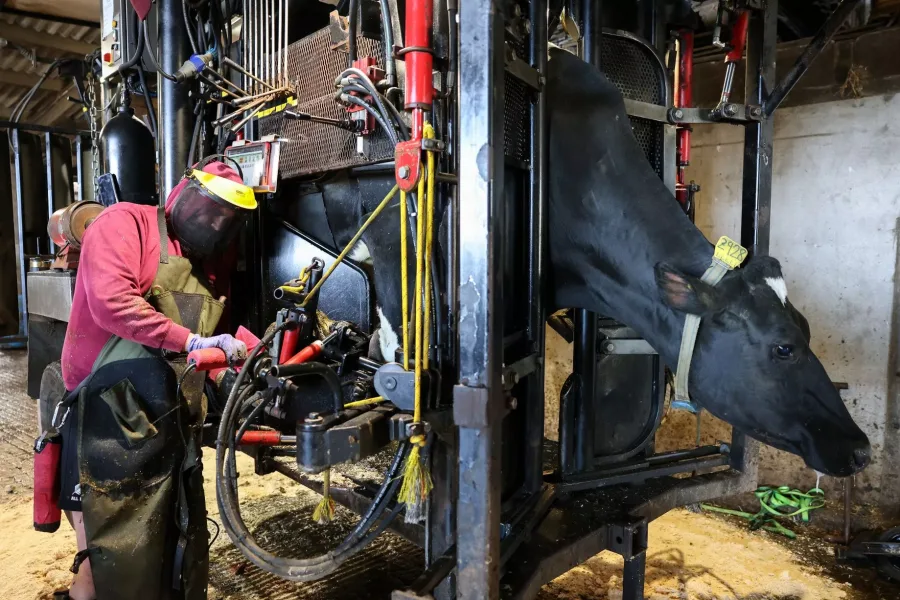
Explore the connections between hoof trimming, milk yield, and cow behavior. Could the ideal trimming schedules boost both dairy farm profitability and animal welfare? Discover the insights here.
Summary:
Hoof trimming is a critical aspect of herd health, affecting cow productivity and well-being. Its timing during lactation is debated, with some experts advocating for routine trimming and others for a more personalized approach. Neglecting hoof care can result in significant financial losses, including reduced milk output, increased veterinarian expenses, and a shorter herd lifetime. Lameness can decrease milk output by up to 15%, necessitating costly medical treatments or culling. The additional manpower required for handling and treating lame cows can also increase running costs. Hoof health is not only welfare but also an economic necessity, with each case of lameness costing between $90 and $300 per cow annually. Modern dairy farms are utilizing cutting-edge technologies like sensors, herd management systems, and hoof-trimming software to enhance herd management and hoof care. Real-time data on cow behaviors, such as eating, rumination, and activity, enables early lameness identification. Integrating modern technology in hoof care is a game-changer, enabling dairy producers to implement evidence-based hoof clipping, improving animal welfare and financial effectiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- Hoof trimming is essential for preventing lameness but optimal timing remains debated, especially during lactation.
- Restraining cows during trimming may have both immediate and lasting effects on milk production and behavior.
- Advanced technologies, including AccuTrim, DairyComp 305, and Sensoor EarTags, provide valuable insights into hoof health and its impact on dairy cows.
- First parity and multiparous cows trimmed after 110 days in milk (DIM) showed higher milk production than those trimmed before 110 DIM.
- Lame cows exhibited a significant reduction in eating time starting two weeks before trimming, with this decline continuing for up to six weeks post-trimming.
- Activity levels in lame cows were notably reduced both before and after trimming compared to those requiring only routine hoof care.
- Understanding the behavioral and productivity impacts of hoof trimming can guide more refined strategies, enhancing animal welfare and farm profitability.

Hoof trimming, a crucial aspect of dairy production, is more than a routine task—it’s a key determinant of herd health, significantly impacting cow productivity and well-being. Its primary goal is to prevent lameness, but its effects on milk output and behavior spark discussions about the best time during lactation. This article delves into studies that unveil the vital connection between foot trimming, milk production, and cow behavior. Discover why optimizing hoof trimming, a balance between animal welfare and economic efficiency, is paramount for your dairy operations and approach to hoof health.
