October data: Production ↑3.7%, Herd ↓6,000 cows. First reduction of 2025. What smart producers know that you might not.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: October revealed dairy’s inflection point: producers culled 6,000 cows while production rose 3.7%, proving that margin math now trumps expansion momentum. At $16.91 milk and $165 cull values, keeping a cow losing $45/month means refusing $1,950 in immediate cash—a calculation thousands of farm families have already made. The heifer shortage (the lowest since 1978) has pushed replacements to $4,200, effectively locking the industry into its current size regardless of dreams of price recovery. Geography has become destiny, with new processing plants creating permanent $1.50/cwt advantages that no amount of good management can overcome. While some wait for $22 milk to return, successful operations are already adapting through component optimization, forward pricing, and even geographic relocation. October’s 6,000-head reduction isn’t a statistic—it’s 6,000 individual decisions that collectively signal dairy’s new reality: adapt to $17-19 milk or exit.

This caught my attention because it suggests we’re witnessing a pivotal moment where operational economics are beginning to override expansion momentum. After spending the week talking with producers and economists across Wisconsin, Texas, Idaho, and New York, what struck me is how this single data point reflects deeper strategic shifts happening across the industry.
Looking at the USDA’s October milk production report released this afternoon, total production reached 19.47 billion pounds, continuing the growth trend we’ve seen all year. But that 6,000-cow reduction? That’s producers voting with their culling decisions, signaling that margin pressures are finally forcing hard choices.

Dr. Marin Bozic, who tracks dairy economics at the University of Minnesota, offered an interesting perspective during our discussion. He noted that these patterns remind him of previous structural adjustments in commodity markets—times when the industry had to recalibrate expectations.
“What we’re observing isn’t just price pressure—it’s the convergence of biological lags from past breeding decisions meeting current economic realities. The industry is essentially paying for decisions made three years ago.”
— Dr. Andrew Novakovic, E.V. Baker Professor of Agricultural Economics, Cornell University
Here’s what’s particularly interesting—industry perspectives vary considerably on what this means. Some analysts I’ve spoken with suggest we’re seeing a temporary oversupply that could resolve with strong export demand or weather-related production disruptions by late 2026. Others see signs of more fundamental market restructuring.
And honestly? Both camps make compelling arguments.
Let me walk you through what the data tells us, and you can draw your own conclusions…
October 2025: The Numbers Behind the Decision
| Metric | Value | Source |
| National Herd Size | 9.35 million head | USDA Milk Production Report |
| Year-over-Year Change | +12,000 head | USDA NASS |
| October Adjustment | -6,000 head | USDA NASS |
| Milk Production | 19.47 billion lbs (+3.7% YoY) | USDA NASS |
| Class III Milk Price | $16.91/cwt | USDA-AMS |
| Cull Cow Value | $165/cwt (Southern Plains avg) | USDA Direct Cattle Report |
| Replacement Heifer Cost | $3,010 (July avg) | USDA-AMS Auctions |
| Daily Feed Investment | $8.50/cow | UW Extension |
The Math Behind October’s Culling Decisions
Here’s what struck me as particularly revealing: the national herd stands at 9.35 million head—essentially flat with only 12,000 more cows than in October 2024. Given all the processing capacity that’s come online recently, you’d expect more aggressive expansion. But that’s not what we’re seeing.
