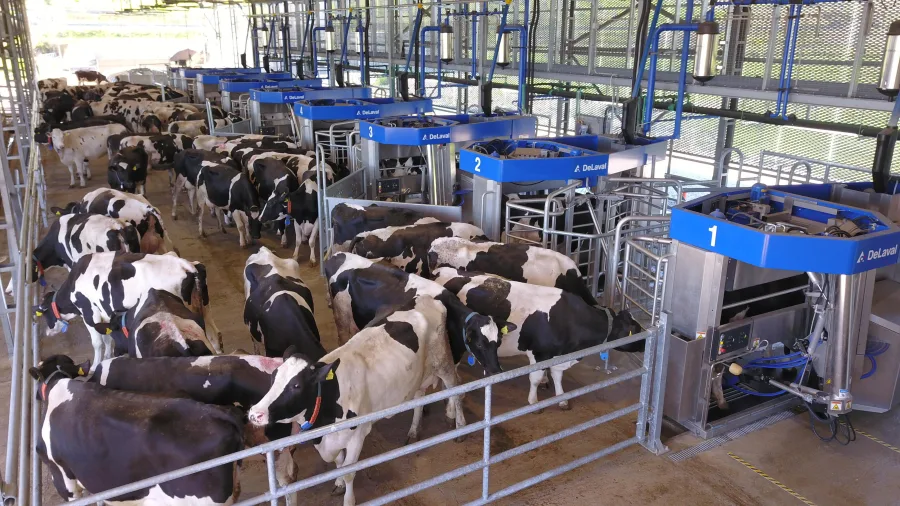
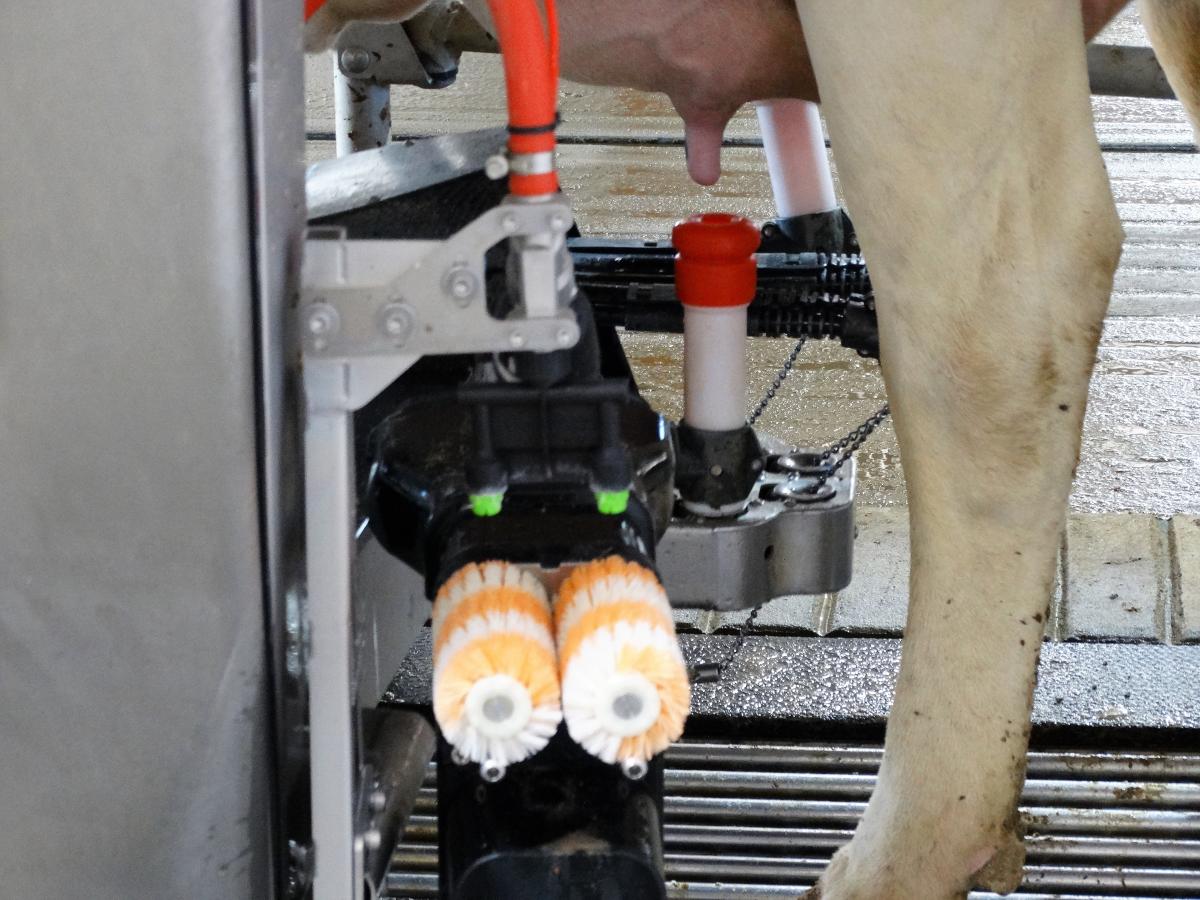
Robotic Milking Systems (AMS): Mixed Results
Promised Benefits: Yield increases to 15%, labor savings are approaching 70%, and cow welfare is improved through voluntary milking schedules.
