What farmers are discovering is simple—the most valuable time on the dairy isn’t the visit itself, but the preparation before it.
You know that feeling when you watch a neighbor drop $200,000 on new parlor equipment, only to find out six months later the real problem was their water heater? Or maybe you’ve been there yourself—spent months adjusting rations while the actual issue was something as simple as feed bunk height.
Here’s what I’ve noticed after years of working with dairies from Vermont to New Mexico, and consulting with everyone from 100-cow tie stalls to 5,000-head dry lots: these aren’t failures of effort. They’re failures of preparation. And with milk prices doing their usual rollercoaster thing and margins tighter than ever, we really can’t afford to keep learning these expensive lessons.
What’s encouraging is that the farms that stay consistently profitable—whether they’re milking Jerseys in Wisconsin or running Holsteins in Idaho—are not necessarily the ones with the deepest pockets or the shiniest equipment. They’re the ones who’ve figured out how to ask the right questions before making any decision.
The $50,000 Question Nobody’s Asking
So there’s this dairy I worked with recently—typical Midwest setup, about 450 cows, been in the family since the grandfather started with 30 head back in the ’60s. Good people, working hard every single day.
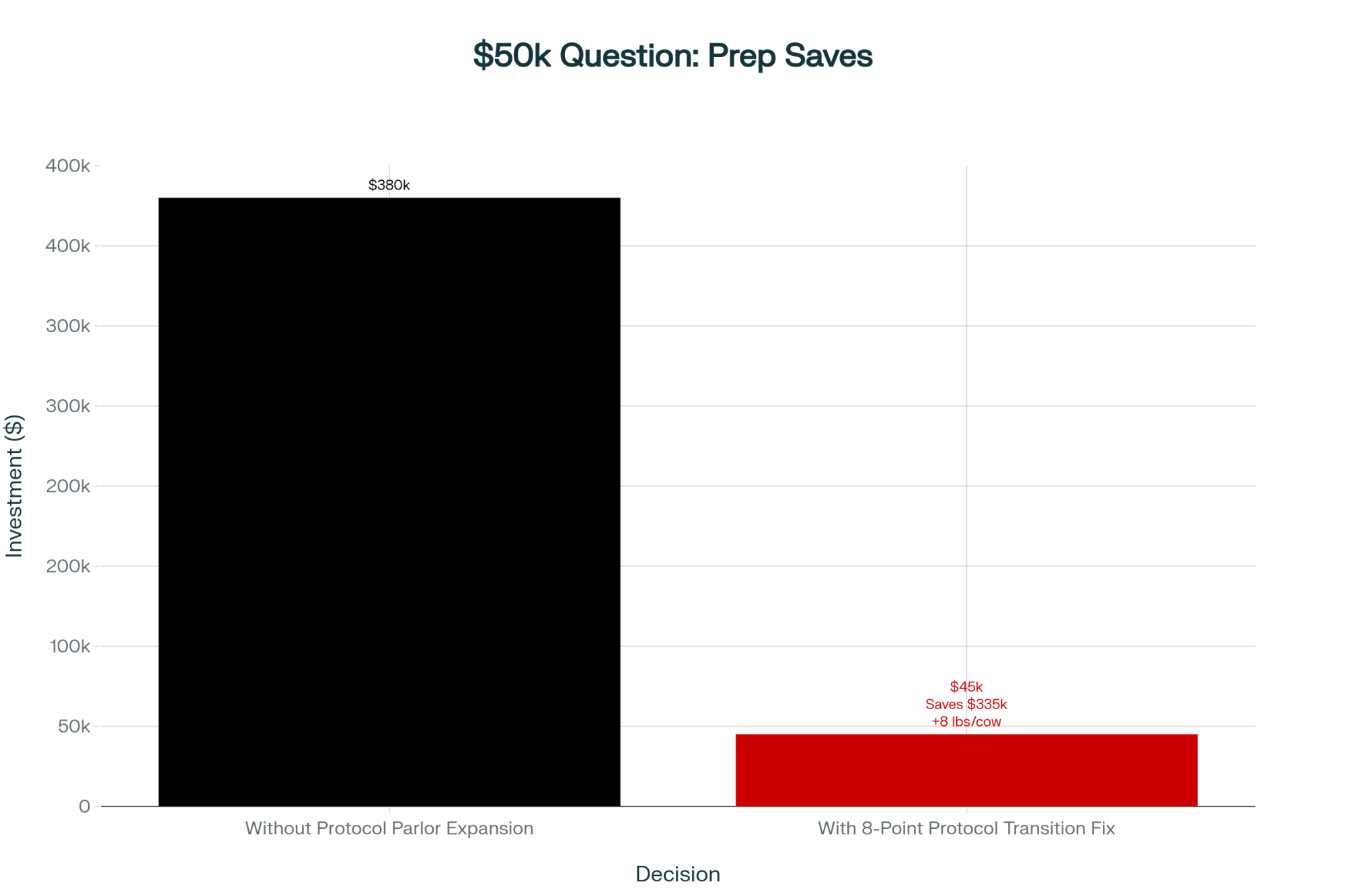
They were ready to expand their parlor. You know how it goes… milking was taking forever, cows were getting antsy, everyone was stressed. The contractor’s quote came in around $380,000. Not exactly pocket change, even when milk’s at decent prices.