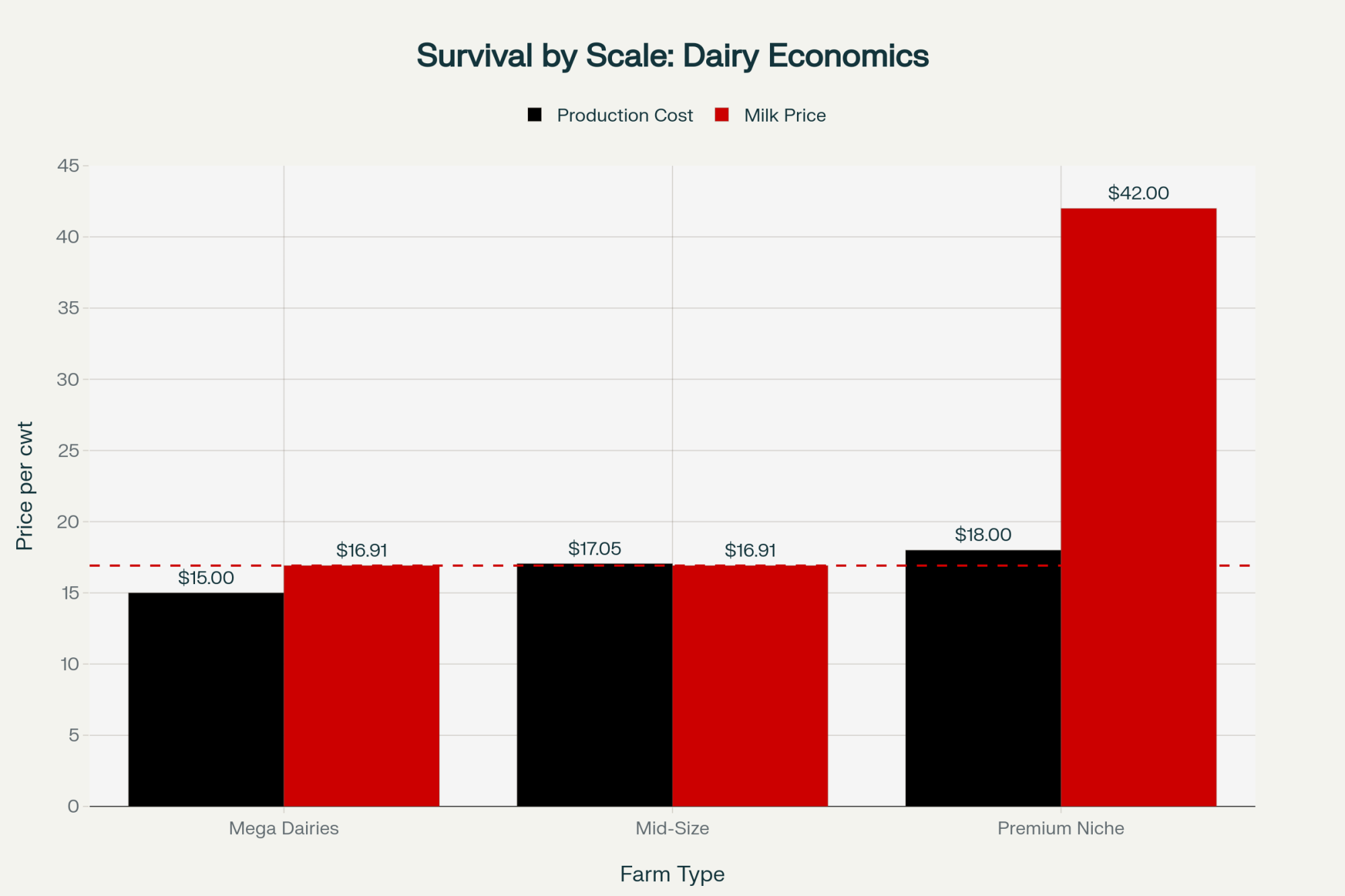
I spent time this week with a Wisconsin dairy operator managing 2,100 cows who walked me through their October decision-making. With Class III milk at $16.91 and feed costs around $8.50 daily, their bottom-quartile cows—those averaging 65 pounds versus the herd average of 85—were generating negative margins of about $45 monthly.
Meanwhile, cull values in the Southern Plains were hitting $165 per hundredweight.
Think about that calculation for a moment: $1,950 in immediate cash versus continued negative margins. It’s not an easy decision, but it’s becoming increasingly common.