Optimizing Hoof Trimming: Balancing Animal Welfare and Economic Efficiency
Proper hoof care ensures cows can move freely to access feed and water, supporting their overall health and productivity. The debate on the optimal timing for hoof trimming during lactation persists, with some experts endorsing routine trimming at set intervals. In contrast, others advocate for a more tailored approach based on individual needs.
| Aspect | Cost Per Cow | Annual Savings Per Cow | Additional Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Routine Hoof Trimming (Every 6 Months) | $30 | $70 | Reduced incidence of lameness |
| Reactive Treatment for Lameness | $150 | – | Recovery time, decreased milk yield |
| Preventative Measures (Proper bedding, nutrition) | $25 | $50 | Improved overall hoof health |
Neglecting hoof care can lead to significant financial losses, including reduced milk output, increased veterinarian expenses, and a shorter herd lifetime. Lameness alone can decrease milk output by up to 15%, and severe cases may require costly medical treatments or culling. The additional manpower needed for handling and treating lame cows can also raise running costs. These financial implications underscore the importance of proactive hoof care in maintaining farm profitability.
Hoof health is not just a matter of welfare, but also an economic necessity. By emphasizing the importance of good hoof care techniques, it’s clear that each case of lameness could cost between $90 and $300 per cow annually. This underscores the financial benefits of implementing regular trimming plans and utilizing modern data analytics, as recommended by producers, to proactively prevent lameness.
Producers are concerned that restricting cows for foot clipping might induce stress, influencing milk output and behavior. The main concern is whether this temporary restriction has long-term consequences such as changed food or activity habits and lower milk output. These issues have prompted the development of evidence-based trimming regimens that balance animal welfare with production using contemporary agricultural technology.
The Power of Technological Integration in Modern Hoof Care
Modern dairy farms are leveraging cutting-edge technologies such as sensors, herd management systems, and specialist hoof-trimming software to enhance herd management and hoof care. Real-time data on cow behaviors—eating, rumination, and activity—provided by sensors like Sensor Ear Tags enable early lameness identification. This integration of technology not only improves animal welfare but also contributes to farm profitability by optimizing hoof care.
By combining this sensor data with milk production records, herd management systems like DairyComp 305 help find ideal periods for hoof clipping, reducing stress and preserving high milk output.
AccuTrim and other hoof-trimming applications monitor the time, frequency, and results of trimming sessions, providing essential information on good hoof care techniques. Synchronizing this information with herd management tools helps farmers be aware of hoof conditions in general.
The integration of modern technology in hoof care is a game-changer. It enables dairy producers to implement evidence-based hoof clipping, thereby improving animal welfare and financial effectiveness. By reducing lameness, increasing milk output, and enhancing general farm sustainability and productivity, these techniques offer a promising future for dairy production.
Unveiling the Benefits of Flexible Hoof Trimming Schedules in Dairy Production
The first study, which took place on a Wisconsin dairy farm with a variable hoof-trimming schedule, used AccuTrim software and DairyComp 305 milk production statistics. The findings demonstrated that milk production was higher in cows clipped for the first time after 110 days in milk (DIM) than in those clipped earlier. When foot cutting was postponed beyond 110 DIM, first parity, and multiparous heifers showed better milk production.
| Category | Trim Timing (DIM) | Milk Production (kg/day) | Eating Time (minutes/day) | High Activity Time (minutes/day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Parity (Trimmed >110 DIM) | >110 | 35.2 | 420 | 180 |
| First Parity (Trimmed <110 DIM) | <110 | 33.8 | 415 | 175 |
| Multiparous (Trimmed >110 DIM) | >110 | 38.5 | 430 | 185 |
| Multiparous (Trimmed <110 DIM) | <110 | 36.9 | 425 | 180 |
| LAME (Pre-trim) | N/A | N/A | 367 | 143 |
| LAME (Post-trim) | N/A | N/A | 350 | 143 |
The results show the advantages of delaying the first hoof trim until 110 DIM; cows clipped later in lactation produce much more milk. This result highlights the possible benefits of besting milk output by adjusting hoof clipping schedules.
