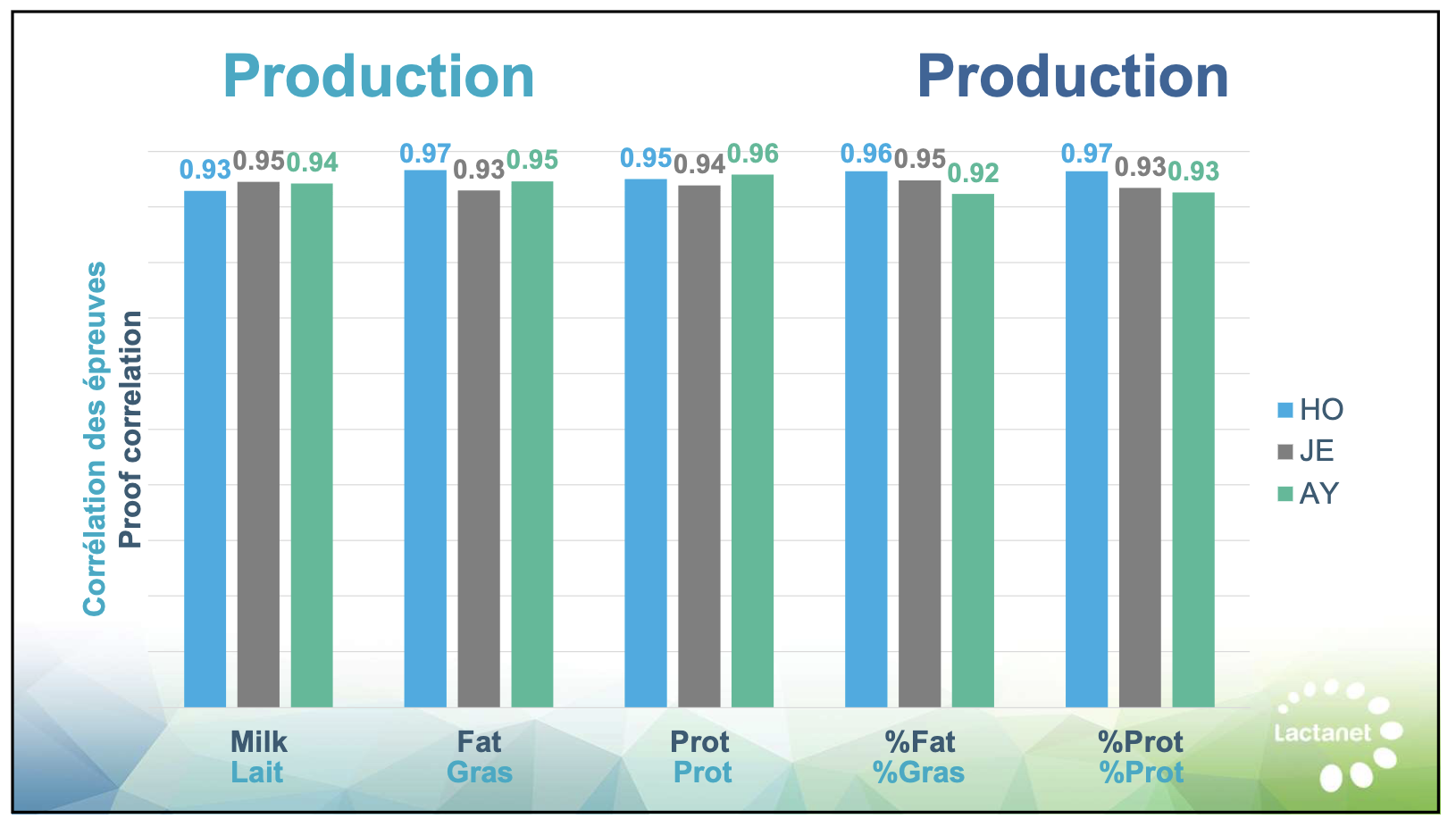
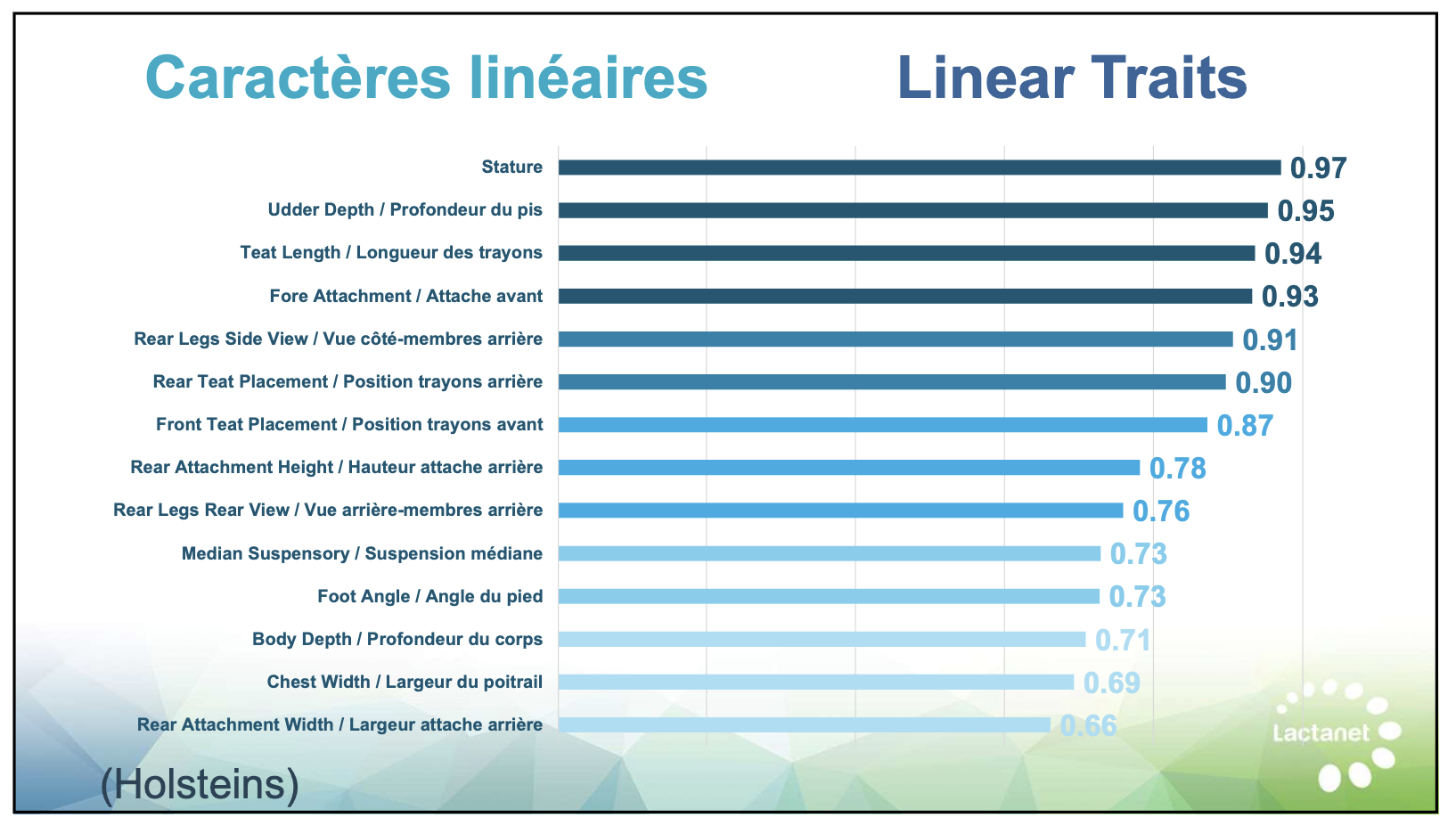
Find out how Canadian dairy breeders can now avoid the U.S. herdbook restrictions for genomic evaluations. Could this new choice simplify your breeding efforts?

Canadian dairy breeders are on the verge of an exciting change. Soon, you’ll be able to get genomic evaluations for domestically bred cows without needing to register them in National Breed Association herdbooks. This breakthrough will make it easier for all Canadian-born dairy cattle to receive genomic evaluations based on Canadian standards. Announced at Lactanet’s Open Industry Session, this change will simplify the process for Canadian dairy farmers, reducing the hassle of herdbook registration. Additionally, there’s a proposed fee waiver if you register your cattle promptly.
Genomic Evaluations in Canadian Dairy Breeding: Overcoming Challenges
Genomic evaluations are essential in modern dairy breeding, predicting future performance based on genetic makeup. Lactanet provides these services in Canada but faces challenges, especially for cows not registered in the National Breed Association herdbooks.
All genomic testing relies on the U.S. Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding (CDCB), which handles genotype quality assurance and haplotype analysis. The process involves higher costs and longer times, as breeders must go through CDCB directly, particularly for non-registered animals, costing US$6 per animal.
This system adds bureaucratic layers and financial strain, potentially discouraging breeders from using genomic evaluations entirely. Despite these challenges, genomic testing remains invaluable, allowing precise predictions of an animal’s potential and aiding better breeding decisions. However, until changes are implemented, Canadian dairy farmers navigate an inefficient system, limiting their ability to expand their genetic base and achieve top-rated status for their dairy herds.
Evolution in Genomic Accessibility: Canadian Calculations for All Dairy Breeders
Brian Van Doormaal, chief services officer at Lactanet, has announced fundamental changes that will make it easier for Canadian breeders to obtain genomic evaluations for cows not registered in National Breed Association herdbooks. This shift allows these evaluations to be conducted within Canada using Canadian calculations. Previously, breeders had to work directly with the U.S. Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding (CDCB) for such evaluations.