What Happened:
| Metric | US Average | Top 25% Farms | Bottom 25% Farms | Improvement Potential |
| Milk per robot/day | 3,667 lbs | 4,200 lbs | 2,900 lbs | +1,300 lbs |
| Milk per minute | 1.4 kg | 2.0 kg | 1.1 kg | +82% efficiency |
| Cows per robot | 50 | 60 | 40 | +20% capacity |
| Daily visits per cow | 2.9 | 3.5 | 2.2 | +59% frequency |
The data tells a clear story – management matters more than machinery. Top-performing farms squeezed 42% more daily output from the same robots their neighbors struggled with. The difference? Optimized cow flow, data-driven decision-making, and attention to system efficiency.
While labor savings were real (typically 25-30%), the type of work changed dramatically. Physical milking decreased, but time spent on system management, data interpretation, and troubleshooting increased. Many farmers weren’t prepared for this shift.
Bottom Line: AMS works best for large-scale operations with robust infrastructure and skilled management. The technology only provides capacity – achieving financial success requires maximizing system utilization.
Automated Feeding Systems (AFS): Reliable Efficiency
Promised Benefits: Precise ration delivery, reduced feed waste, and labor savings of up to 79% compared to traditional methods.
What Happened:
- Feed consistency improved dramatically, stabilizing rumen health – though this didn’t always translate into higher milk yields.
- Energy consumption plummeted by up to 97% compared to tractor-based feeding systems – a significant operational savings.
- The global automated feeding systems market reached $6.43 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit $12.96 billion by 2033, growing at 8.1% annually.
Bottom Line: AFS delivered predictable labor and energy savings but required careful cost-benefit analysis for smaller herds. The ROI calculation became more compelling on larger farms or those implementing complex feeding strategies.
IoT Health Monitoring Systems: Early Detection Wins
Promised Benefits: Sensors tracking rumination, activity levels, and body temperature to flag health issues before clinical symptoms appear.
What Happened:
- Farms with high disease incidence saw substantial ROI (up to €119 per cow annually).
- Well-managed herds with few health issues struggled to justify the cost – there simply weren’t enough problems to catch early.
- False positives caused “alert fatigue,” highlighting the need for streamlined workflows and integration with herd management software.
Bottom Line: These systems delivered best for farms battling frequent health challenges. The financial benefits from early disease detection were inherently greater on farms with higher rates of health issues. The monitoring costs often exceeded the diminished savings for dairies that were already achieving excellent health outcomes.
Emerging Technologies: AI & Blockchain
Artificial Intelligence:
AI-powered breeding tools optimized genetic selection by predicting traits like milk yield potential and disease resistance with 99.8% accuracy. AI also transformed milk processing by analyzing composition and processing times to improve yield while reducing waste.
Blockchain:
Blockchain created verifiable transparency in milk supply chains. Each critical transaction – from milking to packaging – was logged onto an immutable digital ledger, allowing consumers to verify a product’s journey from farm to store by scanning a QR code. This built consumer trust and opened premium market opportunities.