Behavioral Shifts Linked to Lameness: Insights from Sensor Data
Using information from a Wisconsin dairy farm over two years, the second research examined behavior data from Sensor Ear Tags and hoof-trimming records. Sensor data were gathered six weeks before and six weeks after each pruning session. Two groups were formed from cows: “TRIM” for those cut free from lesions and “LAME” for those detected as lameness or lesions during trimming.
| Days in Milk (DIM) | First Parity (Blue) – Milk Production (kg) | Multiparous (Orange) – Milk Production (kg) |
|---|---|---|
| ≤ 110 DIM | 28.7 | 34.5 |
| > 110 DIM | 32.1 | 38.2 |
Two weeks before cutting, eating time for LAME cows dropped; the week of trimming saw the most notable drop—53 minutes. This drop continued for up to six weeks after turning. Starting two weeks before cutting, high activity levels in LAME cows also dropped by 12 minutes; they stayed lower for up to five weeks after cutting.
Juxtaposing Studies: Unraveling the Complex Relationship Between Hoof Trimming, Milk Production, and Cow Behavior
The two research studies offer critical new perspectives on the interaction between cow behavior, milk output, and foot clipping. According to the first research, milk output increases when cows are trimmed after 110 days in milk (DIM). This implies that changing pruning regimens helps to maximize milk production.
The second research on behavioral effects primarily distinguishes between cows diagnosed with lameness (LAME) and those having regular trimming (TRIM). Beginning two weeks before cutting, LAME cows demonstrated an apparent decrease in feeding time; this trend remained throughout the following trimming week. Lower activity levels emphasize their pain even more.
These results underline the need for dairy producers to know the different behaviors of LAME and TRIM cows. While lameness requires careful treatment to address welfare issues, routine clipping may be deliberately scheduled to improve milk output. Dairy farmers using this dual method must maximize cutting plans and apply focused lameness treatments.
Advanced record-keeping systems and sensor data are among the modern technologies that provide farmers with a comprehensive understanding of cow activity and health. Using these instruments helps create better hoof care routines, enhancing cow welfare and farm profitability. Understanding and meeting the different demands depending on trimming and lameness state can help to make wise choices, thereby improving output and animal welfare.
Addressing Limitations and Future Research: Charting a Path Forward for Comprehensive Hoof Health Studies
Although these studies show encouraging outcomes, there are restrictions, especially regarding their generalizability to dairy farms with more excellent lameness rates than those in Wisconsin. The particular management techniques of the investigated farms could only represent a few situations in the dairy sector.
Further study is vital to confirm these results across various distances and herd sizes in other farm environments. Larger-scale, long-term studies can provide a more thorough understanding of the continuous effects of hoof clipping on milk output and cow behavior, guiding appropriate hoof care techniques.
While these results represent a significant step forward in understanding the relationship between dairy output and hoof condition, it’s crucial to remember that ongoing research is necessary. This research is not just about improving animal welfare and farm profitability, but also about contributing to the knowledge base of the entire agricultural community, making your role in this process even more significant.
The Bottom Line
Modern dairy production depends on accepting sophisticated data collecting and integration technology. Coupled with behavioral data from sensors, the correlation between hoof trimming time and improved milk production emphasizes the value of a data-driven strategy. Using instruments like AccuTrim software, DairyComp 305, and Sensoor Ear Tags, farmers may maximize hoof trimming schedules, therefore improving milk output and cow well-being for higher farm profitability.
Along with streamlining farm operations, this technical development marks the beginning of a new era of ethical and environmentally friendly animal handling. Data analysis of these systems allows hoof care plans to be customized to the demands of every herd, therefore combining animal welfare with financial effectiveness.
Every dairy sector participant should welcome these developments and pledge constant learning and adaptation. This will guarantee improved health results for dairy cows and financial gains, strengthening and enabling a strong dairy industry.
Learn More:
- Lameness in Dairy Cattle: Identifying Risk Factors and Overcoming Barriers to Best Practices
- Healthy Hooves, Healthy Herd: The Ultimate Guide to Reducing Cow Lameness in Transition Cows
- When to Get a Cow Pregnant for Maximum Milk Production and Profitability
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Bullvine Daily is your essential e-zine for staying ahead in the dairy industry. With over 30,000 subscribers, we bring you the week’s top news, helping you manage tasks efficiently. Stay informed about milk production, tech adoption, and more, so you can concentrate on your dairy operations.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!