Zoetis is a global animal health company with 60 years of experience. Zoetis, formerly Pfizer Animal Health, was a business unit within Pfizer Inc. On February 1, 2013, Zoetis became a stand-alone animal health company. Zoetis is a publicly traded company on the NYSE.
When DNA profiling in herds, the program at Zoetis is to get dairy producers to focus on genotyping the entire heifer group. This allows breeders to make selection and management decisions, before investing the full cost of raising each heifer. Depending on where breeders are located, the cost of raising a heifer ranges from $2000 to $3500 (Read more: Should you be raising your own heifers?) By testing animals at a young age, breeders can decide if they want to sell the heifer, breed her to a beef sire, use her as an embryo recipient or consider flushing her. It’s about making accurate choices and, ultimately, profit.
Which Benefit Category Works for YOU?
- Do you have an excess of heifers?
DNA profiling means you can manage your heifer inventory more precisely and invest your rearing budget in the heifers that you need to keep. Keeping control of the heifer inventory also has an indirect health benefit. Reduced numbers prevents heifer facilities from being overcrowded. A less stressful environment reduces calfhood and heifer diseases. Remember that heifer rearing is the third largest on-farm cost after labor and feed. - Do you use sexed semen?
This higher priced tool can be best applied to the top 50% of heifers based on their genetic merit. Doing so is a significant step toward elevating the genetic potential of the next generation of heifers in your herd. - Is your herd unregistered?
You have the most to benefit from genomic testing because you will be going from zero genetic information to more genetic information than you could ever get from simply registering your animals. Now you can make better selection and mating decisions. - Is profitability your first priority?
The top priority profitability traits for most herds are selection for milk components, with the remaining emphasis on traits that contribute to longer herd life (SCS, DF, HL, F/L and mammary). LPI is a great index to use as a first sort in selecting the most profitable animals.
Analysis. Assessment. Action.
Zoetis has developed the “CLARIFIDE” program. Veterinarians are trained in understanding the basics of genomics and how this information can be integrated as part of the herd’s management program. There are over 100 veterinarians across Canada that have been given the designation of “CLARIFIDE Accredited Veterinarian”. Many of them underwent a multi-day training program taught by representatives from Zoetis, CDN, Holstein Canada and Semex. Today, if a local vet has not been trained through the CLARIFIDE program, but they have a client that is interested in submitting through CLARIFIDE, Zoetis will conduct training with these vets either in person or on-line.” Dr. Melodie Chan, Zoetis Business Lead and Manager Veterinary Services, concludes. “With access to this information, breeders are able to allocate their resources more effectively. As genomic research progresses, we may even be able to consider health protocols to match each animals’ potential to respond – such as response to vaccination.”
Clarifying Genetic Potential
The goal of every dairy breeder is to identify and act upon the genetic potential of their dairy animals. “Through the CLARIFIDE program, Zoetis has worked closely with its Alliance partners.” says Dr. Chan, who outlines the benefits and potential. “By working closely with CDN, Holstein Canada and Semex, the CLARIFIDE genomic consulting program offered through Zoetis provides a truly Canadian perspective. Furthermore, this Alliance has also fostered research initiatives and collaborative funding towards projects that ultimately benefit the Canadian dairy industry. In 2012-2013 Zoetis funded genotyping of approximately 2,000 Canadian proven sires so that their offspring could be included in the genome pool. The addition of this genetic information will aid in the predictive value of genomic testing, in particular for Canadian only traits, such as temperament and milking speed.”
ZOETIS + SEMEX + HOLSTEIN CANADA + CDN – Combined Strengths. Collaborative Approach.
Effective May 1, 2012, Zoetis (formerly Pfizer Animal Health) joined the existing alliance between the Canadian Dairy Network (CDN), the Holstein Association of Canada (Holstein Canada), and the Semex Alliance (Semex). Dr. Chan describes the strategy. “The intent of this alliance is to foster a collaborative approach to delivering predictive genetic information to the Canadian dairy industry, to promote female genotyping and to assist Canada’s dairy producers in using genetic information to make sound management decisions and propagate desired traits. “The members of the alliance feel that by engaging in this partnership, breeders ultimately benefit from the combined strengths of each organization.”