What made October particularly significant was this convergence of pressures:
- Milk prices are settling at $16.91, well below the $20-23 range that justified 2023-2024 expansion plans
- Feed costs are stabilizing around $8.50 per cow daily (University of Wisconsin Extension’s November data)
- Cull cow values are reaching near-historic levels at $165/cwt in the Southern Plains
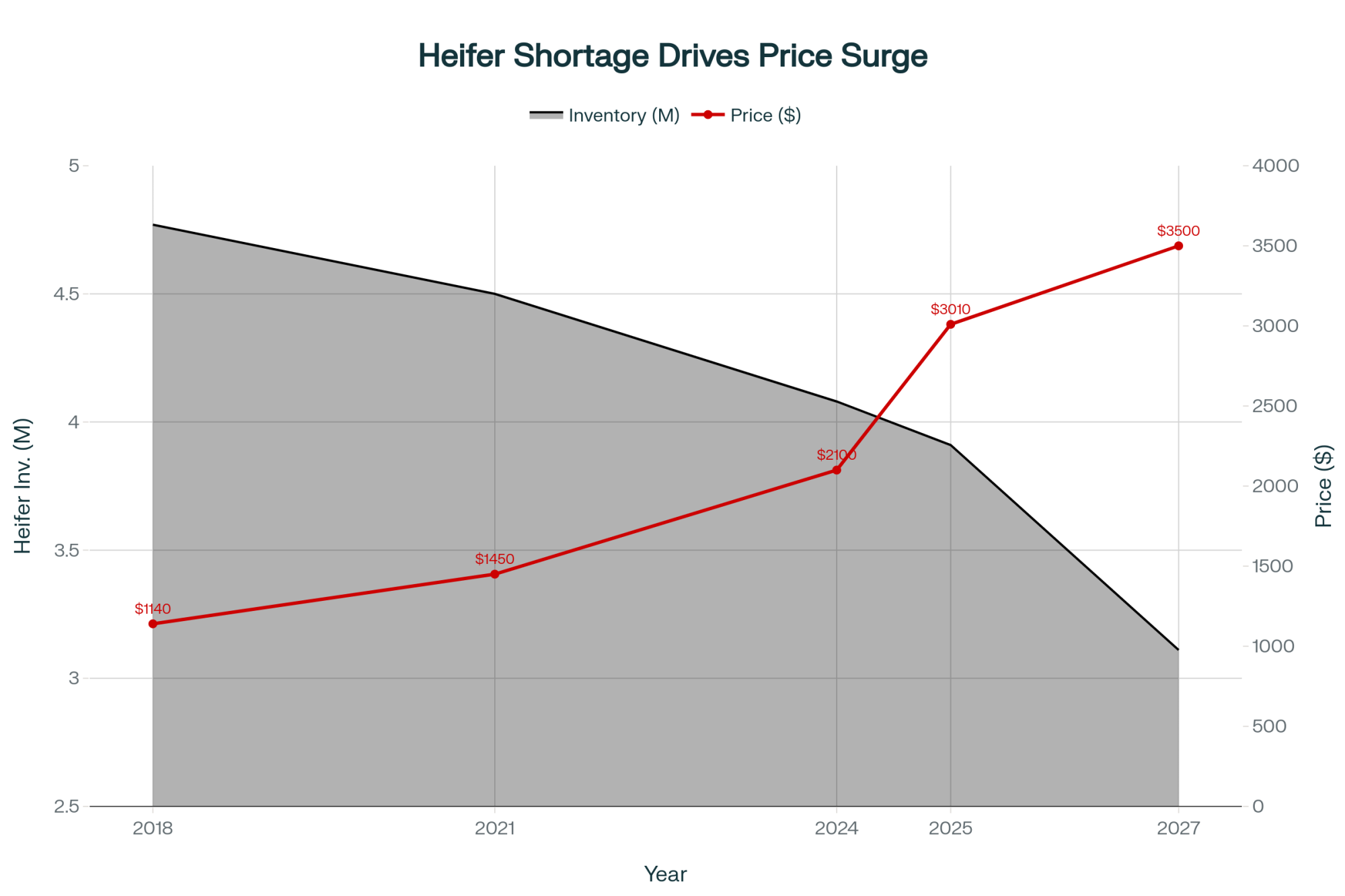
- Replacement heifers averaging $3,010, up from $1,720 in April 2023
- December Class III futures are showing $17.21 on the CME—not exactly a recovery signal
- Processing facilities are dealing with utilization challenges despite $10 billion in recent investments (CoBank’s August assessment)
An Idaho producer I spoke with, managing 450 cows near Twin Falls, described it this way: “We’re evaluating every animal’s contribution to cash flow. It’s about making data-driven decisions, not emotional ones.”