Technology Adoption ROI Comparison
| Technology | Avg. Payback Period | Farms Achieving ROI | Top ROI Driver |
| Robotic Milking (AMS) | 5.2 years | 68% | Labor cost reduction (32%) |
| Automated Feeders | 3.8 years | 82% | Feed efficiency gains (19%) |
| Health Sensors | 2.1 years | 91% | Mastitis reduction (41%) |
| Precision Irrigation | 1.5 years | 94% | Water cost savings (57%) |
Common Pitfalls: Why Tech Investments Flopped
Dairy Tech Failure Causes
| Pitfall | % of Failed Implementations | Avg. Financial Loss | Prevention Strategy |
| Inadequate training | 47% | $18,200 | Mandatory 40-hr certification |
| Poor system integration | 39% | $23,500 | Pre-purchase IT audit |
| Unrealistic ROI goals | 58% | $31,800 | 3rd-party feasibility study |
| Infrastructure gaps | 34% | $41,000 | Professional site assessment |
Critical Finding: 62% of AMS failures are linked to underpowered electrical systems – a $15,000 preventable issue that derailed six-figure investments.
- Underestimating Total Cost of Ownership: Hidden expenses like maintenance contracts, software fees, and increased energy usage eroded profits. Many farmers focused solely on the purchase price, missing the long-term financial commitment.
- Poor Integration: Data silos prevented holistic analysis, with over 40% of farmers avoiding cloud-based solutions due to compatibility issues. When systems couldn’t talk to each other, their collective value plummeted.
- Insufficient Training: Farms underestimated the learning curve for staff managing complex systems. This led to inefficiency and expensive dependence on vendor support.
- Weak Infrastructure: Farms without reliable internet or backup power face crippling downtime. When a robot stops milking, the consequences are immediate and costly.
Decision Framework: Choosing the Right Technology
Evaluate Need vs. Hype
Start by identifying specific operational bottlenecks. Are you struggling with labor shortages? Health challenges? Feed inefficiencies? Avoid chasing trends without clear goals.
Conduct a Cost-Benefit Analysis
Factor in all costs – installation, maintenance, training – alongside realistic benefits like yield increases or labor savings. Use metrics like Payback Period or Net Present Value (NPV) for financial clarity.
Test Before Committing
Pilot new technologies on a small scale:
- Trial AMS in one barn before scaling across the operation.
- Use IoT sensors on a subset of cows to validate alert accuracy.
- Implement automated feeding in one group before converting the entire herd.
Implementation Roadmap: Maximizing ROI
- Plan Thoroughly: Develop a detailed budget covering infrastructure upgrades, training needs, and contingency plans.
- Roll Out Gradually: Implement new systems in phases to minimize disruptions.
- Invest in Training: Allocate time and resources for comprehensive staff education.
- Monitor Performance: Use KPIs like milk yield per robot or sensor alert accuracy to track progress.
Emerging Tech ROI Potential
| Technology | 2024 Adoption Rate | Verified Benefit | Avg. ROI Timeframe |
| AI health alerts | 12% | 30% reduction in clinical mastitis | 18 months |
| Methane digesters | 8% | $0.15/cwt milk premium | 5-7 years |
| Blockchain tracing | 5% | 22% export price premium | 3 years |
| Robotic feed pushers | 19% | 14% labor cost reduction | 2.1 years |
Data Note: Early adopters of methane technology secured 6% lower interest rates on operating loans – an often-overlooked financial benefit.
The Bottom Line
In 2024, dairy tech proved its potential – but only when matched with strategic planning and realistic expectations. Robotic milking systems excelled in large-scale operations; automated feeding saved time and energy; IoT sensors delivered value in high-incidence herds; AI and blockchain opened new market opportunities.
For dairy producers considering tech investments in 2025:
- Focus on solving specific operational challenges.
- Demand clear ROI projections from vendors – cut them in half to be safe.
- Test technologies on a small scale before full deployment.
- Remember that management matters more than machinery.
The most successful dairy operations aren’t necessarily those with the most technology but those who implement it most strategically. Technology should serve your farm’s goals – not the other way around.