But here’s where things got interesting.
Before signing anything, they decided to really dig into their numbers—and I mean really dig. What they found changed their thinking entirely. The bottleneck wasn’t milking capacity at all. It was their transition cow program.
Now, we all know transition cows can make or break you. Cornell’s been doing some fascinating work on this, and their PRO-DAIRY program keeps showing how every little hiccup in that transition period just cascades through the whole lactation. This particular farm? They were losing about 3 pounds per cow across the entire herd because their fresh cow area was, honestly, a disaster.
Instead of that $380,000 parlor expansion, they put about $45,000 into fixing their transition facilities and tightening up protocols. Two months later, they were up 8 pounds per cow.
Do the math on that—it’s real money. And it came from asking different questions.
Eight Things That Matter More Than You’d Think
After watching farms navigate good times and bad—from the 2014 milk price crash to today’s volatility—I’ve noticed there are about eight areas that really set the ones that thrive apart from those just trying to survive. What’s interesting is that none of these require a huge investment. They just require thinking a bit differently.
1. Who’s Really Driving This Decision?
This one’s subtle, but it matters more than you’d think. When a problem is raised during your dairy consulting visit or farm meeting, who raises it makes all the difference.
I’ve noticed that when employees bring stuff up, they’re usually seeing the daily friction—things that slow them down or make their jobs harder. When owners identify problems, they’re often looking at the bank statement. When your vet flags something, they’re seeing patterns they’ve noticed across multiple herds. Your nutritionist? They’re thinking about ration efficiency and feed costs.
Each perspective is valid. But incomplete. The magic happens when you get all these viewpoints in the same room—or better yet, in separate conversations where people feel safe being honest.
2. Your Herd Tells Stories You’re Not Reading
You probably know this already, but your herd structure is basically a crystal ball for the next two years.
Got a bulge in third-lactation cows? That’s telling you something about breeding decisions from way back that’ll affect you for years to come. Wisconsin’s extension folks have been talking about this forever—imbalanced herd demographics can quietly eat away at efficiency, and you won’t even notice until it’s too late.
Looking at research in the Journal of Dairy Science on herd dynamics, farms with balanced age distributions consistently outperform those with demographic bulges. It’s like having a slow leak in your tire. You don’t notice day to day, but suddenly you’re on the side of the road.
3. Yesterday’s Numbers, Tomorrow’s Reality
Here’s something we’ve all learned the hard way: today’s snapshot usually lies.
When you’re just looking at this month’s report, that “sudden” drop in components might actually be a gradual slide that finally got bad enough to catch your attention. The extension services have been preaching this for years—farms that look at a full year of data or more catch problems much earlier than those that just watch current reports.
The 2023-2024 Cornell Dairy Farm Business Summary really drives this home, showing that top-performing herds spend significantly more time analyzing historical patterns than average performers. Think about it like this… you wouldn’t judge your whole crop by looking at one plant, right?
4. Comfort Beats Genetics (Most of the Time)
Now, this might ruffle some feathers, but here it is: most production problems aren’t actually production problems. They’re comfort problems.
Comfort Factor | Impact | Dollar Loss |
|---|---|---|
| Lying Time -2 hours | -5+ lbs milk/day | $300-$400 |
| Poor Water Access | -3 lbs milk/day | $180-$240 |
| Inadequate Bunk Space | -4 lbs milk/day | $240-$320 |
| Heat Stress (unmanaged) | -10+ lbs milk/day | $600-$800 |
| Stall Comfort Issues | -5 lbs milk/day | $300-$400 |
| CUMULATIVE NEGLECT | Up to -27 lbs/cow/day | $1,620-$2,160/cow/year |
Research from the University of Wisconsin’s Dairyland Initiative keeps confirming this—when cows spend less time lying down, even just a couple of hours less, they can drop 5 pounds of milk or more. At today’s prices, that’s real money walking out the door every single day. Water access, bunk space, how deep your stalls are bedded… these “little things” often drive more profit than any fancy genetic program or feed additive.
