Decode dairy cow fertility. Explore groundbreaking research to increase your herd’s productivity. Ready to elevate your success?
Summary:
The intricate landscape of dairy cow reproduction encompasses technological advancements, nutrition, health, and the influences of environmental and genetic factors. As the demand for sustainable food sources rises, enhancing cow fertility becomes paramount. According to Dr. Emily Grant, integrating precision management and genetic evaluation could elevate fertility rates and increase herd longevity. Understanding the reproductive cycle aids farmers in optimizing herd management, which in turn enhances efficiency and milk yield. Innovations such as artificial insemination, embryo transfer, and genomic selection have significantly improved productivity. Farmers must also consider body condition, management practices, and preventive healthcare. Balancing these technological advances with ethical responsibilities is crucial for fostering a harmonious blend of innovation and care within the industry.
Key Takeaways:
- Dairy cow reproduction is a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and nutritional factors that requires careful management and understanding.
- Technological advancements, such as automated monitoring systems, have revolutionized fertility management, leading to better reproductive outcomes.
- Ethical considerations and animal welfare are increasingly integral to reproductive strategies in the dairy industry, prompting innovations that prioritize humane practices.
- Nutrition directly impacts fertility, highlighting the necessity for balanced diets and health management to optimize reproductive success in dairy cows.
- Understanding the genetic and environmental influences on fertility can help make informed breeding decisions that improve herd sustainability.
- Striking a balance between technological interventions and ethical farming practices is crucial for future dairy reproduction industry standards.
- Farm productivity and profitability are closely linked to effective reproductive management, emphasizing the need for continuous improvement and innovation.

In farms and modern barns, dairy cow reproduction plays a crucial role in agriculture, impacting the economy and the environment. Fertility is essential for farmers and the entire industry’s success. As the demand for sustainable food grows, improving cow fertility becomes essential. Minor improvements can increase farm profits and lower environmental impact [ScienceDirect]. This article explores new advancements in dairy cow reproduction, examining how these innovations can boost cow fertility and productivity, leading to more sustainable farming practices.
The Fertility Puzzle: Decoding Dairy Cow Reproduction
As a dairy farmer, your role in managing cow reproduction has become even more critical. Fertility rates are all over the map, and we must maximize productivity. This can be tricky, as it requires balancing genetic selection, management practices, and environmental pressures. As dairy farms expand worldwide, nutrition and disease add layers of complexity. Your role in the industry is pivotal.
Fertility rates have dropped because we’ve been selecting cows for their milk production. This genetic selection has increased milk output but also led to about a 20% decline in fertility over recent decades (ScienceDirect, 2022). This drop has hefty economic impacts, with yearly losses of over $200 per cow due to reproductive issues (Journal of Dairy Science). Improving fertility is crucial. Dr. Emily Grant, a veterinary science expert, recommends blending precision management with genetic evaluation to turn around declining fertility and boost herd longevity (Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 2023).
These reproductive challenges increase production costs and often lead to animal culling. We need a new approach encouraging farmers to balance productivity and substantial reproduction. As the dairy industry strives for sustainability, dealing with these reproductive challenges using innovative strategies and teamwork is crucial for long-term success.
The Dance of Life: Navigating Dairy Cow Reproduction
The life cycle of a dairy cow centers around reproduction. The key part is estrus when a cow is ready to conceive. This happens about every 21 days. During estrus, cows become restless and loud as ovulation nears—when an egg is released and needs to meet sperm for conception. Timing is crucial here.
If fertilization is successful after ovulation, the cow is pregnant for about nine months, similar to humans. The cow’s body significantly changes during this time to nurture the growing calf. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone control estrus and pregnancy, so managing these hormones is essential for fertility. Stress, poor nutrition, or health issues can upset these hormones and cause fertility problems, which is a big worry for dairy farms.
Knowing the reproductive cycle helps farmers manage their herds better, improving reproductive efficiency and milk production. By optimizing each phase of estrus, ovulation, and pregnancy, farmers can keep cows healthier and more productive.
Revolutionizing Dairy: The Technological Advancements in Cow Reproduction
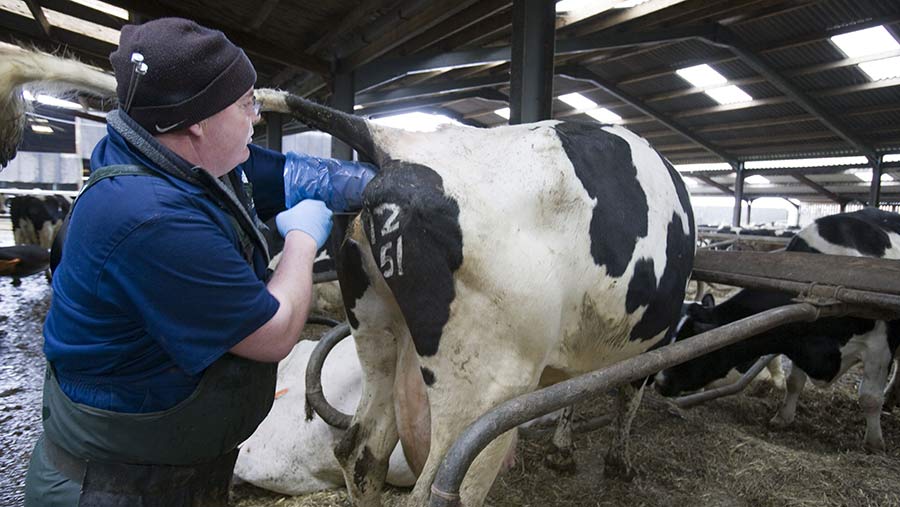
The integration of reproductive technologies into dairy farming has significantly boosted productivity. Artificial insemination is a crucial method that involves collecting semen from a bull and introducing it into a cow’s reproductive tract. This approach enhances dairy cow fertility and herd productivity. It improves herd quality by allowing precise breeding control [Frontiersin, source]. This technique reduces time and costs while increasing pregnancies, enabling the use of semen from top-quality bulls to improve herd genetics.
