Next winter, one dairy will have fewer sick fresh cows and better margins. Yours or your neighbor’s? The gap starts now.

You know that feeling when you’re doing morning checks and spot a cow that’s just… off? Maybe she’s standing away from the bunk, head low, looking like she’d rather be anywhere else.
We’ve all been there. And we all know what comes next—that cow’s probably about to cost you anywhere from three hundred to a thousand dollars, depending on whether she develops ketosis, metritis, or decides to really complicate your week with multiple problems.
So here’s what’s interesting about the research coming out of Penn State lately. Adrian Barragan and his team over in their veterinary school think they’ve found a better way to prevent these crashes before they happen—and the thing is, they’re not asking you to buy fancy new equipment or send blood samples to a lab every week.
They’re using information most of us already collect.

THE ECONOMICS: Clinical ketosis costs $300-$350 per case in treatment plus 600-800 pounds of lost milk, while metritis runs $300-$500 per case—based on foundational research adjusted for current costs
You probably know the basic economics already, but it’s worth laying out just how expensive transition problems really are. Foundational research by McArt and colleagues, adjusted for current feed and treatment costs, estimates clinical ketosis at $300-$350 per case. And that’s before you count the 600 to 800 pounds of milk you’re typically losing over that lactation.
Metritis? Cornell and other research groups have been tracking this for years. More recent estimates put the true cost at $300 to $500 per case when you factor in treatment, lost production, and downstream fertility impacts.
And here’s the kicker—when a cow gets multiple diseases (and research shows that happens about 35% of the time in that first month), you’re looking at losses that easily top a thousand dollars per cow. Makes you think, doesn’t it?

But—and this is where it gets complicated—the farms that could benefit most from this approach are often the ones that can’t actually implement it. Let me explain what I mean.
Understanding Which Cows Need Help (And When)

What farmers are finding with targeted cow management is that it’s surprisingly straightforward, at least in theory. Barragan’s framework focuses on three windows we’re all managing anyway: dry-off (about 60 days before calving), close-up (those critical two to three weeks before), and calving itself.
At each of these points, there are specific red flags that predict trouble ahead.

Take dry-off, for instance. We all know overconditioned cows are trouble—anyone with a body condition score of 3.75 or higher is asking for metabolic problems. Penn State tracked thousands of cow lactations over several years, and these cows produced about 560 pounds less milk during the first 16 weeks of their next lactation. Plus, they have 10% more health events.
That’s not exactly news to most of us. But having the hard numbers helps justify why we need to manage the condition more carefully.
Here’s another risk factor worth watching: high producers at dry-off. Cows still making 45 pounds or more when you’re trying to dry them off face increased risk of milk leakage and intramammary infections. The combination of high production and high body condition at dry-off? That’s your highest-risk group right there.
And then there’s the somatic cell piece. Pam Ruegg at Michigan State and Noelia Silva del Rio out at UC Davis have both shown that cows over 200,000 cells at dry-off have compromised colostrum quality. Their calves end up with lower antibody levels. These cows will produce about 1,000 fewer pounds of milk over the first 16 weeks, too.
Quick Reference: Targeted Cow Risk Windows
- Dry-off (60 days before calving): Flag cows with BCS ≥3.75, high production (>45 lbs/day), or SCC >200,000
- Close-up (21-14 days before): Watch for feed intake drops >30%, pen moves, DCAD balance issues
- Calving: First-calf heifers, twins, and dystocia cases need immediate targeted protocols
Why Timing Changes Everything in Transition Management
Looking at this from a different angle, we’ve always known intuitively that some cows need more attention than others. Good managers—you know the type—they have that sixth sense about which cows are going to crash.
What’s fascinating here is how precision transition research actually quantifies what we’ve suspected all along. The same cow might need completely different interventions depending on when you catch her.
The anti-inflammatory work is particularly revealing. In peer-reviewed trials, Barragan’s team tested meloxicam at multiple time points. First-calf heifers treated a day or two before expected calving showed remarkable responses—up to 10 to 11 pounds more milk per day over the early lactation period in some trials, though results do vary by herd and individual cow.
A quick regulatory note here: meloxicam use in dairy cattle is considered extra-label in the United States, meaning it requires a valid veterinarian-client-patient relationship and prescription. This isn’t something you can pick up at the farm store—work with your vet if you’re considering this protocol.