The Heifer Shortage Nobody Saw Coming (Except Everyone Should Have)

What’s fascinating—and honestly, a bit frustrating—is how predictable the current heifer shortage was, yet how unprepared we seem to be for it.
The price explosion from $1,720 to over $4,000 isn’t inflation; it’s the bill coming due for decisions made years ago.
According to USDA data, dairy heifer inventory hit 3.914 million head in January 2025—the lowest since 1978. I had to double-check that number because it seemed impossible. But it’s real, and it stems from entirely rational decisions made during the challenging price environment of 2015-2021.
When milk prices stayed in that $12-14 range for years, producers did what made economic sense: they bred with beef semen instead of raising dairy replacements. The National Association of Animal Breeders reports beef semen sales to dairy operations nearly tripled from 2017 to 2020.
We essentially removed 800,000 dairy heifers from the pipeline—about 130,000 per year.
Here’s the kicker that keeps me up at night: those breeding decisions from 2019-2021? Those missing heifers would be entering herds right now. Instead, we’ve got producers competing fiercely for the limited genetics available.
A procurement specialist for a large Texas Panhandle operation shared something revealing: “We locked in heifer contracts in early 2023 at $1,900, thinking we were being conservative. Those same genetics are $4,200 today. If we’d modeled $16.91 milk instead of $21, our entire expansion strategy would’ve been different.”
There’s a glimmer of hope, though. Gender-sorted semen sales jumped 17.9 percent from 2023 to 2024—1.5 million additional units, according to the National Association of Animal Breeders.