Embryo transfer is another method for quickly boosting genetic lines. By transferring high-value embryos to recipient cows, offspring from elite dairy cows can be increased without the stress of repeated pregnancies. This accelerates genetic progress beyond traditional breeding [ScienceDirect, source].
Genomic selection uses genomic data to predict breeding value. It revolutionizes breeding by focusing on genetic potential, not appearance. The result is better herd management and a significant return on investment. Genomic selection reduces generation intervals and increases genetic gain, thus boosting milk production [PLOS ONE, source].
Case studies show the successful use of these technologies. One dairy farm used genomic selection to increase milk yield and improve herd health. These outcomes underscore the advantages of advanced technologies for dairy farmers.
These innovations provide dairy farmers with essential tools for enhancing productivity and meeting global food demands. They pave the way for greater efficiency and promise further innovation and progress.
Nurturing Fertility: Harmonizing Nutrition and Health in Dairy Cows
The reproduction of dairy cows involves much more than just breeding. It includes a mix of nutrition, health, and management practices. Getting nutrition and health right is key to fertility. Good nutrition is crucial for dairy cow fertility. Balanced diets support both life and reproduction. Cows need the proper nutrients, like energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals, for a healthy reproductive system [1]. If not balanced, cows might have delayed estrus and poor conception rates.
It’s crucial to manage body condition. Cows that are too thin or too fat face reproductive challenges. Poor nutrition can affect ovulation, while excess weight can lead to metabolic disorders, making pregnancy difficult. Farmers should watch body conditions and adjust their management practices [2]. Preventing disease is essential, too. Diseases affecting the reproductive tract or metabolism can reduce fertility. Herd management should include preventive healthcare like vaccinations and health screenings. Biosecurity protocols help minimize disease outbreaks, improve herd health, and boost reproduction.
Farmers should regularly check nutrition and adjust feed for cows based on their life stages and needs to improve healthand fertility. Technology, like metabolic profiling and precision feeding, helps refine these practices. Routine veterinary checks can detect diseases early and allow timely intervention, boosting health and fertility [3].
In summary, ensuring fertility in dairy cows requires balancing nutrition, body condition, and disease prevention. With proper management and care, dairy farmers can unlock their herds’ reproductive potential, leading to successful and thriving herds.
Beyond the Barn: Navigating Environmental and Genetic Influences on Dairy Cow Fertility
Environmental and genetic factors play a significant role in dairy cow reproduction. Recent studies show these have a substantial effect on fertility in dairy herds. Changes in temperature and humidity can upset dairy cows’ hormonal cycles, lowering fertility rates. For example, heat stress is linked to reduced pregnancy success because it harms egg quality and embryo growth [J. Dairy Sci., 2023]. Reproduction efficiency often decreases when it’s hotter [1], so adjusting how farms are managed during these times is key. Handling these environmental factors well is critical for keeping fertility rates high in dairy herds.
On the genetic front, new genomic tools help with selective breeding for better fertility traits. Choosing cows with traits like shorter calving intervals and higher conception rates builds more substantial herds. Combining genetic markers with traditional methods is promising in finding cows with better reproductive abilities [PLOS ONE, 2017]. Traits like better heat tolerance and disease resistance are added to dairy genetics, offering better fertility and overall animal health[J. Reprod. Dev., 2021]. Selecting these traits is a smart financial and scientific strategy that boosts milk production efficiency and profitability. Studies suggest a balanced approach combining environmental control and genetic enhancements to improve dairy farming standards [2].
Walking the Tightrope: Ethical Challenges in Dairy Cow Reproduction
As we examine dairy cow reproduction, we must consider challenges and ethical issues. The drive for more productivity often pushes the limits between innovation and ethics. One big challenge is animal welfare. Methods aimed at increasing milk production raise concerns about cow well-being. Overbreeding can cause health problems, affecting both the physical and mental state of cows.
Genetic diversity is also essential. Focusing on traits like high milk production can reduce genetic variation, making herds less resilient and prone to disease. Balancing selective breeding with maintaining genetic diversity is challenging.
Can we balance productivity with ethical responsibility? This question pushes the industry to make smart innovations. Are current practices sustainable, or are we reaching an ethical limit? As we move forward, discussions must stress the planet’s health, animals, and human needs. We need to consider the effects of every technological and breeding advancement carefully.
The Bottom Line
The complex issue of dairy cow reproduction requires a mix of traditional methods and new ideas. We’ve examined how environmental and genetic factors affect a cow’s reproduction ability. Technological advances, like precision farming and genetic selection, offer ways to improve reproductive performance. However, every step forward brings ethical questions that we must carefully consider. Good nutrition and health are vital for ensuring fertility, highlighting their importance for successful reproduction.
In this rapidly changing field, ongoing research is helpful and necessary. Understanding and improving dairy cow reproduction is key to keeping our farms sustainable and efficient. As we move forward to create a future where innovation and care work together, we should consider balancing new technology with ethical responsibilities.
Learn more:
- When to Get a Cow Pregnant for Maximum Milk Production and Profitability
- Maximizing Dairy Cow Fertility Through Genetic Selection: Current Strategies and Future Directions
- Transforming Young Heifers to Mature Cows: Boosting Dairy Herd Longevity
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Bullvine Daily is your essential e-zine for staying ahead in the dairy industry. With over 30,000 subscribers, we bring you the week’s top news, helping you manage tasks efficiently. Stay informed about milk production, tech adoption, and more, so you can concentrate on your dairy operations.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!