Even at the conservative end, we’re talking 450 to over 1,500 pounds of extra milk over 150 days. At current market values averaging around $20 per hundredweight, that’s real money. And what really got my attention—stillbirth rates in these treated heifers dropped by about 20 percentage points in Penn State’s research.
But here’s where it gets interesting. Older cows? They showed a different pattern. They didn’t show the same positive response to prepartum treatment and, in some trials, showed no economic benefit from blanket prepartum protocols. Mike Overton from Elanco has been tracking these protocols on commercial dairies, and he’s finding that the timing question really matters by parity.
So that one-size-fits-all protocol we’ve been using for years? Turns out we need to be smarter about it.
The Reality Check: Making This Work on Real Farms
Let’s have an honest conversation about implementation. Knowing what to do and actually getting it done consistently are two completely different animals, right?
I’ve been tracking operations from Vermont to New Mexico, trying to implement these precision protocols, and here’s where things typically fall apart. First, somebody has to reliably score body condition—every cow, every time. Research from Wisconsin and other land-grant schools shows that when two people score the same cow, they disagree by half a point or more, roughly a third of the time. That’s enough to misclassify a cow completely.
Then you need to track which cows got flagged. Your feed crew needs different TMR specs for different risk groups. The fresh cow team needs to know which protocol applies to whom.
And here’s what nobody talks about at conferences—when José takes a few days off, and Miguel covers his shift, does Miguel know that cow 1847 is on the high-risk protocol? In many cases, probably not.
Marcia Endres at the University of Minnesota has been a leader in precision dairy research for years. What her work consistently shows is that farms with integrated herd management software—where BCS scores, milk weights, and health events flow into a single system—have significantly higher adoption rates for precision protocols than farms that try to manage everything in spreadsheets.
The gap is substantial. That tells you something right there.
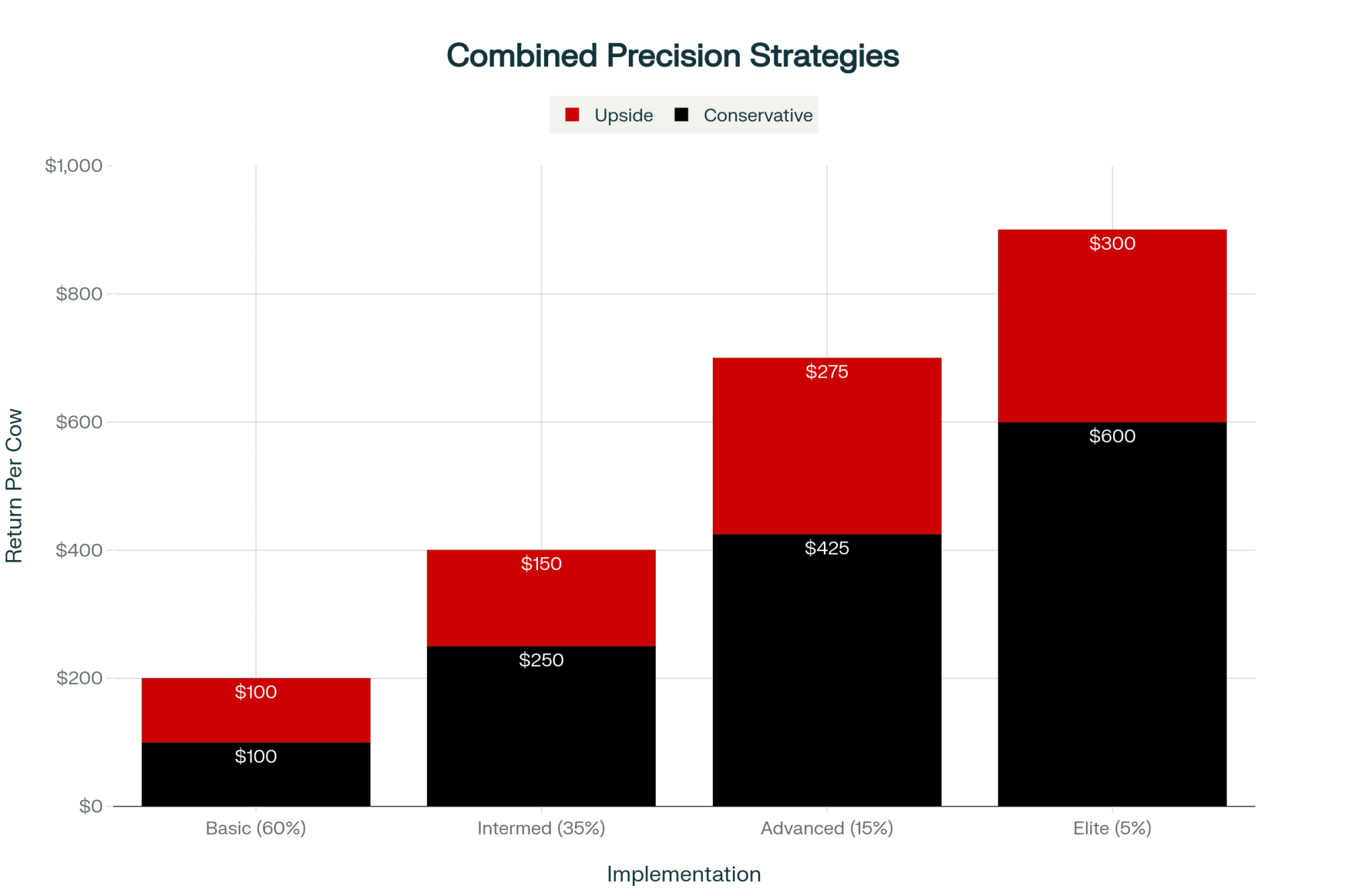
The Economics: Traditional vs. Targeted Approaches

KEY FINDING: Field trials show farms implementing targeted transition protocols can achieve $200-$500 net benefit per cow per lactation through reduced disease and improved milk production
Looking at actual implementation data from extension-supported trials, the numbers tell a compelling story.
With traditional blanket treatment, you’re treating every cow the same at dry-off. Costs you about $45 to $60 per cow across your whole herd. Fresh cow disease rates typically run 27 to 35% in the first 60 days (that’s from NAHMS data), and you’re losing 600 to over 1,500 pounds of milk per affected cow.