I mean, you can have the best genetics in the county, but if your cows aren’t comfortable, what’s the point?
5. Know Where You Really Stand Financially
Every farm exists in three financial worlds at once. There’s where you are right now (usually tighter than you’d like), where you’re headed (hopefully better), and what you can actually afford to change (often less than you think).
Cornell’s Dairy Profit Monitor has been tracking this stuff for years, and what’s fascinating is that the most profitable farms aren’t necessarily the big spenders. They’re the ones whose spending actually matches their financial reality. A farm digging out of debt needs completely different strategies than one setting up the next generation.
Hope isn’t a business strategy, as much as we’d all like it to be.
6. When Everyone’s Pulling in Different Directions
This is a tough one. When your milkers think success means getting done fast, your feeder thinks it means spotless bunks, and you think it means high butterfat… well, you’re basically running three different farms that happen to share an address.
Getting everyone rowing in the same direction—that’s worth more than any piece of equipment you could buy. And it’s something every dairy consultant will tell you matters more than almost anything else.
7. Your Failures Are Actually Gold
“We tried that already.”
How many times have you heard that? Or said it yourself? But here’s the thing—knowing why something failed three years ago might be exactly what you need to make it work today. Different people, different feed prices, different weather patterns… everything changes.
That disaster from 2022 might be 2025’s breakthrough. But only if you remember what actually went wrong.
8. Your Employees See Things You Never Will
This is huge, and it gets missed all the time. Your employees—especially the ones who’ve been around a while—they see patterns you don’t even know exist.
But here’s the catch: they won’t bring it up in a meeting. Too risky. Get them alone, though, maybe while you’re fixing something together, and suddenly you’re hearing about that water trough that’s been dry every afternoon since spring, or how the fresh cows always look stressed after the weekend crew.
That’s intelligence you can’t buy. And it’s exactly what smart dairy consultants tap into during farm visits.
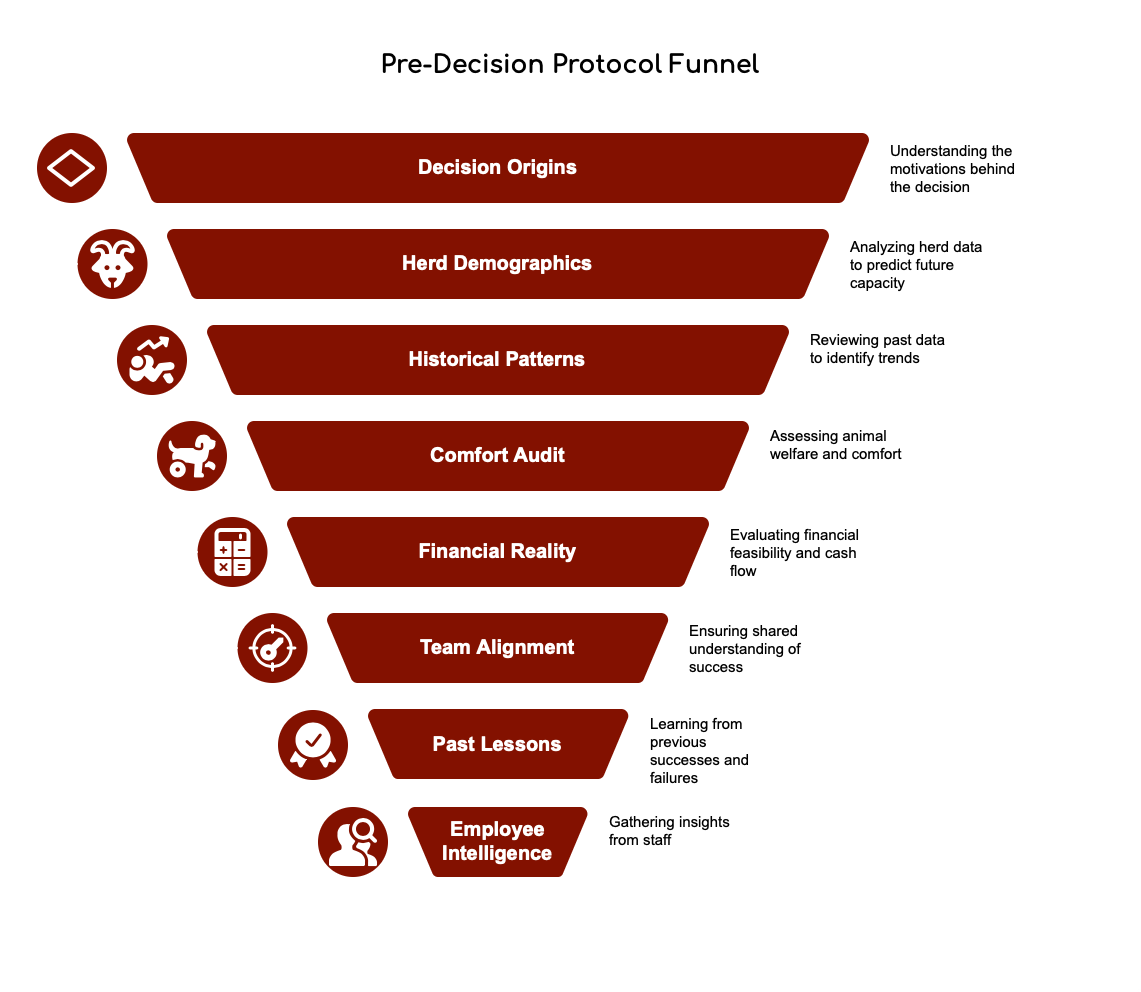
Your Complete Pre-Decision Protocol: The 8-Point Checklist + Action Plan
Want a printable version? Save this checklist for your next big decision.
Before any major decision or consulting engagement, here’s your roadmap:
☐ Decision Origins – Who identified this need, and what’s their real motivation?
Action: Ask each stakeholder privately why this matters now
