You invested $2M in facilities but never spent $50 to test what’s costing you $43,800 every year
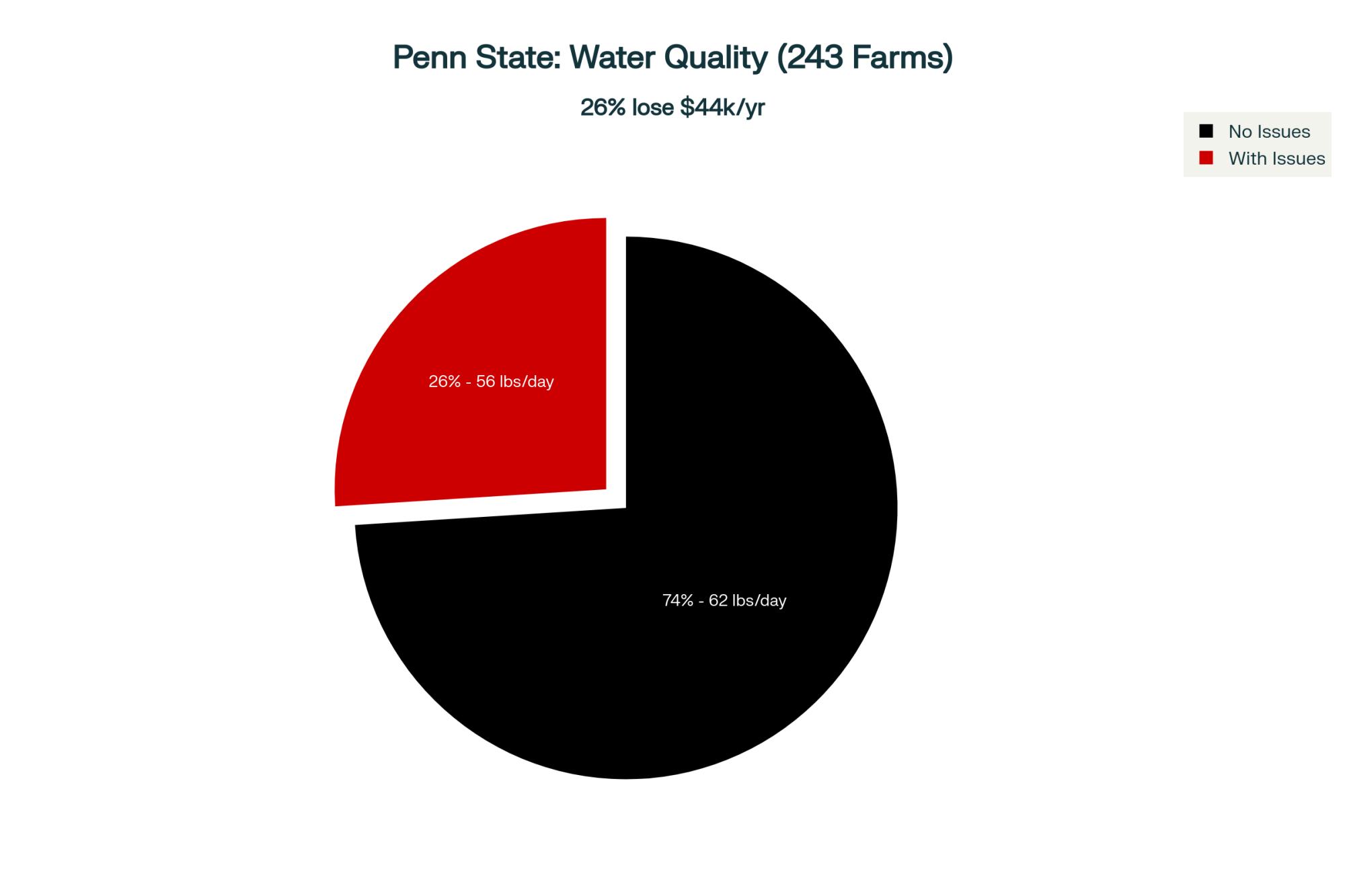
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: While dairy producers invest millions in genetics and technology, contaminated water silently steals $43,800 annually from the typical 100-cow operation. Penn State’s study of 243 farms revealed the stunning truth: water quality alone accounts for a 6-pound daily production gap, with clean-water operations hitting 62 pounds per cow versus just 56 for those with contamination. This isn’t just about lost milk—contaminated water creates a devastating cascade of mastitis, reproductive failure, and premature culling that costs $63,000-74,500 in just six months of delay. The solution is surprisingly accessible: a $50 test identifies problems, and treatment systems ranging from $1,300 for iron removal to $25,000 for comprehensive purification pay for themselves within 6-12 months. Leading operations have already transformed water from an overlooked utility into a managed production input, gaining compound advantages while their competitors wonder why they can’t hit benchmarks. The question facing every producer is simple: Will you keep letting water constrain your operation’s potential, or will you join the 26% who’ve discovered this hidden profit opportunity?