Now with the targeted approach, you’re identifying high-risk cows at each transition point and customizing what they get. Low-risk cows might only need $15 to $25 worth of attention. High-risk animals receive $65 to $95 in targeted support.
What happens? Disease rates can drop to 18-24% in the critical first 60 days—we’re talking a 25-30% reduction, based on what extension programs are seeing in the field. And you’re recovering 500 to 1,000 pounds of milk per prevented case.
When it all shakes out, farms are seeing net benefits of about $200 to $500 per cow per lactation. But—and Chuck Guard from Cornell’s ambulatory clinic emphasizes this—that’s only if you can execute consistently. Big “if” there.
Why 80% of Farms Can’t Jump on This Yet

Here’s something we need to address head-on. Most of us are running on razor-thin margins right now. USDA’s latest economic outlook shows roughly half of dairy farms are projected to be profitable this year.
The all-milk price averaging around $20 per hundredweight sounds okay until you factor in elevated feed costs and labor shortages, pushing wages up into the double digits from recent years. Suddenly, that margin disappears real quick.
When you’re worried about making December’s feed payment, investing in new management protocols—even ones that pencil out great on paper—feels like a luxury you can’t afford.
There’s also the behavioral economists’ “prevention paradox.” Jennifer Van Os over at Wisconsin has been studying how farmers make decisions, and it’s fascinating. When you prevent ketosis, nothing visible happens. The cow doesn’t get sick. There’s no vet bill. No treatment record. It’s… psychologically unsatisfying, if that makes sense.
But when you miss one, and she crashes? That’s immediate, visible, and it sticks with you.
I heard an illustrative story at a recent producer meeting that captures this perfectly. A Wisconsin dairyman shared anonymously: “We tried targeted dry-off protocols for six months. Caught most of the high-risk cows. But we lost one valuable genomic heifer that we misclassified. That $3,000 loss is what I remember—not the dozen we saved.” Whether that’s one producer’s experience or a composite of many I’ve heard, it reflects a genuine psychological barrier that the research confirms is widespread.
Lessons from Europe’s Regulatory Push

You want to know what actually drives industry-wide change? Europe’s experience with selective dry cow therapy offers a masterclass.
The EU implemented Regulation 2019/6, which banned prophylactic antibiotic use—including blanket dry cow therapy—effective January 28, 2022. That date matters because it forced a complete industry shift.
According to European research, about two-thirds of Italian dairy farms had transitioned to selective protocols by the end of 2022. The Netherlands has become the gold standard, going from relatively low adoption to over 80% in just a few years.
The difference? Farmers changed because they had to.