☐ Herd Demographics – What’s your lactation distribution telling you about future capacity?
Action: Pull a current herd inventory report and map out your next 24 months
☐ Historical Patterns – Review 12-24 months of data, not just this month’s snapshot
Action: Block out 3-4 hours this week to analyze your long-term trends
☐ Comfort Audit – Check water access, bunk space, stall comfort before genetics or nutrition
Action: Spend an hour just watching cows—no agenda, just observe
☐ Financial Reality – Match investments to actual cash flow capacity over 24 months
Action: Run the numbers with your banker or financial advisor before committing
☐ Team Alignment – Ensure everyone defines “success” the same way
Action: Have one-on-one conversations with key employees this week
☐ Past Lessons – Document why previous attempts failed or succeeded
Action: Write down what you’ve tried before and why it didn’t work
☐ Employee Intelligence – Conduct private one-on-one conversations with key staff
Action: Schedule individual coffee breaks with your milkers and feeders
Total time investment: 12 hours over 2 weeks
Potential savings: $50,000-$200,000 in mistargeted investments
ROI on preparation: Often 100:1 or better
The Backwards Logic of Preparation

What’s fascinating—and kind of backwards when you first think about it—is that the more time you spend preparing before a decision, the less time you waste fixing mistakes later.
Based on what I’ve seen work across dozens of farms and validated by dairy management research, a good pre-decision assessment might take:
- Maybe 3-4 hours, really going through your records
- Another few hours talking with your team (one-on-one, not in groups)
- Some time just watching, with no agenda
- An hour or two connecting all the dots
So let’s say 12 hours total. Those 12 hours routinely save months of going down the wrong path and tens of thousands of dollars in investments that miss the mark.
Trust Changes Everything
Here’s something I didn’t expect when I started paying attention to this stuff: preparation builds trust like nothing else.
When you come to a discussion already understanding the history, respecting what’s been tried, seeing the patterns… it changes the whole dynamic. People stop defending and start collaborating.
I’ve watched this shift happen over and over. That skeptical producer who crosses their arms when the consultant walks in? They lean forward when they realize someone’s done their homework. Employees who usually stay quiet? They start sharing ideas when they see you actually care about the details.
And this isn’t just feel-good management talk—it directly affects your bottom line. Farms where everyone trusts the process implement changes faster and actually stick with them.