But meaningful relief? We’re probably looking at 2027.
Regional Realities: Why Your Zip Code Matters More Than Ever

Looking at the October state-by-state data, what jumped out at me was how dramatically different the dairy economy looks depending on where you’re standing.
The growth stories:
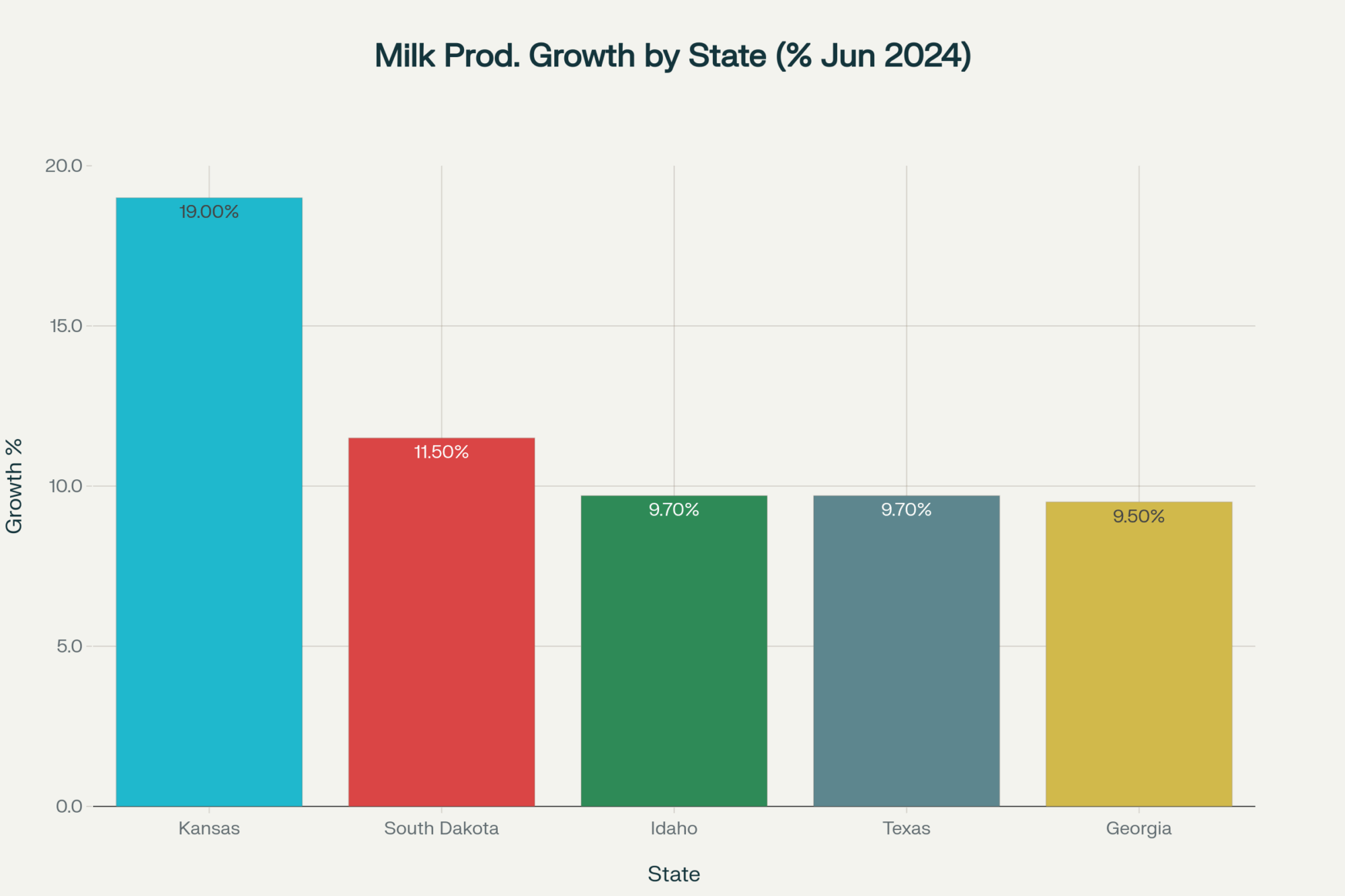
- California: Up 6.9 percent (though comparing against last year’s bird flu challenges)
- Idaho: Up 7 percent (that new Glanbia cheese plant in Twin Falls is pulling everything)
- Texas: Added 26,000 cows despite yield challenges
- Michigan: Up 4.3 percent
- New York: Up 4 percent
But here’s where it gets interesting. A Pacific Northwest producer managing 1,800 cows near Lynden, Washington, shared their reality: “We’re getting $16.16 per hundredweight while Idaho producers see $17.66. That $1.50 difference? It’s because we’re shipping to powder plants while they’re shipping to cheese plants.”
This illustrates something I’ve been tracking for a while—the growing divide between regions with new processing investments and those without. The Federal Milk Marketing Order system, despite updates in 2024, still creates these regional disparities based on fluid demand assumptions from another era.
Processing investments are reshaping the geography of dairy: Leprino Foods’ $870 million Lubbock facility, Fairlife’s $650 million New York expansion, and Great Lakes Cheese in Abilene.
These aren’t just plants; they’re creating new centers of gravity for milk production.
Success Stories: Adaptation in Action
While challenges dominate headlines, I’ve encountered several operations that have successfully navigated current conditions through strategic adaptation.