You know what’s interesting? Producers across the industry commonly report investing millions in new parlors, upgraded genetics, and precision feeding technology—but when you ask about water testing protocols, there’s often that long pause. “We’ve been meaning to get to that,” they’ll say.
Sound familiar?
This disconnect between our investment in visible technology and invisible fundamentals is costing dairy operations more than we realize. Pennsylvania State University’s comprehensive study tracking 243 farms across 41 counties discovered something remarkable: farms with water quality problems averaged 56 pounds of milk per cow daily, while those with clean water hit 62 pounds. Six pounds difference. Every single day.
And here’s what that means in real terms—run the numbers on that gap: six pounds per cow, 100 cows, 305-day lactation, twenty dollars per hundredweight, and you’re looking at $43,800 annually walking out the door. Or more accurately, never walking in at all.
Phil Elkins, a veterinarian who’s spent years researching water quality after founding FarmWater Ltd., describes it perfectly: “Water flows through every dairy operation like blood through a body. You can’t see it working when everything’s right, but when it’s wrong, the whole system crashes.”

Understanding the Production Gap: It’s More Complex Than We Thought
What I’ve found digging into the biological mechanisms behind these production differences is genuinely fascinating. This isn’t just about cows drinking less water—though that certainly happens. We’re looking at multiple cascading effects that compound throughout the animal’s system.
Consider iron contamination first. The USDA’s National Animal Health Monitoring System documented iron exceeding 0.3 parts per million on 40% of dairy operations surveyed. Now, that might not sound dramatic, but here’s what happens: cows detect that metallic taste and reduce water consumption. Michigan State research confirms that each 1% drop in water intake corresponds to a 0.5-1% reduction in dry matter intake. Less feed means less milk. Simple as that.
But the story gets more interesting. Iron in water exists primarily as ferrous or ferric ions—highly bioavailable forms that absorb rapidly in the rumen. Unlike the iron bound in organic compounds in feed, this water-borne iron creates oxidative stress through the Fenton reaction. More concerning still, it antagonizes copper absorption by more than 50%, according to Cornell’s trace mineral research team.
Nutritionists working across the Midwest commonly report seeing operations triple their copper supplementation, adding expensive organic minerals to the ration, and still not getting the response they expect. Then they test the water and find iron at 2-3 ppm. Suddenly, everything makes sense.
Sulfate presents its own challenges, particularly in regions with certain geological formations. Wisconsin, South Dakota, parts of Minnesota—these areas commonly see sulfate levels exceeding 1,000-1,500 ppm in well water. In the rumen, that sulfate converts to sulfide, which then binds copper, selenium, zinc, and other trace minerals into complexes that the animal can’t absorb.
Dr. William Weiss from Ohio State, who led the National Research Council’s revision of mineral requirements for dairy cattle, has documented this extensively. His research shows that high-sulfate water essentially forces producers to double or triple dietary copper supplementation just to maintain marginally adequate levels. Even then, the antagonism often wins.
What’s particularly noteworthy for operations in limestone regions—and I’m thinking especially of Pennsylvania and parts of Wisconsin here—is how geology creates perfect conditions for both iron and manganese contamination. Meanwhile, western operations face different challenges with high total dissolved solids from mineral-rich aquifers. California producers frequently report TDS running 4,500 ppm during drought years, forcing them to blend multiple water sources. Each region has its own unique water-quality fingerprint.
Down in the Southeast, operations in Georgia often find the challenge is bacterial contamination from warm, humid conditions that promote biofilm growth. Producers in the region commonly describe cleaning troughs on Monday and finding them coated again by Friday. The heat and humidity just accelerate everything.
A Case Study That Changed Perspectives
Let me share what happened on a 260-cow operation in Somerset, England. This story has made waves across the industry because it clearly demonstrates what we might be missing.