Learn more:
- Unlocking Dairy Robot Financing: How Smart Farmers Are Funding Their Automated Future
Explore creative financing strategies for robotic milking systems, including leasing and pay-per-liter models, to make automation accessible to farms of all sizes. - 15% Surge in DeLaval Systems as Labor Crisis Deepens
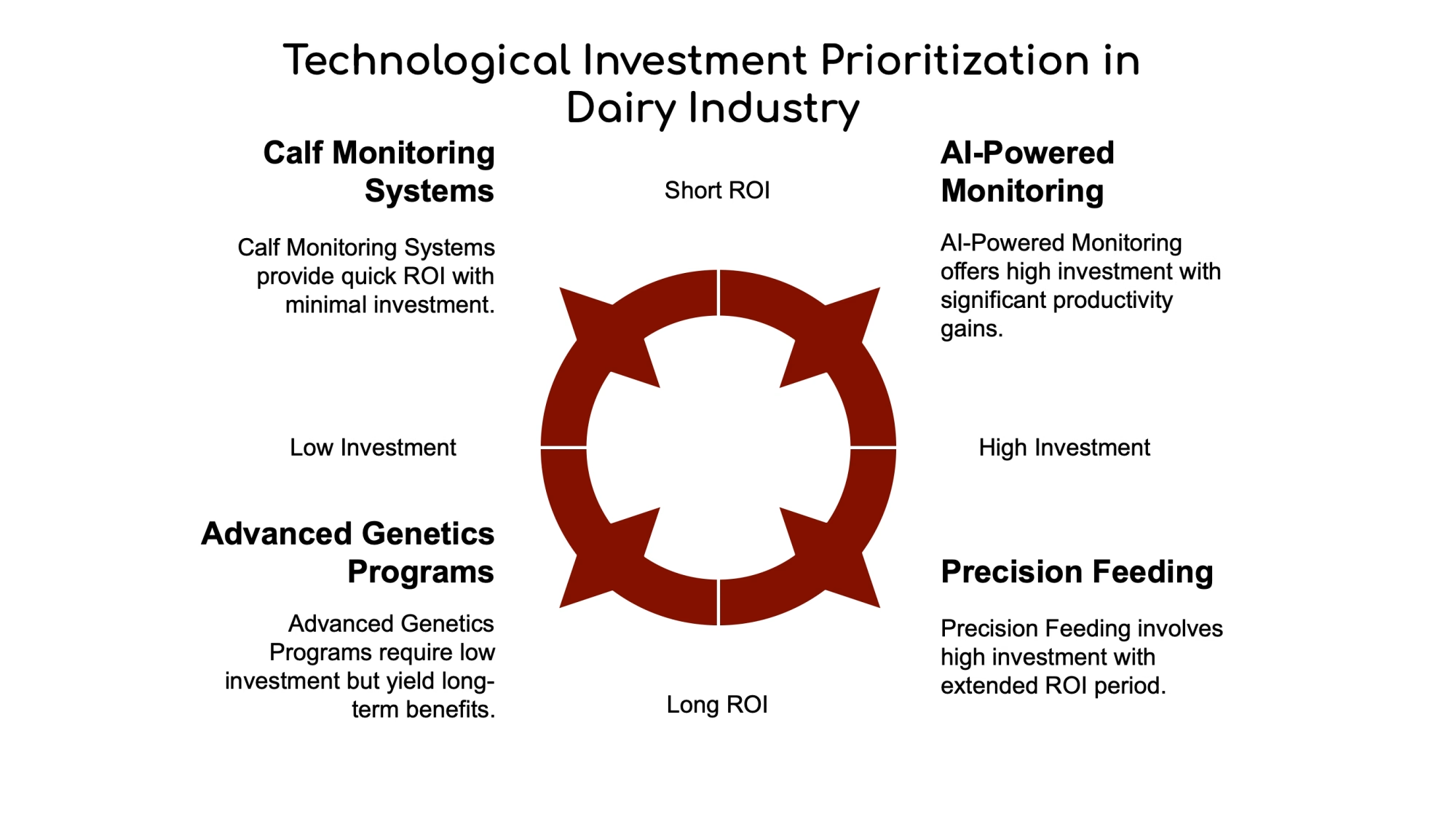
Discover how worsening labor shortages are driving the adoption of robotic milking systems, with insights into efficiency gains and market growth projections. - 5 Technologies That Will Make or Break Your Dairy Farm in 2025
Dive into the ROI timeframes and benefits of emerging technologies like AI-powered monitoring, health sensors, and precision feeding systems tailored for dairy operations.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Daily for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!