A 1,200-cow operation in central New York completely restructured their approach this summer. They shifted focus from volume to components, reformulated rations to optimize butterfat (accepting a 4 percent volume decrease in exchange for a 0.35 percent butterfat improvement), and locked in 70 percent of their 2026 production through forward contracts.
The result? They’re projecting positive margins even at $17.50 milk.
Another success story comes from a Wisconsin cooperative that pooled resources among five family farms to negotiate better component premiums directly with their processor. By guaranteeing consistent high-component milk, they secured an additional $0.85/cwt premium above standard pricing.
In Pennsylvania, a 600-cow operation near Lancaster took a different approach entirely. They invested in on-farm processing, launching a farmstead cheese operation that now processes 30 percent of their production.
“We realized we couldn’t compete on commodity milk,” the owner explained. “But we could capture more value through differentiation. Our cheese sales are covering the losses on our fluid milk.”
What these operations share is a willingness to challenge traditional approaches and adapt to new realities rather than waiting for old conditions to return.
The Export Paradox and What It Really Means
Here’s something that initially puzzled me: September exports were phenomenal—cheese up 28 percent, butterfat exports nearly tripled according to the USDA.
Yet farm-level milk prices remain depressed. How does that math work?
The answer reveals an uncomfortable truth about global competitiveness. CME cheese at $1.56 per pound versus European cheese at approximately $1.90 (converted from euros) gives us an 18 percent price advantage.
We’re competitive precisely because our prices have fallen.
After processing and logistics, that $1.56 cheese price translates to farm-level milk values around $12.40 per hundredweight. That’s below breakeven for most operations.
So yes, exports are strong, but they’re preventing collapse, not driving recovery.
Mexico accounts for about 30 percent of our exports, according to the U.S. Dairy Export Council. But Rabobank’s November analysis flags something concerning: Mexico is actively building domestic production capacity with government support.
If they reduce imports by even 20 percent, that would be a significant demand shock.
Risk Scenarios: What Could Change Everything
While I’ve focused on current trends continuing, it’s worth considering what could dramatically shift the market:
Disease outbreak: An H5N1 resurgence affecting 5-10 percent of the national herd would immediately tighten supply and drive prices higher. Nobody wants this scenario, but it remains a possibility.
Weather extremes: A severe drought across the Midwest in summer 2026 could quickly reduce production by 3-4 percent. Combined with current tight heifer supplies, this could push milk prices back above $20.
Trade disruptions: New tariffs or trade agreements could fundamentally alter export dynamics. A comprehensive trade deal with Southeast Asian nations could open significant new demand.
Processing consolidation: If one or two major processors face financial stress and close facilities, regional oversupply could quickly become undersupply.
These aren’t predictions—they’re reminders that dairy markets can shift rapidly when unexpected events occur.
Practical Strategies for Navigating Current Conditions
Based on conversations with producers successfully adapting to current conditions, several strategies deserve consideration:
Margin-Based Management
Evaluating individual cow contributions monthly provides objective retention criteria. Several producers mentioned using $40 monthly contribution as their threshold, though your specific number will depend on your cost structure.
Component Optimization
With butterfat premiums at $0.50-1.50/cwt above base (varying by cooperative), optimizing for components rather than volume can improve margins. This might mean accepting lower production for higher component percentages.
Geographic Assessment
Honestly evaluating your regional competitive position matters more than ever. If you’re in a structurally disadvantaged region, consider whether repositioning—through relocation, market channel changes, or value-added production—makes sense.
Risk Management Tools
Forward pricing isn’t about predicting markets; it’s about creating certainty. Several producers described securing 50-70 percent of future production at known prices, allowing them to plan with confidence.
Collaborative Approaches
Producer cooperation—whether through joint marketing, shared resources, or collective bargaining with processors—is gaining traction as a strategy for improving positioning.