Although genomic testing will still occur in the United States, integrating with Lactanet means these genotypes can be shared in Canada. This eliminates the need to navigate the U.S. system for your genomic predictions, saving time and resources.
This change aims to increase inclusivity in genetic evaluations within the Canadian dairy industry. It expands the genetic base accessible to breeders and leverages Canadian service providers’ expertise and infrastructure. An associated fee may apply, but if an animal is registered within two months of testing, the fee could be waived, offering a cost-effective solution for breeders.
Lactanet is working with the CDCB on a new record-keeping process to ensure accurate tracking of these evaluations. Non-registered cattle will receive an alphabetic country code, differentiating them from registered animals and streamlining the identification process. This change will also align with other advancements, such as Lactanet’s transition to monthly official evaluations for Canadian females, potentially allowing more dairy cows in Canada to achieve top-ranked status in genetic rankings.
Ensuring Accuracy and Trust Through The Genomic Testing Process
The genomic testing process is key to accurately evaluating dairy cattle, with the U.S. Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding (CDCB) playing a crucial role. When you send a sample, the CDCB ensures quality through genotype validations and haplotype analysis. While future evaluations will be based on Canadian standards, the core testing and quality assurance will still rely on the CDCB’s infrastructure. This ensures that Canadian dairy farmers get consistent and reliable genomic evaluations, with the added benefit of local calculations.
New Logistics and Fee Structure for Genomic Evaluations
With the proposed changes, dairy breeders will see new logistics for obtaining genomic evaluations. Currently, the cost is US$6 per animal through CDCB. However, the fee structure might change once done in Canada, though specifics are still pending.
An exciting part is the potential fee waiver. If you register an animal within two months of testing, the fee might be waived, saving you money and encouraging timely registration.
Lactanet is working with CDCB on a solid record-keeping system to manage this. Registered animals will still have numeric country codes, while non-registered cows will get unique alphabetic country codes. This ensures explicit tracking and accurate genomic identification, enhancing trust in the genomic data.
Understanding the Logistics of this New Process is Crucial for Dairy Breeders
Understanding the logistics of this new process is crucial for dairy breeders. While genomic testing will still be done by the U.S. Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding (CDCB), Canadian service providers like Lactanet will handle the submission process. This means breeders can send samples through these providers, easing the workflow.
Regarding costs, though the exact fee is undecided, sending samples via Canadian providers will incur a charge. However, if an animal is registered within two months of testing, this fee might be waived, promoting timely registration.
Lactanet collaborates with the CDCB on a robust tracking system to ensure accurate record-keeping. Registered cattle will have numeric country codes, while non-registered cows will get alphabetic codes. This differentiation helps maintain clear genomic identification.
These logistics aim to make genetic evaluations more accessible and integrated within Canadian dairy breeding, leading to higher genetic standards and better breeding outcomes.
The Bottom Line
This new genomic option is a game-changer for Canadian dairy breeders. It will make genomic evaluations based on Canadian calculations available to all domestically bred cows. Although testing will still happen in the U.S., the process will be more streamlined and affordable for non-registered cattle in Canada. With the rise of automated milking systems and more accessible genotyping, this change is set to roll out later this year, transforming genetic evaluation and breeding for Canadian dairy producers.
Key Takeaways:
- Canadian genomic evaluations for non-herdbook dairy cows may be available later this year.
- Testing will still be conducted in the United States by the U.S. Council on Dairy Cattle Breeding (CDCB).
- Genomic evaluations will be based on Canadian calculations, making them more relevant and beneficial for Canadian dairy operations.
- The potential change allows all Canadian-born dairy cattle to receive a genomic evaluation, regardless of their herdbook registration status.
- Fees are yet to be determined but might be waived if the animal is registered within two months of testing.
- A new record-keeping process is being developed to differentiate between registered and non-registered cows via Canadian service providers.
Summary:
Canadian dairy breeders can now receive genomic evaluations for domestically bred cows without needing to register them in National Breed Association herdbooks. This change simplifies the process for Canadian dairy farmers and offers a proposed fee waiver if cattle are registered promptly. Genomic evaluations are essential in modern dairy breeding, predicting future performance based on genetic makeup. Lactanet, a Canadian service provider, has announced fundamental changes that will make it easier for Canadian breeders to obtain genomic evaluations for cows not registered in National Breed Association herdbooks. The change aims to increase inclusivity in genetic evaluations within the Canadian dairy industry and leverages Canadian service providers’ expertise and infrastructure. An associated fee may apply, but if an animal is registered within two months of testing, the fee could be waived. The new record-keeping process will ensure accurate tracking of genomic evaluations.