The farm had actually abandoned one of its boreholes five years earlier—workers had been getting sick from the water. Yet despite excellent management and hygiene protocols, they continued battling chronic mastitis, elevated somatic cell counts, and persistent calf health issues.
Phil Elkins was consulting on the farm and suspected water might be the missing piece. Testing revealed something interesting: colony forming units ranged from zero at the source to 176 cfu/ml at various troughs. Classic biofilm contamination throughout the distribution system.
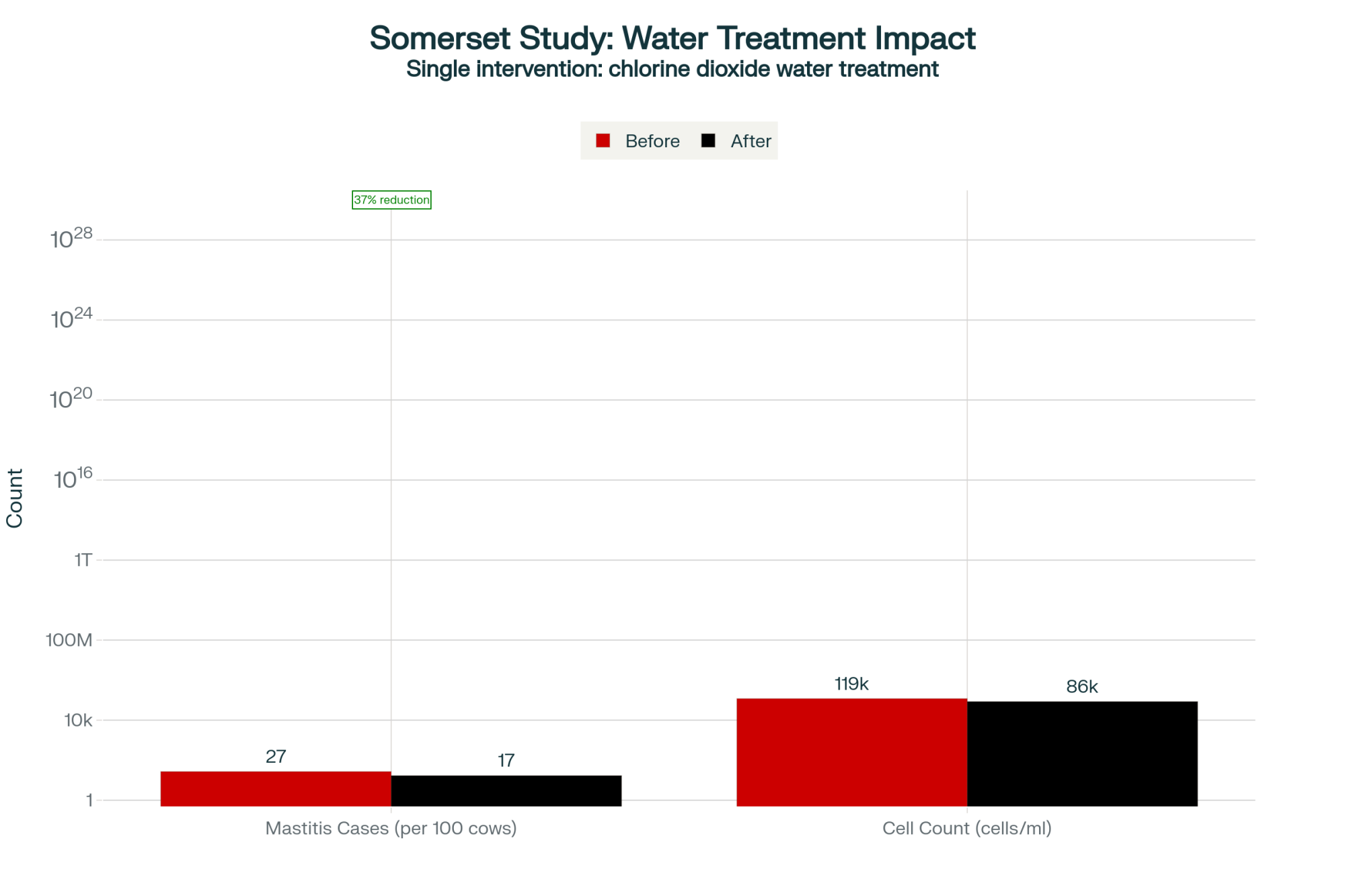
They installed a chlorine dioxide treatment system specifically designed to penetrate and eliminate biofilm. No other management changes were made during the study period—same feeding program, identical milking procedures, no facility modifications. Just treated water.
