Learn how leaky gut makes heat stress worse for dairy cows, affecting their health and productivity. Find out effective ways to manage and reduce these effects.
Imagine a sweltering summer day—now imagine being coated in fur without escape. For many dairy cows throughout the globe, this is their reality. Not only is heat stress unpleasant, it seriously compromises health and output. Given the increasing frequency of harsh weather, controlling heat stress in cattle is vital. Reduced feed intake only explains 20–50% of milk production reduction during heat stress; however, other elements are essential. Economic survival and animal welfare in agriculture depend on an awareness of and a solution to this problem. Let’s explore how heat stress affects dairy cows, with an eye on “leaky gut syndrome” and how it affects metabolism and milk output.
High-Producing Dairy Cows: Navigating the Perils of Heat Stress
High-Producing Dairy Cows: Navigating the Perils of Heat Stress Due to their high metabolic rates and the significant heat generated during milk production, high-producing dairy cows are particularly vulnerable to heat stress. Unlike lower-producing cows, these animals must dissipate tremendous heat to maintain an average core temperature. When ambient temperatures and humidity rise, their ability to shed this heat decreases, leading to various physiological stresses.
A key metric for managing heat stress in dairy cows is the Temperature-Humidity Index (THI). This index combines temperature and humidity to reflect the environmental stress on the animal. As THI increases, so does heat stress, negatively impacting health and performance. Higher THI values correlate with reduced feed intake and drops in milk production. Elevated THI also exacerbates metabolic disturbances and impairs gut health, compromising milk yield and cow well-being. Farmers can implement timely interventions to mitigate heat stress and protect their herd’s productivity and health by monitoring THI.
Beyond Feed Intake: Unraveling the Complexities of Milk Production Loss During Heat Stress
But early 2000s studies by Drs. Lance Baumgard, a renowned animal scientist, and Rob Rhoads, a respected veterinarian, disproved this presumption. They found that about 20% to 50% of the milk production reduction could be ascribed to lower feed intake under heat stress. This suggests other intricate systems are also in action.
Dr. Baumgard and Dr. Rhoads have described how heat stress causes surprising metabolic alterations in dairy cows. Most famously, it boosts glucose use and lowers fat oxidation. This is not the typical metabolic reaction; lower feed intake lowers glucose consumption and promotes fat breakdown. Understanding these complex metabolic changes is crucial for developing effective strategies to combat heat stress.
These metabolic changes significantly affect the general production and use of nutrients. Higher glucose consumption, using sugar for energy, points to energy diverted to functions including immunological responses and core body temperature maintenance, limiting glucose available for milk synthesis and decreasing milk production. The decrease in fat oxidation, the process of breaking down fats for energy, exacerbates the energy shortfall, so cows cannot effectively utilize their fat stores to offset lowered glucose.