Update on Pilot Study Results
Dr. Josh Lindenbach, Warman Saskatchewan, a Clarifide Approved Veterinarian, shared some of the economic analyses that he did with two of the Zoetis pilot-project herds. In both herds, Dr. Lindenbach sorted the animals based on LPI and compared it to kg of BF shipped. “In Herd #1, there was a $960 average gross profit advantage between the top 1/3 and bottom 1/3 of the herd based on LPI (48 animals genotyped). In Herd #2, there was a $1345 average gross profit advantage between animals that had an above average LPI number vs. a below average LPI number.”
THEY’RE TALKING about CLARIFIDE
Zoetis has received the following comments from breeders and vets involved in the CLARIFIDE program:
- “This gives us a better way to manage the heifer inventory by knowing which ones to keep, sell or use as recips, and which ones to use sexed semen on.”
- “Herd weaknesses were known before but now we find them younger and more accurately“
- “We are now buying semen from bulls that address herd weaknesses as identified by genomics”
- “More targeted use of sexed semen”
- “We have more open discussions of breeding discussions involving both vets and AI reps, sometimes even together!”
- “By culling my bottom end heifers, the heifers coming into the milking herd are more solid producing animals. We have higher milk production and have been able to raise the overall health level of our herd.”
- “It’s not the top half of my herd that I ever have to worry about – it’s the bottom half. I want to be able to know ahead of time who could potentially cause me problems and be able to manage my heifer inventory appropriately, based on this knowledge.”
ZOETIS and TOP BREEDERS
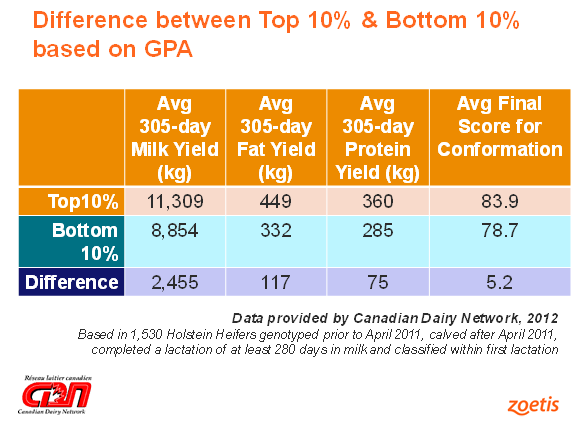
There have been interesting results from three different groups from the Zoetis field trial as Dr. Chan reports. “Breeders that are in the top 10% ,from a farm management standpoint, who are excellent at raising calves and keeping them alive, have reached a plateau with their production and are looking for the “next thing” that they can improve on to help them become more profitable were the first ones to trust in genomic technology and see its value. Dr. Chan states, “The key is to make sure you have invested fully in your calf raising program to ensure that disease issues are kept to a minimum and calves have doubled their birth weight at 56 days – then you can be assured that these heifers will reach their full genetic potential.” She continues with the benefits for two other groups.”Breeders that are sitting on excess heifers and looking at their expenses were also quick to jump on board. For a group of Hutterite breeders that are limited to the use of natural service bulls only, genomics provided them with an opportunity to push their genetic progress by culling some of the bottom end animals and replacing them with purchased animals that ranked higher on LPI.” Using data that CDN supplied, Dr. Chan in 2012 looked at phenotype vs. genotype. “We took the CDN database as being “one herd” and took the raw data without adjusting for any environmental effects. Despite that, we were still able to show a significant difference in performance, if we used genomics as a predictor for performance.”
The Bullvine Bottom Line
This sounds like every breeder’s dream. It checks off several breeder, service provider and advisor goals. “Now breeders not only know a heifer’s genetic potential early in her life but have the information to find more accurate ways to allocate resources.” Whenever the tools advance dairy breeders` goals and profitability, that’s a win-win for everybody.
Get original “Bullvine” content sent straight to your email inbox for free.