The 12-month results, published in Veterinary Record:
- Mastitis cases dropped from 27 to 17 per 100 cows annually (37% reduction)
- Bulk tank somatic cell count fell from 119,000 to 86,000 cells/ml
- Samples exceeding 100,000 cells/ml dropped by 69%
- Bactoscan readings plummeted from 86,000 to 16,000/ml
Producers involved in similar water-quality improvements consistently reflect on how they changed teat dips, replaced milking liners, and adjusted dry cow therapy protocols—nothing made a real difference until they addressed the water. The frustrating part, they say, is how simple the solution was once they identified the actual problem.
Economically, the system paid for itself in about 60 days. Treatment costs were approximately £2 per cow per month, while the combination of reduced mastitis treatment, elimination of milk quality penalties, and improved production delivered immediate returns.
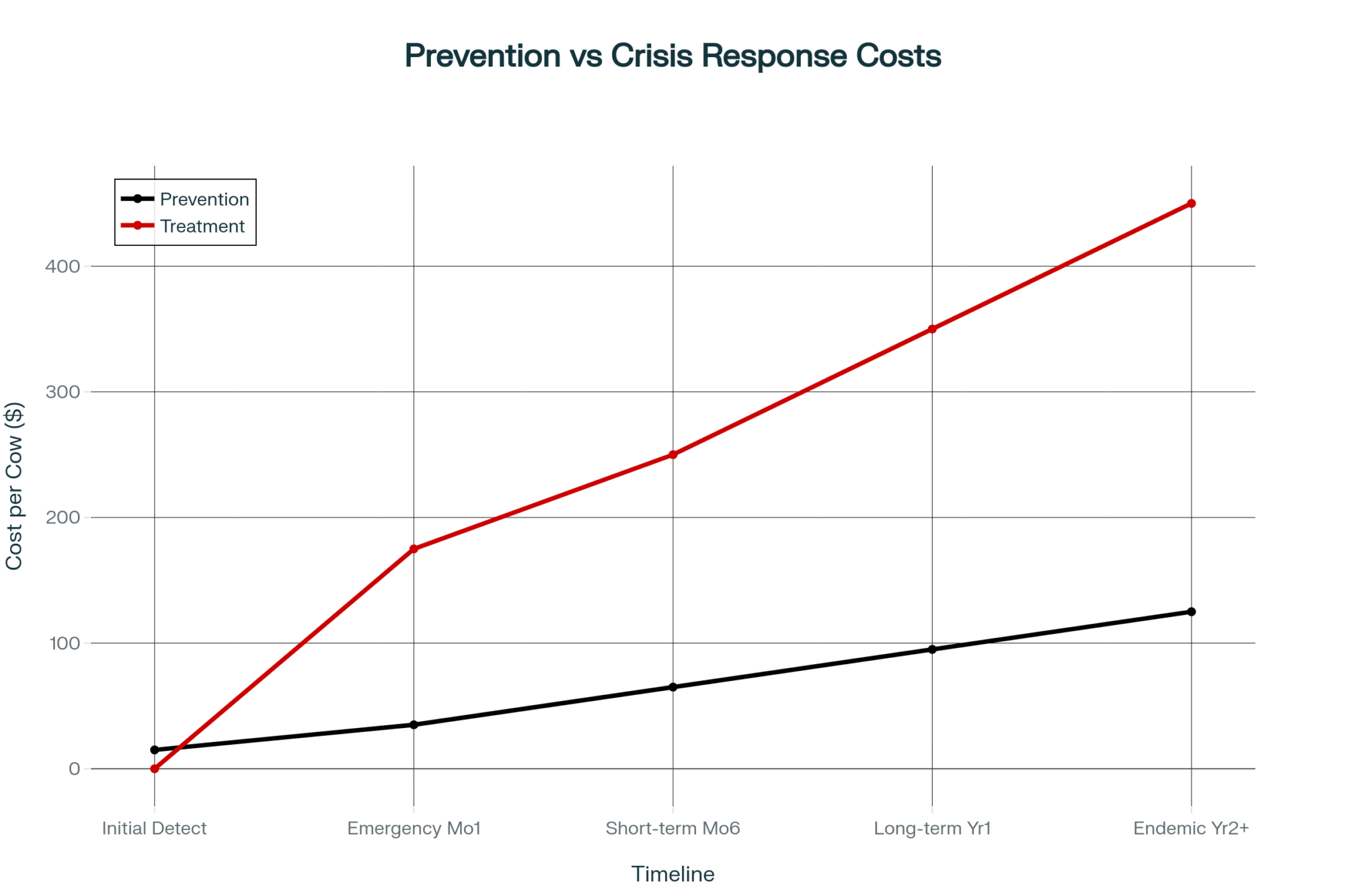
The Compounding Cost of Delay
This is where the economics become truly sobering. The University of Wisconsin’s School of Veterinary Medicine recently analyzed the full cost of delaying water quality interventions. Their findings suggest that six months of procrastination on a 100-cow operation costs between $63,000 and $74,500.