Looking Ahead: Key Indicators to Watch
The November and December production reports will reveal whether October’s 6,000-head reduction was an isolated adjustment or the beginning of something bigger.
Here’s what I’ll be watching:
Herd trajectory: Another 5,000+ reduction would signal systematic adjustment. Stabilization suggests October was an anomaly.
Per-cow production: Changes exceeding seasonal norms could indicate compositional shifts in the national herd—are we keeping the best and culling the rest?
Regional divergence: Continued growth in Texas/Idaho, while other regions contract, would confirm geographic consolidation.
Component trends: Rising butterfat with declining volume would indicate a strategic focus on quality over quantity.
The Bottom Line: Adaptation, Not Capitulation
October’s 6,000-head culling amid production growth tells us something important: the industry is beginning to self-correct, with individual producers making rational decisions based on economic reality rather than expansion momentum.
This isn’t about doom and gloom—it’s about adaptation. The operations that recognize current conditions as a new reality rather than a temporary disruption are positioning themselves for long-term success.
They’re not waiting for $22 milk to return; they’re building businesses that work at $17-19.
What’s becoming clear from my conversations across the industry is that successful navigation requires three things: an honest assessment of your specific situation, a willingness to challenge traditional approaches, and the courage to make difficult decisions based on data rather than hope.
The dairy industry has weathered massive transitions before—the shift from small diversified farms to specialized operations, the technology revolution, and multiple trade upheavals. Each time, those who adapted thrived while those who resisted struggled.
Current conditions represent another such transition. How individual operations choose to respond will determine not just their immediate survival but their long-term positioning in whatever structure emerges.
As we await the next production reports, remember that behind every data point are real farming families making real decisions about their futures. The 6,000-head reduction isn’t just a statistic—it represents thousands of individual choices, each reflecting unique circumstances and strategic calculations.
The market is speaking. The question isn’t whether to listen, but how to respond thoughtfully and strategically to what it’s telling us.
Resources for Further Information:
- USDA Milk Production Reports: www.nass.usda.gov
- University Extension Dairy Programs: Contact your state extension service
- Federal Milk Marketing Order Administrators: www.ams.usda.gov/about-ams/programs-offices/federal-milk-marketing-orders
- Risk Management Tools: Contact your milk cooperative or CME Group Agriculture
- Dr. Andrew Novakovic’s market analysis: Charles H. Dyson School of Applied Economics, Cornell University
- Component Premium Information: Contact your regional cooperative
Key Takeaways:
- The October Calculation: Keeping a marginal cow means refusing $1,950 cash today to lose $45/month tomorrow—that’s why 6,000 left the herd despite record milk production
- The 2027 Reality: With heifers at $4,200 and inventory at 45-year lows, the industry is locked into current size until 2027, regardless of price recovery
- Location Determines Survival: Processing investments have created permanent $1.50/cwt regional pricing advantages that no amount of good management can overcome
- Three Paths Forward: Optimize for components (butterfat premiums worth $0.50-1.50/cwt), lock in 50-70% of production at $17-19, or relocate to advantaged regions
- Bottom Line: October proved the market has fundamentally shifted—build a business that works at $17-19 milk or become a statistic
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Is Beef-on-Dairy causing America’s Heifer Shortage? – Reveals the structural root of today’s replacement crisis, detailing how the aggressive shift to beef genetics created the current inventory gap and why the recovery timeline is longer than market forecasts suggest.
- Strategies for Dairy Farmers: Managing Feed Variation to Minimize Economic Stress – Provides actionable strategies for tightening feed bunk management and TMR consistency to protect margins, a critical tactical adjustment for producers navigating the current high-cost, tight-margin environment.
- Optimize Your Dairy Farm: Lean Processes for Cleaner, More Efficient Operations – Demonstrates how to apply industrial “Lean” principles to dairy workflows, helping operations identify hidden inefficiencies and reduce labor costs without requiring significant new capital investment.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!