Real Numbers from a Real Decision
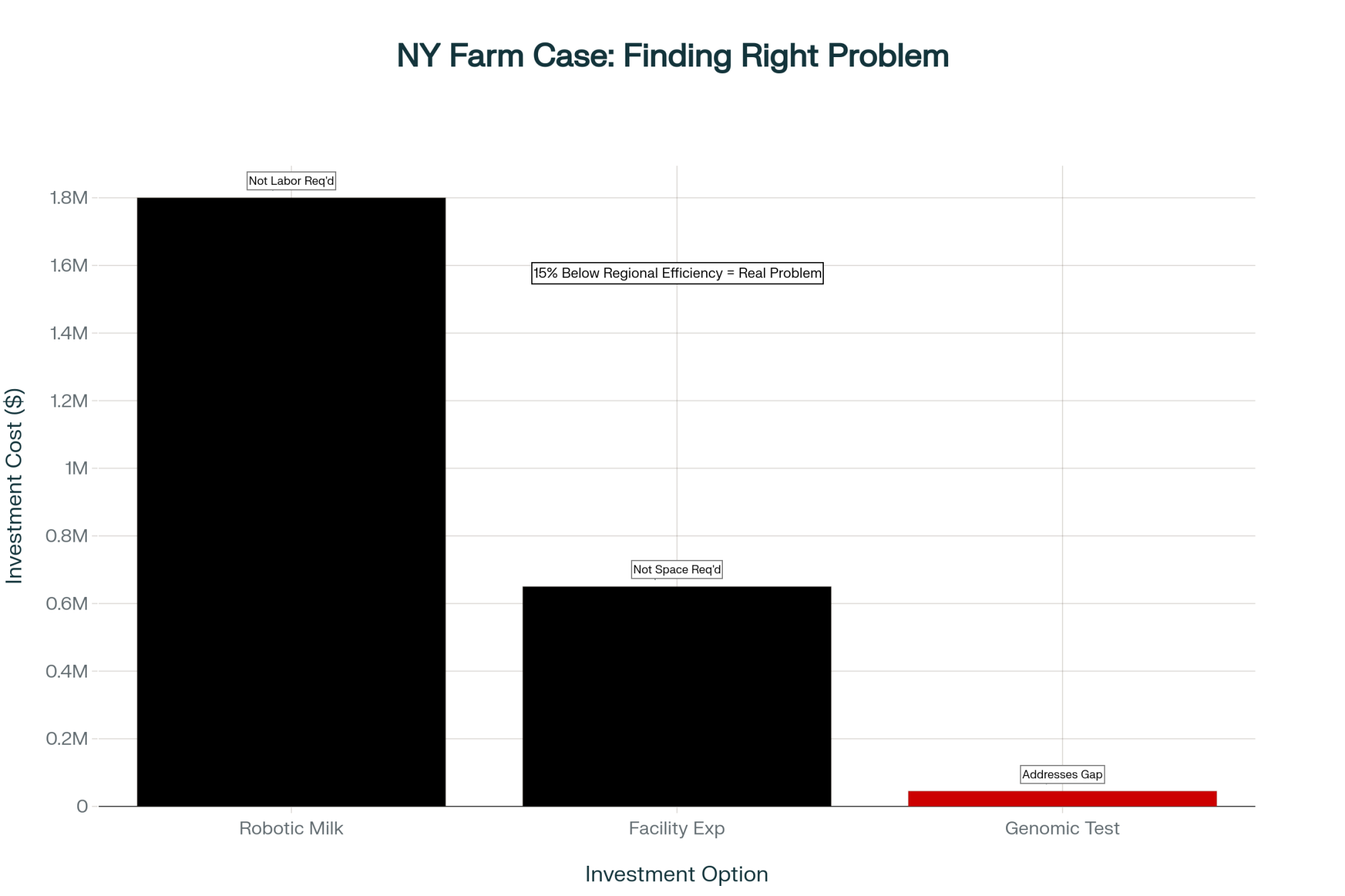
Let me share something that really drove this home. There’s a 600-cow operation in central New York—good people, been at it for generations.
They were looking at three big options: robotic milkers (about $1.8 million all in), expanding facilities (roughly $650,000), or really ramping up their genetics program with genomic testing (around $45,000 per year).
Instead of just picking what felt right, they spent two weeks really digging in. Used the 2023-2024 Cornell Dairy Farm Business Summary benchmarking data, talked to everyone individually, and looked at their five-year patterns.
What they discovered caught everyone off guard. Their constraint wasn’t labor—so robots didn’t make sense. It wasn’t space—so expansion was unnecessary. It was genetic potential. They were running about 15% behind the regional average in efficiency, and that was costing them way more than they realized.
That genomic testing investment? According to research published in the Journal of Dairy Science on the ROI of genetic improvement, programs like this typically start paying for themselves within 2 years. But without that preparation, they might’ve dropped nearly $2 million on the wrong solution.