Why such dramatic numbers? Because water-quality problems cause cascading failures throughout your operation.
Start with the obvious: direct production loss. Six pounds per cow daily over 180 days equals 108,000 pounds of lost milk—about $21,600 at current market prices. That’s just the beginning.
Contaminated water harbors what microbiologists term a “persistent pathogen reservoir.” Research from the University of Guelph, published in the Journal of Dairy Science in 2023, calculated mastitis costs averaging $662 per cow annually when bulk tank counts hover around 184,000 cells/ml. Nearly half of these costs come from subclinical infections that never receive treatment.
Wisconsin producers frequently share experiences of treating mastitis case after case, burning through antibiotics, and losing quarters. It often never occurs to them that cows are essentially re-infecting themselves every time they drink.
Then consider reproduction. Water with nitrate-nitrogen above 10 mg/L correlates with increased services per conception, lower first-service conception rates, and extended calving intervals. Sulfate-induced trace mineral deficiencies contribute to retained placentas, early embryonic death, and repeat breeding.
The economic analysis from UW-Madison and Penn State Extension puts numbers to these problems: retained placentas cost around $300 each, pregnancy losses run $600-1,000, and each additional day open costs $2-5. Over six months, reproductive losses alone can reach $9,450 on a typical 100-cow dairy.
Perhaps most concerning is accelerated culling. Cows suffering from chronic mastitis, reproductive failure, and immune suppression from trace mineral deficiencies leave the herd prematurely. USDA data suggests that if poor water quality increases involuntary culling from 18% to 25% annually, those seven additional culls cost $14,000 in replacement expenses alone, plus lost production from younger animals.
How Progressive Operations Are Responding
The most successful operations I’ve observed aren’t simply installing treatment systems and moving on. They’re fundamentally reconsidering water as an actively managed production input.
Take continuous monitoring, for instance. Systems developed in the Netherlands, in collaboration with Wageningen University, now provide 24/7 water-quality surveillance across over 500 European dairy farms. When contamination appears or flow rates drop, producers receive immediate alerts.
ATP rapid testing offers another tool. This technology, borrowed from food processing, detects biofilm in seconds. Dutch Animal Health Service research shows that maintaining ATP levels below 100 relative light units is associated with sustained daily milk yield increases of 2.87 pounds per cow.
Michigan producers managing larger herds commonly describe their approach: monthly ATP testing takes five minutes and costs thirty dollars. It alerts them to biofilm development before it becomes a mastitis outbreak. The economics are obvious.
Individual cow water tracking represents another frontier. UC Davis researchers have developed systems integrating RFID ear tags with flow sensors to monitor individual drinking behavior. Penn State Extension recommends installing water meters—available from various suppliers for a few hundred dollars—to establish baseline consumption patterns.
Many producers discover something unexpected: trough cleaning schedules can actually suppress water intake. By avoiding cleaning during the hour after milking—when 30-50% of daily consumption occurs—operations frequently report gaining 3 pounds of milk per cow per day.
The real breakthrough comes from integration. Platforms combining water data with activity sensors, milk meters, and rumination monitors can identify problems days before clinical signs appear. Dr. Jeffrey Bewley at the University of Kentucky, who’s extensively researched precision dairy technologies, explains: “Water intake often provides the first indication something’s wrong—preceding milk drop, visible illness, everything else.”
Regional Considerations Shape Treatment Approaches
Geography matters tremendously in water quality management. What works in Wisconsin might not apply in New Mexico or Ontario.