But here’s what’s encouraging—Volker Krömker from Copenhagen University has been tracking outcomes, and after some initial resistance, Dutch farmers using selective protocols actually saw mastitis rates drop below what they had with blanket treatment. The whole infrastructure adapted: vet schools started requiring SDCT training, milk buyers provided protocol support, and software companies built decision trees right into their platforms.
Meanwhile, U.S. voluntary adoption is sitting at roughly one in four farms. The contrast is pretty striking.
Where Targeted Management Actually Works Today
Despite all the challenges, certain operations are making these protocols work brilliantly. What separates them?

Looking at successful implementations from Maine to California, you see patterns. Scale helps, but it’s not everything. Sure, a 3,000-cow operation in Idaho finds it easier to justify the cost of dedicated transition management software. But I’m also seeing 300-400 cow herds in places like Wayne County, Ohio, succeeding because their co-op provides shared advisory support.
Regional variations matter too. Down in New Mexico and Arizona, where heat stress just compounds everything, producers like Tom Barcellos out in Tulare County tell me precision management becomes even more critical. As he puts it, “When it’s 110°F in July, you can’t afford to guess which cows need extra support.”
In Florida, where the humidity is brutal, a group near Okeechobee adapted the protocols to conduct twice-daily body condition scoring during summer. Over in Texas, some of the larger operations near Stephenville are finding that targeted protocols help offset the stress of their long summers. Up in Vermont, where winter housing gets tight, farms are focusing more on the close-up pen management side of things.
And out in the Pacific Northwest—you know how wet it gets there—the larger dairies near Yakima Valley are finding targeted protocols help manage the stress that mud and moisture put on transition cows. One producer in Sunnyside told me they flag any cow that spent more than 2 weeks in the hospital pen during the last lactation. Those girls automatically get extra attention at dry-off, regardless of other metrics.
What do successful operations have in common? Three things keep coming up: integrated data systems (increasingly using cameras for BCS scoring), strong veterinary partnerships for ongoing tweaks, and what Nigel Cook from Wisconsin calls “implementation discipline”—basically, someone owns the process and reviews outcomes every month without fail.
Implementation Timeline: What to Really Expect
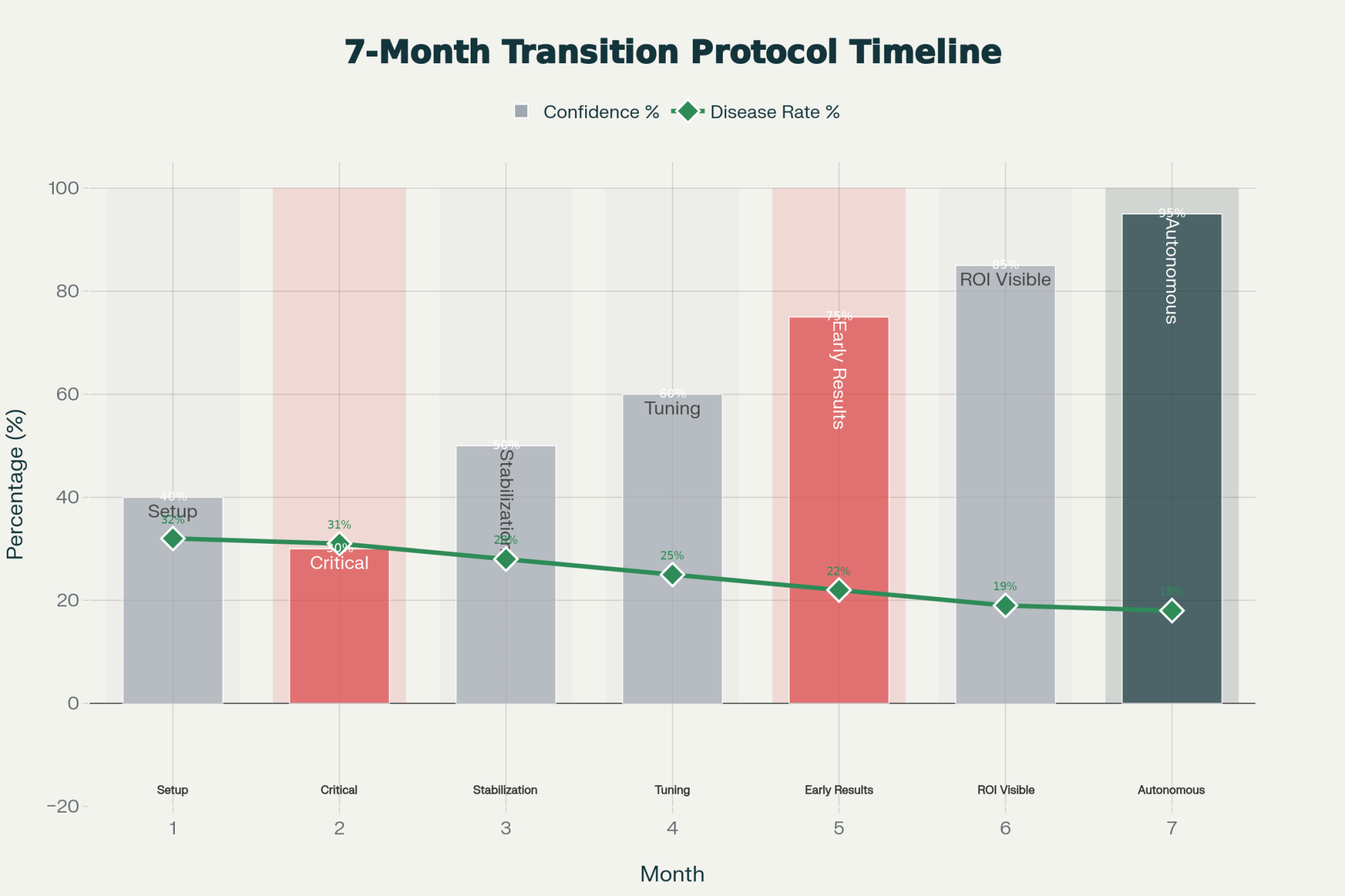
- Weeks 1-4: Set up protocols, train your team, get baseline numbers
- Weeks 5-12: Work out the bugs, build staff confidence
- Months 3-4: Don’t panic—temporary plateau is normal
- Months 5-6: Positive trends start showing up, fine-tune protocols
- Month 7+: Full ROI kicks in, system runs itself