The Cost-Benefit Reality Check
Let’s put this in perspective with real dairy economics:
- 12 hours of structured preparation = roughly $600 in time value
- Average mistargeted investment prevented = $50,000-$200,000
- Time saved on wrong implementations = 50-100 hours
- ROI on preparation time = Often 100:1 or better
When you look at it like that, can you really afford NOT to prepare? Especially when dairy consulting rates run $150-$300 per hour, making that preparation invaluable?
The New Math of Dairy Success
The folks at Cornell who put together the 2023-2024 Dairy Farm Business Summary keep finding the same pattern: farms that spend time planning consistently outperform those making decisions on the fly. We’re not talking small differences either.
In Wisconsin, operations that are really focusing on systematic decision-making—taking time to think things through—they’re seeing notably better returns. Research from the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Center for Dairy Profitability backs this up year after year. And when a couple of percentage points separate making it from losing it, that’s everything.
Looking at data from Texas to Pennsylvania, from Idaho to Florida, the pattern holds: preparation drives profitability more reliably than any single technology or management change.
The Bottom Line
As we push through 2025, with milk futures bouncing around and feed costs doing their thing, there’s less room for expensive mistakes than ever.
But here’s what gives me hope: the dairies that’ll thrive won’t necessarily be the ones with the biggest checkbooks or the fanciest technology. They’ll be the ones that master the simple discipline of thinking before doing. Of turning information into understanding, understanding into decisions, and decisions into profit.
The approach is proven. The patterns are clear. The protocol is right there in that 8-point checklist. The only question is whether you’ll invest those 12 hours of thinking to avoid a much more expensive education.
Because in today’s dairy world, being unprepared isn’t just costly—it’s dangerous.
What This All Means for Your Dairy Operation:
- That 12 hours of thinking before a big decision? It routinely saves months of mistakes and thousands in misplaced investments
- Transition cow management is often where the real money is—fixing it usually costs way less than expanding while delivering faster returns
- Your employees know things you need to know—but they’ll only tell you one-on-one, away from the group
- Looking at 18-24 months of data reveals patterns that this month’s snapshot completely hides
- The most profitable dairies aren’t the biggest spenders—they’re the ones whose investments actually match their financial reality
- Smart dairy consulting starts with preparation—the best consultants spend hours reviewing data before they ever step on your farm
Executive Summary:
The difference between a $45,000 fix and a $380,000 mistake? About 12 hours of asking the right questions. That’s what one Midwest dairy discovered when they ran through an 8-point checklist before signing that parlor expansion contract—turns out their real problem was transition cows, not milking capacity. This pre-decision framework, backed by Cornell’s latest research and proven across operations from 100-cow tie-stalls to 5,000-head dry lots, transforms how farms approach big decisions. The protocol covers eight critical areas: from reading your herd’s demographic story to those coffee-break conversations with employees who see problems you’ll never notice. Real-world results show that farms using this approach save $50,000-$200,000 per major decision, with returns often exceeding 100:1 on the time spent preparing. In today’s dairy economy, it’s not about having all the answers—it’s about asking all the right questions first.
Based on extensive work with dairy operations across North America and insights gathered from Cornell PRO-DAIRY programs, the 2023-2024 Cornell Dairy Farm Business Summary, Wisconsin Extension resources, University of Wisconsin-Madison Center for Dairy Profitability research, and the shared experiences of hundreds of dairy producers from 2023-2025.
Learn More:
- Why 150 Well-Managed Cows Beat 500 Poorly-Run Ones – Cornell data reveals how top 150-cow operations consistently outperform 500-cow dairies by $100K+ annually through superior management metrics, providing a proven 3-phase roadmap for capturing this profit gap without major capital investment.
- Transition Cow Success: Winning The High-Stakes Game That Makes or Breaks Your Dairy’s Profit Margin – Master the 90-day window that determines 75% of disease events and lactation success, with proven strategies for negative DCAD diets, 80% stocking density targets, and proactive health monitoring that boost milk yield by 10-20%.
- From Data to Dollars: Small Steps to Maximize Dairy Profits Through Accurate Herd Management – Transform intuition-driven hunches into data-backed decisions that drive measurable improvements across production, animal welfare, and sustainability—real-world examples show how systematic data analysis delivers immediate ROI.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!


































 Meet Holstein Canada’s new leaders for 2024-2025. How will President Gilles Côté and his team drive the future of the organization? Discover their strategic vision.
Meet Holstein Canada’s new leaders for 2024-2025. How will President Gilles Côté and his team drive the future of the organization? Discover their strategic vision.