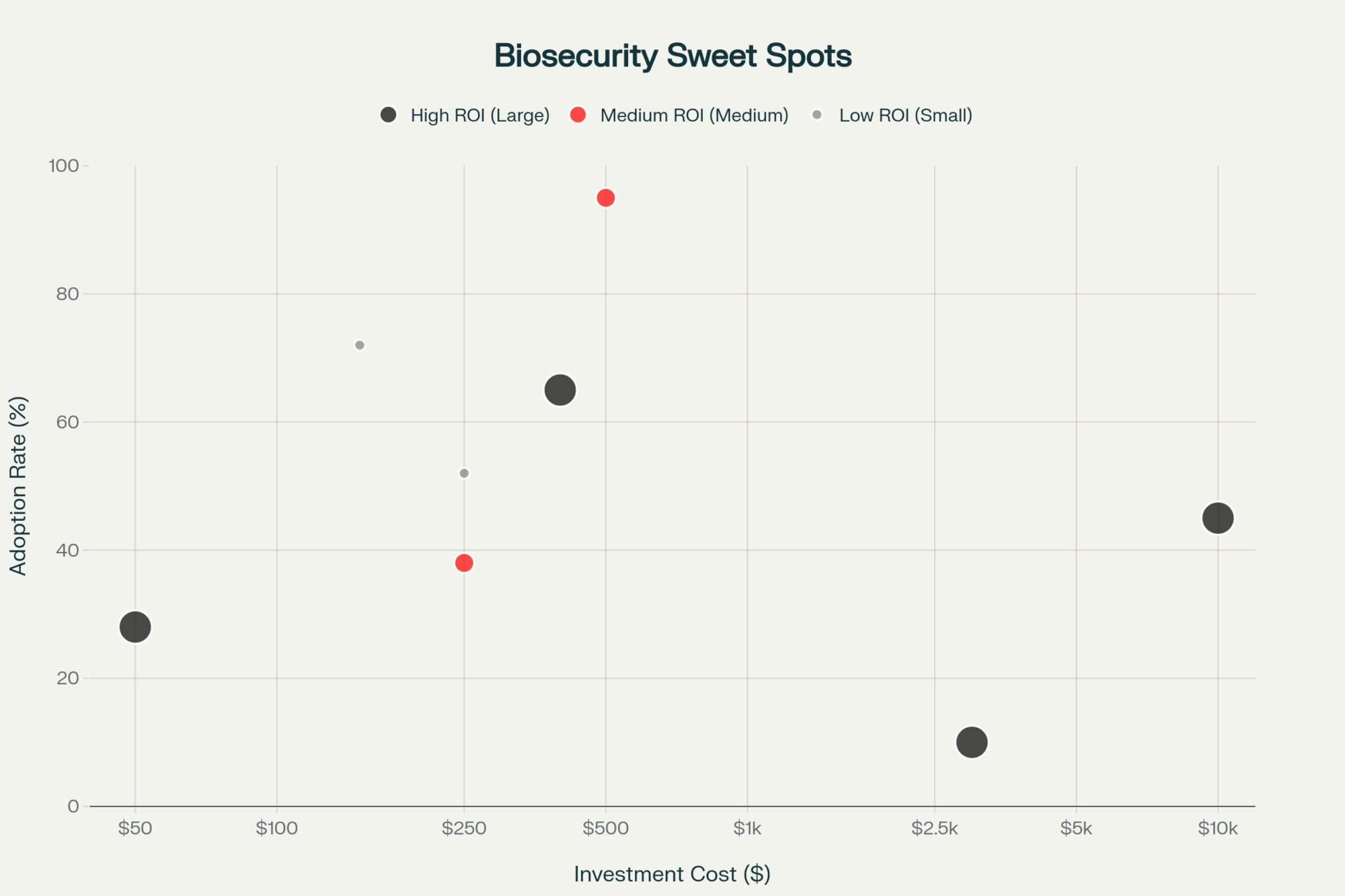
Limestone regions across Wisconsin, Pennsylvania, and parts of Ontario commonly face challenges with iron and manganese. The bedrock chemistry creates conditions that mobilize these minerals. Hydrogen peroxide injection systems work particularly well here—typically around $1,300 installed, plus about $800 annually for chemicals. Systems require minimal maintenance beyond annual pump inspection and occasional filter changes.
Western states deal with different issues. High total dissolved solids from mineral-rich aquifers often require reverse osmosis or blending with municipal water when TDS exceeds 3,000-5,000 ppm. These systems represent larger investments but may be the only viable solution. Membrane replacement runs every 3-5 years, depending on water quality and pretreatment.
The Corn Belt faces nitrate contamination from both point and non-point agricultural sources. Since nitrate removal is complex and expensive, deeper wells or alternative water sources often prove more practical. Test in late summer, when nitrate levels typically peak.