Making Targeted Protocols Work on Your Farm
After watching dozens of operations try this, here’s my practical advice if you’re thinking about it.

Start ridiculously simple. Pick ONE intervention for 90 days. I’d suggest dry-off BCS flagging. Now, this next part is my own practical recommendation, not part of any formal research protocol: get yourself an orange livestock marker. Every cow over 3.75 gets an orange stripe on her tailhead. That’s it. Everyone knows orange means “controlled energy dry cow ration.” Simple, cheap, and visible to every person who walks through that pen.
Set realistic expectations. Research on implementation curves suggests the average time to positive ROI is around five to six months. Some farms see a temporary production dip in month two as systems adjust. You need to budget for that.
And here’s crucial—involve your entire team from day one. Not a memo. Not a meeting where half the guys are checking their phones. A hands-on session where your feeders, fresh cow crew, and whoever does dry-off physically walk through the process together. Gustavo Schuenemann from Ohio State found that farms with hands-on training show significantly better compliance with protocols than those using written SOPs alone.
Track only what matters. Pick three things: fresh disease rate (shoot for under 20%), 60-day milk average (watch the trend, not the absolute number), and days to first service (target under 70). Review them monthly. Ignore everything else at first—you’ll drive yourself crazy otherwise.
The Hard Truth About Implementation Readiness
I need to be direct here. If you’re struggling to cover operating expenses, targeted transition management shouldn’t be your priority right now. This approach works best for farms with positive cash flow and at least six months of operating capital in reserve.
It’s one of those cruel ironies—the farms that most need efficiency gains are often least equipped to implement them. Chris Wolf, the ag economist at Cornell, calls this the “productivity trap.” The bottom 40% of farms by profitability are producing at significantly higher cost than the top 40%, but they lack the capital to make improvements that would close that gap.
Critical Limitations to Consider
Let’s be clear—targeted transition management isn’t universally applicable. Genetic differences matter. Jersey herds show different risk thresholds than Holsteins. Kent Weigel’s genomic research at Wisconsin shows cows with high genetic merit for health traits may show less dramatic response to targeted interventions—they’re already more resilient.
Facility design impacts success, too. Farms with two-row freestalls and adequate bunk space see better results than overcrowded three-rows. Peter Krawczel from Tennessee documented that overcrowded facilities—stocking densities in the 110-120% range and above—negate a significant portion of targeted protocol benefits as the stress from overcrowding overwhelms the precision interventions.