This two-fold metabolic disturbance compromises food partitioning and energy balance, causing production losses. Developing sensible plans to reduce the negative impacts of heat stress on dairy farming depends on an awareness of this interaction between heat stress and metabolic health in dairy cows.
Heat-Induced Leaky Gut Syndrome: A Silent Thief of Dairy Efficiency
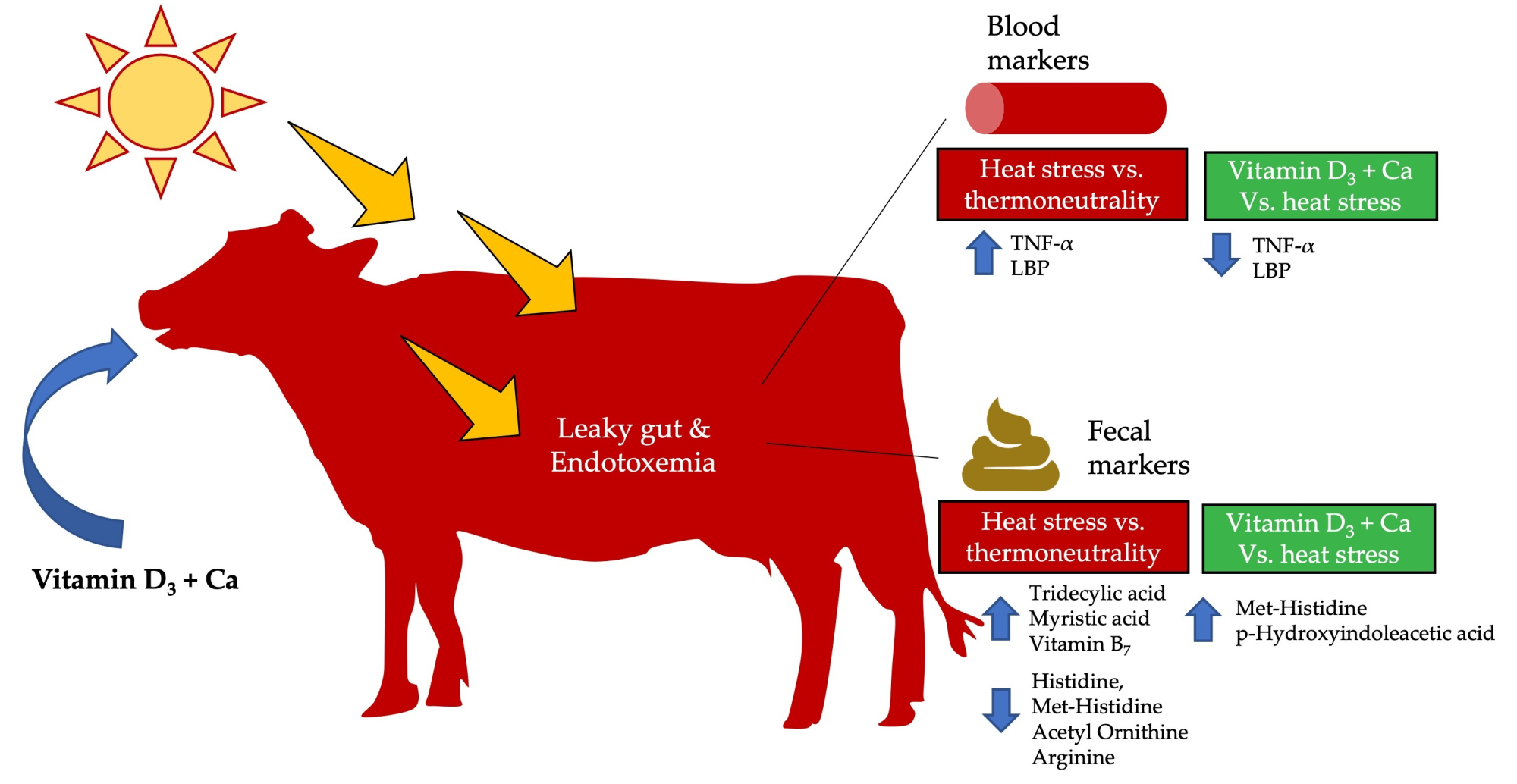
One crucial metabolic problem related to heat stress is leaky gut syndrome. This condition is considered a ‘leaky’ or compromised intestinal barrier, lowers dairy output, and impairs the intestinal barrier. It’s intimately associated with cows’ physiological reaction to heat. Cows must disperse more body heat via vasodilation, or widening blood vessels close to the skin, to effectively remove heat as temperatures increase. Still, this adaptation has expenses.
Vasodilation at the skin surface requires vasoconstriction in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract to sustain blood pressure, lowering blood flow to the enterocytes and the gut lining cells. This limitation results in hypoxia and nutritional deficits, which deplete energy and induce oxidative stress that compromises the gut lining. Crucially, compromised tight connections between enterocytes increase intestinal permeability, which is crucial for leaky gut syndrome.
Because bacterial components and endotoxins may enter the circulation via this compromised gut barrier, local gut inflammation and, perhaps, systemic inflammation are set off. Energy-intensive, the immune response takes essential nutrients away from milk output. Under heat stress, the systemic inflammatory state fits metabolic alterations such as higher glucose consumption and lower fat oxidation, tying leaky gut syndrome to GI problems and worse dairy efficiency.
Heat Stress and Gastrointestinal Compromise: From Vasoconstriction to Systemic Inflammation
Beginning with lower blood supply to the enterocytes, heat stress sets off a sequence of destructive consequences in the gastrointestinal system. Essential for preserving blood pressure elsewhere, this vasoconstriction unintentionally limits nutrients and oxygen in these vital cells. The outcome is oxidative stress and cellular energy loss, compromising the gut’s structural integrity. Tight connections between enterocytes break down, increasing intestinal permeability and enabling bacterial endotoxins to enter.
As the immune system responds to these increased permeability breaches, intestinal inflammation results. Unchecked, this localized inflammation might expand systemically and exhaust the animal’s metabolic reserves. These alterations compromise the intestinal barrier, endangering animal health and output under heat stress.
Inflammatory Cascade: The Energy Drain that Diminishes Dairy Productivity During Heat Stress
Heat stress weakens the intestinal barrier, letting bacterial chemicals and endotoxins like lipopolysaccharides (LPS) flood into the circulation. This breach causes local gut inflammation and, if unchecked, may cause systemic inflammation, triggering the whole body’s immunological response.