In the Pacific Northwest, operations commonly deal with seasonal variations tied to snowmelt and rainfall. Oregon producers report that iron levels have tripled during spring runoff, requiring seasonal adjustments to their treatment protocols. Testing in March and September captures both extremes.
Drought-prone regions see seasonal concentration effects. Texas operations typically experience sulfate levels doubling in summer. Many blend purchased water during the worst months—costs run about $200 a day, June through September—but it’s far cheaper than the production losses. August testing reveals peak contamination levels.
For organic operations, treatment options become more limited. While mechanical filtration and certain oxidation methods are permitted, many chemical treatments aren’t. Vermont organic producers often invest heavily in multiple filtration stages and UV treatment to meet both certification requirements and water-quality standards. Some equipment suppliers offer financing options, and USDA programs may assist qualifying operations with water quality improvements.
Making the Investment Decision: A Clear Cost-Benefit Analysis
Let’s address the economics directly. For a farm facing typical contamination—say iron at two ppm, sulfate at 1,200 ppm, TDS at 3,500 ppm—here’s the investment landscape:
Water Treatment Investment Breakdown (100-cow herd):
Hydrogen peroxide injection for iron removal: roughly $1,300 in setup costs and $800 in annual operating costs. This converts soluble iron into forms that precipitate, eliminating both the taste issue and oxidative stress. Filter replacement runs quarterly at about $50 each.
Reverse osmosis for high TDS and sulfate: $15,000-25,000 for agricultural-scale systems, plus $2,000-4,000 annually for membranes and electricity. While expensive, it’s a proven technology that removes 80-90% of dissolved solids. Membrane replacement every 3-5 years costs $3,000-5,000.
Chlorine dioxide for biofilm control: about $8,000 for generator equipment, $2,400 yearly for chemicals. This addresses distribution system contamination—critical because even perfect source water can be compromised as it passes through biofilm-laden infrastructure. Monthly chemical adjustments take 30 minutes.
Combined investment for comprehensive treatment: approximately $29,300 upfront, $6,200 annual operating costs. Against $43,800 in annual production losses, the math becomes straightforward.
Wisconsin producers consistently describe their decision process similarly: when they see iron at three ppm and sulfate over 1,500, that $25,000 for treatment suddenly looks like a bargain. Many realize they’re already spending more than that on trace mineral supplementation that isn’t working.

Understanding the Psychology of Inaction
Purdue University’s agricultural economics team has researched why producers delay addressing water quality issues despite compelling economic incentives. Their findings offer insights worth considering.
We all exhibit what behavioral economists call visibility bias—prioritizing obvious over hidden factors. New genetics produce visible offspring. Robotic milkers operate in plain sight. Water quality improvements occur underground, making returns feel less tangible even though they are measurably higher.
There’s also uncertainty aversion at play. Installing proven technologies like automated feeding systems feels predictable. Water quality investment raises questions: Will testing reveal problems? Will treatment deliver results? This uncertainty drives status quo bias—maintaining current practices even when change would clearly benefit the operation.
The industry itself bears some responsibility. Technology companies effectively market milk yield increases and labor savings. Water quality gets framed as compliance or problem-solving rather than a profit opportunity, despite superior ROI.
| Contaminant | Safe Level | Problem Level | Impact on Production | Treatment Solution | Est. Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) | <1,000 ppm | >3,000 ppm | Reduced intake, dehydration | Reverse osmosis | $15k-$25k |
| Iron (Fe) | <0.3 ppm | >2 ppm | 6 lb/day milk loss, oxidative stress | Hydrogen peroxide | $1,300 |
| Sulfate (SO4) | <500 ppm | >1,500 ppm | Mineral antagonism, reduced copper absorption | RO or blending | $15k-$25k |
| Nitrate-Nitrogen | <10 mg/L | >20 mg/L | Reproductive failure, conception issues | Deeper well or alternative source | Variable |
| Bacteria/Biofilm | 0 CFU | >100 CFU/ml | Mastitis, immune suppression | Chlorine dioxide | $8,000 |
| Chloride (Cl) | <250 ppm | >500 ppm | Salty taste, reduced intake | Alternative source | Variable |
Practical Steps Forward: Your 60-Day Action Plan
For producers ready to address water quality, here’s a systematic approach:
Week 1-2: Test comprehensively. Contact Midwest Laboratories (402-334-7770) or Penn State’s Agricultural Analytical Services Lab (814-863-0841). A livestock suitability test runs $43-75 and should include TDS, pH, sulfate, chloride, iron, manganese, nitrate, sodium, hardness, and bacterial counts. Sample where animals actually drink, not just at the source. Best testing months vary by region: August in Texas (peak drought), March in Oregon (spring runoff), September in the Corn Belt (nitrate peak).