And geographic factors can’t be ignored. What works in Wisconsin’s climate needs adjustment for Louisiana’s humidity or Colorado’s altitude. You’ve got to calibrate locally.
What Would Accelerate Industry Adoption
Three things could shift targeted management from “interesting option” to “this is how we do things now.”
First, processor requirements. If the big co-ops like DFA or Land O’Lakes started requiring transition management documentation for quality premiums, adoption would happen overnight. Tillamook’s already doing this with SCC-based dry-off protocols for their suppliers.
Second, cooperative infrastructure. When your co-op provides training, software access, and shared advisory as part of membership, smaller farms can suddenly access the same tools as the big guys. Organic Valley’s vet support program is a good model for this.
Third, federal support. USDA’s got significant funds allocated for precision agriculture through 2027. If they added transition management to their cost-share eligibility, it would substantially lower barriers.
The Bottom Line for Your Dairy
The transition period drives the majority of our health problems. We’ve known this for decades. What targeted cow management offers is a systematic way to identify and prevent these problems before they turn into expensive disasters.
But as we’ve talked about, knowing what to do and being able to do it are vastly different challenges. The science is solid. The economics work. Whether this becomes standard practice really depends on how the industry chooses to support implementation.
My advice? If you’re interested, start small. One protocol. One risk factor. Track your results religiously. And definitely get your vet and nutritionist involved from day one—this isn’t something you figure out alone.
The cows that need help are already in your barn. You walk past them every day. The question is whether you can build a system to identify and support them before each one costs you $500 to $1,000.
Some operations can absolutely do this today. Others need infrastructure development first. Understanding which category you’re in—honestly, without wishful thinking—that might be the most valuable assessment you make this year.
And here’s the thing that keeps me up at night: if you won’t pick one simple flag and execute it for 90 days, your neighbor probably will. In a year from now, one of you will have lower fresh-cow disease, better butterfat levels, and a stronger balance sheet.
Which one do you want to be?
Key Takeaways:
- The savings are proven: Farms executing targeted transition protocols cut fresh cow disease rates by 25-30%, saving $200-$500 per cow per lactation—and the gap between early adopters and everyone else is widening
- Inaction costs more than you think: Ketosis runs $300-$350 per case, metritis $300-$500, and over a third of fresh cows develop multiple problems in their first month
- Most dairies aren’t ready yet: Roughly 80% of U.S. operations lack integrated herd software or the cash reserves to implement precision protocols consistently—but that’s changing
- The science scales: European farms mandated to adopt selective dry cow therapy in 2022 now report lower mastitis rates than they had with blanket treatment
- Start with one thing: Flag cows with BCS ≥3.75 at dry-off, track outcomes for 90 days, and involve your vet—simple execution beats sophisticated plans that never happen
Executive Summary:
Transition cow crashes are quietly draining dairy profits—ketosis and metritis each cost $300-$500 per case, and over a third of fresh cows develop multiple problems in their first month. Research from Penn State, Cornell, and Wisconsin shows that targeted protocols identifying high-risk cows at dry-off can cut disease rates by 25-30%, saving $200-$500 per cow per lactation. The challenge? Roughly 80% of U.S. dairies lack the integrated data systems or financial reserves to execute these approaches consistently. European farms mandated to adopt selective protocols in 2022 now report lower mastitis rates than they had with blanket treatment—proof that the science works at scale. Successful U.S. operations share three factors: integrated herd software, strong veterinary partnerships, and someone who owns protocol review every month. The realistic starting point is straightforward: flag body condition scores at dry-off and track outcomes for 90 days. By next winter, the gap between farms preventing fresh cow crashes and those still reacting to them will show up clearly on the balance sheet.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- The 15:1 ROI Protocol: How Anti-Inflammatory Treatment is Cutting Transition Disease in Half – Details specific anti-inflammatory protocols that reduce transition disease rates by 50%. Learn exactly when to treat high-risk cows with meloxicam or aspirin to secure a verified 15:1 return on investment.
- Decide or Decline: 2025 and the Future of Mid-Size Dairies – Analyzes the 2025 financial landscape for mid-size dairies, offering clear benchmarks for debt and efficiency. Essential reading for producers deciding between expansion and optimization to ensure long-term viability.
- The Great Dairy Reversal: How Europe’s Precision Contraction Strategy Could Redefine Global Competitiveness – Investigates the European shift toward “precision contraction,” where technology investments are delivering 200% ROI. Explains why maximizing margins per cow is outperforming traditional herd expansion strategies in the current market.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!