This inflammatory cascade has significant effects. Inflation transfers resources and energy from milk production to support the immune response. Reflecting a metabolic change that maintains inflammation but lowers energy available for breastfeeding, activated immune cells consume more glucose and less fat, lowering milk supply.
Mitigating Heat Stress in Dairy Cows: Advanced Strategies for Complex Challenges
Controlling heat stress is crucial for maintaining dairy cow production and health. Heat stress affects intestinal integrity and energy metabolism, posing complex problems without straightforward answers. Although not characteristic of a lower feed intake, it produces notable metabolic changes, including increased glucose consumption, decreased fat oxidation, and feed intake reduction.
Leaky gut conditions add even more complications. They compromise intestinal walls, causing this disorder, wherein bacterial chemicals and endotoxins may enter and cause inflammation. This inflammatory reaction causes further production losses by redirecting essential nutrients and energy toward immunological processes rather than milk production.
First, one must be thoroughly aware of heat stress and its subdued indicators. Beyond conventional approaches, mitigating efforts must combine modern management techniques, improved feed formulas, genetic selection, and creative feed additives. The urgency of this integrated approach is underscored by the need to enhance dairy cow resilience and well-being in the face of changing global temperatures and erratic precipitation.
Integrated Approaches to Combat Heat Stress: From Barn Design to Genetic Selection
Dealing with the complex problem of heat stress in dairy cows calls for targeted mixed approaches. Good management, like maximizing barn ventilation with fans and misters, may significantly lower ambient temperatures and cut the heat burden. Especially outdoors, where direct sunlight aggravates heat stress, strategic shade, and water-sprinkling devices are crucial.
Still, other essential components are feeding and formulation techniques. Changing diets to include more energy feeds without increasing dry matter consumption helps to preserve milk output. Specific feed additives showing the potential to reverse the metabolic consequences of heat stress include antioxidants, electrolytes, and yeast cultures. These supplements may improve immunity and digestive health, therefore boosting output.
Breaching for heat tolerance helps genetic selection provide a long-term fix. Deliberate breeding programs may make dairy cows more resistant to heat stress, preserving production even as world temperatures increase.
The Bottom Line
Beyond just lower feed intake and milk output, heat stress negatively affects dairy cows, including complicated metabolic changes and gastrointestinal problems, including leaky gut syndrome. Maintaining daily operations worldwide depends on addressing these issues, particularly given the changing climatic tendencies toward hotter climates. Heat stress alters the usage of nutrients, therefore influencing health and output. When intestinal integrity breaks down in leaky gut syndrome, systemic inflammation, and additional metabolic burden are caused. Under heat, vasoconstriction in the gastrointestinal system aggravates these disturbances. The dairy sector has to take a combined strategy to fight heat stress. Through improved management and creative solution investments, we can safeguard the health and output of our dairy cows, minimize financial losses, and improve animal welfare. Acting now will help to protect dairy farming’s future against the growing danger of global heat stress.
Key Takeaways:
- Heat stress significantly impacts the productivity, well-being, and overall health of livestock, especially high-producing dairy cows.
- The reduction in feed intake during heat stress accounts for only a portion of the milk production loss, suggesting other factors are at play.
- Heat stress induces metabolic changes such as increased glucose utilization and decreased fat oxidation, which are atypical for animals consuming less feed.
- The leaky gut syndrome, triggered by compromised blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract, can lead to inflammation and further disrupt nutrient absorption and utilization.
- Endotoxins from Gram-negative bacteria can penetrate the intestinal lining, causing local and potentially systemic inflammation, which competes for energy that would otherwise go towards milk production.
- Current management strategies must be enhanced to address both the visible and less visible signs of heat stress to maintain dairy cow productivity and health.
- A multi-faceted approach, including improved feeding strategies, environmental modifications, and genetic selection, is key to mitigating the adverse effects of heat stress.
Summary:
Heat stress is a major concern for dairy cows worldwide, particularly high-producing ones, due to their high metabolic rates and heat generated during milk production. The Temperature-Humidity Index (THI) is a crucial metric for managing heat stress, combining temperature and humidity. Higher THI values lead to reduced feed intake, decreased milk production, metabolic disturbances, and gut health issues, compromising milk yield and cow well-being. Researchers have found that 20% to 50% of milk production reduction can be attributed to lower feed intake under heat stress, compromising food partitioning and energy balance. Heat-induced leaky gut syndrome affects dairy cows, leading to lower output and compromised intestinal barrier. Controlling heat stress is essential for maintaining dairy cow production and health, and modern management techniques, improved feed formulas, genetic selection, and creative feed additives are necessary to combat heat stress.