Week 3-4: Understand the thresholds. Based on National Research Council guidelines, watch for TDS above 1,000 ppm (serious above 3,000), sulfate above 500 ppm (critical above 1,500), iron above 0.3 ppm, nitrate-nitrogen above 10 mg/L, and any coliform presence.
Week 5-6: Get treatment quotes. Prioritize based on your specific contamination profile. Iron responds well to hydrogen peroxide injection. High TDS and sulfate require reverse osmosis or water blending. Bacterial contamination needs chlorine dioxide treatment throughout the distribution system. Many suppliers offer financing options, and USDA conservation programs may provide cost-share assistance.
Week 7-8: Begin monitoring. Install flow meters to track consumption patterns. Use monthly ATP testing to detect biofilm development. Document pre-treatment production metrics to establish a baseline for ROI calculations.
Most operations see measurable improvements within 30-60 days of implementing treatment. The key is to start the process rather than wait for the “perfect” time.
The Bottom Line
After extensive research and conversations with producers nationwide, several principles have become clear.
The production gap is real and measurable. That six-pound daily difference translates to $43,800 annually on a 100-cow herd, before considering cascading effects on health, reproduction, and longevity.
Testing represents the highest-ROI decision available. A $50 water test reveals whether you’re among the 26% of operations losing money to contamination, based on Penn State’s multi-year survey data.
Treatment systems pay for themselves rapidly. Whether $1,300 for hydrogen peroxide or $20,000 for reverse osmosis, documented payback periods typically range from 6 to 12 months.
Delay multiplies losses exponentially. Six months of procrastination costs $63,000-74,500—more than double the treatment investment. Biology doesn’t pause for our decision-making.
Integration amplifies returns. Operations combining water treatment with comprehensive monitoring and management platforms report transformational improvements across all metrics.
What’s encouraging is that the dairy industry has made tremendous strides in genetics, nutrition, and reproductive management over the past decade. Water quality remains the overlooked variable—the hidden constraint preventing thousands of operations from reaching their genetic and management potential.
Progressive operations recognizing this opportunity aren’t just solving problems; they’re creating value. They’re building competitive advantages that compound annually. Better water enables healthier animals, supporting improved reproduction, extended productive life, and sustained production gains.
The fundamental question facing every dairy producer is straightforward: Will you continue assuming water quality is adequate while competitors who test and treat build increasing advantages? Or will you invest that $50 in testing to potentially transform your operation’s trajectory?
The science provides clear answers. The economics are documented. The only remaining variable is whether this knowledge drives action—or whether another year passes with water silently constraining your operation’s potential, one gallon at a time.
Key Takeaways:
- 6 pounds of milk per cow daily vanishes due to water quality—Penn State proved it across 243 farms ($43,800/year for 100 cows)
- Every month you delay costs $10,500-12,400 in cascading losses from mastitis, reproduction failures, and culling
- ROI exceeds 700% within year one after investing $1,300-25,000 in treatment (depending on your contamination type)
- Testing costs $50. Not testing costs $43,800. Call Midwest Labs (402-334-7770) or Penn State (814-863-0841) today
- Leading operations gain compound advantages by managing water as a production input—while competitors blame genetics
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Cleaner Cows, Better Milk: The Ultimate Guide to Udder Hair Removal for Higher Quality Dairy – Provides a practical guide to udder hair removal as another key tactic for improving hygiene. This directly supports the main article’s goal of reducing mastitis cases, lowering SCC, and boosting milk quality premiums.
- Top 7 Data Points to Track for Optimal Herd Performance – Broadens the strategic focus beyond water, revealing the 7 key data points that drive overall profitability. This demonstrates how to integrate water metrics with feed efficiency and reproductive data for complete, high-performance herd management.
- AI and Precision Tech: What’s Actually Changing the Game for Dairy Farms in 2025? – Details the concrete ROI for adopting the entire precision dairy ecosystem. It provides hard numbers on cost savings and payback periods for AI, sensors, and robotics, reinforcing the main article’s investment-for-profit argument.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!