Boost profits, accelerate genetic gains, and produce valuable calves with embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen. Learn how to revolutionize your dairy farm!
Summary:
This article looks at how embryo transfer with IVF and male-sexed beef semen are transforming dairy farming. These new methods help farmers improve cattle genetics and increase calf value, even though they cost more at first. Smart planning and modern techniques can lead to big profits and give farmers an edge in the market. With more accurate genetic testing, these strategies are set to shape the future of smart dairy farms.
Key Takeaways
- Embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen are cutting-edge technologies that can significantly boost dairy farm profitability.
- Implementing these methods requires strategic planning and careful selection of donor and recipient cows.
- The economic benefits include substantial returns on investment, improving herd genetics and milk production.
- Dairy farmers must navigate challenges such as initial costs and market demand fluctuations.
- As genomic testing advances, these breeding strategies are expected to become more widely adopted.
- Progressive dairy farms leveraging these technologies could gain a significant competitive edge.

Profitability and efficiency are crucial in today’s changing dairy farming industry. Innovative farmers are leveraging advanced tools to overcome these challenges. Two innovative technologies, embryo transfer, and male-sexed beef semen, are gaining traction in the dairy industry due to their potential to revolutionize dairy breeding.
The Power of Precision Breeding
Embryo Transfer: Accelerating Genetic Progress
Embryo transfer, especially in vitro fertilization (IVF), is an excellent way for dairy farmers to improve their herd’s genetics quickly. This method helps increase top-quality cow genetics, boosting the herd’s overall quality.
Key Benefits of Embryo Transfer:
- Faster genetic improvements
- More uniform herd quality
- Fewer twin births
- Better conception in hot months
- Greater lifetime earnings from the herd
Even though embryo transfer costs more than regular artificial insemination, the long-term gains can be much more significant.
Male-Sexed Beef Semen: Optimizing Calf Value
Male-sexed beef semen is another innovative tool for dairy farmers. It helps create high-value beef calves, especially steers, that are popular in the beef market.
Advantages of Male-Sexed Beef Semen:
- More valuable beef calves
- Better growth and feed use
- Chance for higher prices from unique markets
- More choices for managing and breeding the herd
Implementing Advanced Breeding Strategies
Embryo Transfer Best Practices
To get the most from embryo transfer, dairy farmers should follow these steps:
- Choose donor cows with superior genetics to guarantee the birth of healthy and robust calves.
- Pick fit recipient cows with good health to improve the chances of successful pregnancies.
- Work with skilled veterinarians or experts to ensure the transfer process is done correctly.
- Keep detailed records of transfers and pregnancies to improve future breeding choices.
- Consider doing genomic tests on embryos to pick the best traits for your herd.
Effective Use of Male-Sexed Beef Semen
Here are some tips for using male-sexed beef semen effectively:
- Healthy cows are not needed to improve beef calf quality for breeding replacements.
- Focus on young cows for first and second breeding attempts to increase success rates.
- Handle semen carefully to keep it effective during insemination.
- Consider raising the calves to make more money from beef sales.
Breed-Specific Considerations
Different dairy breeds respond differently to embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen:
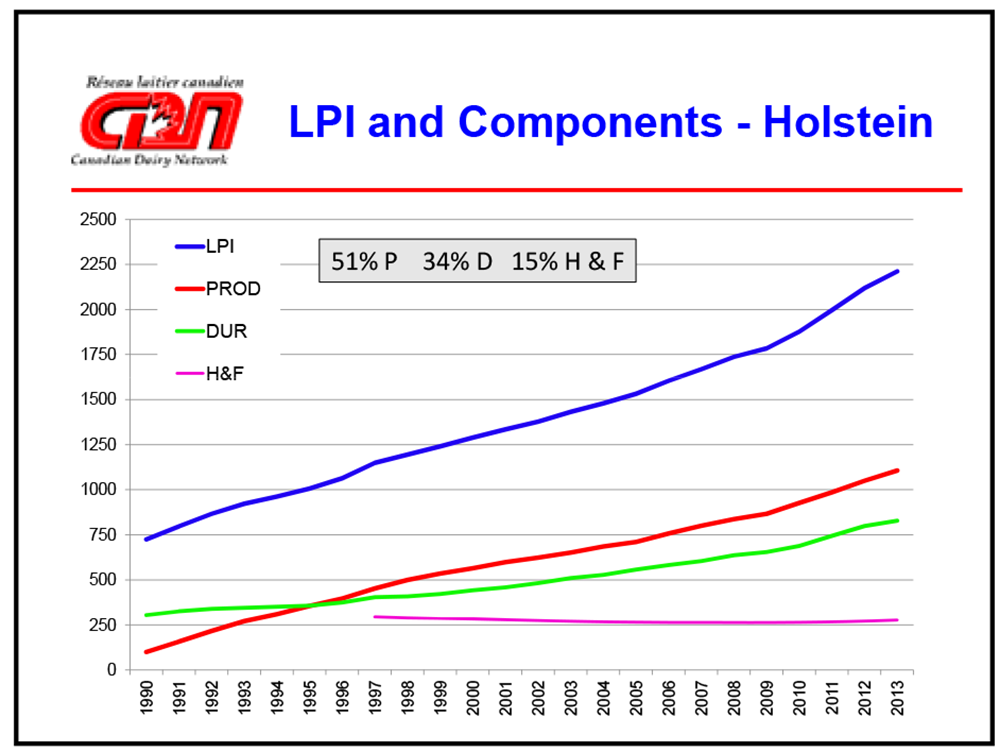
- Holsteins: They generally respond well to embryo transfer. Studies show that Holsteins have a moderate potential for improving embryo numbers and quality traits.
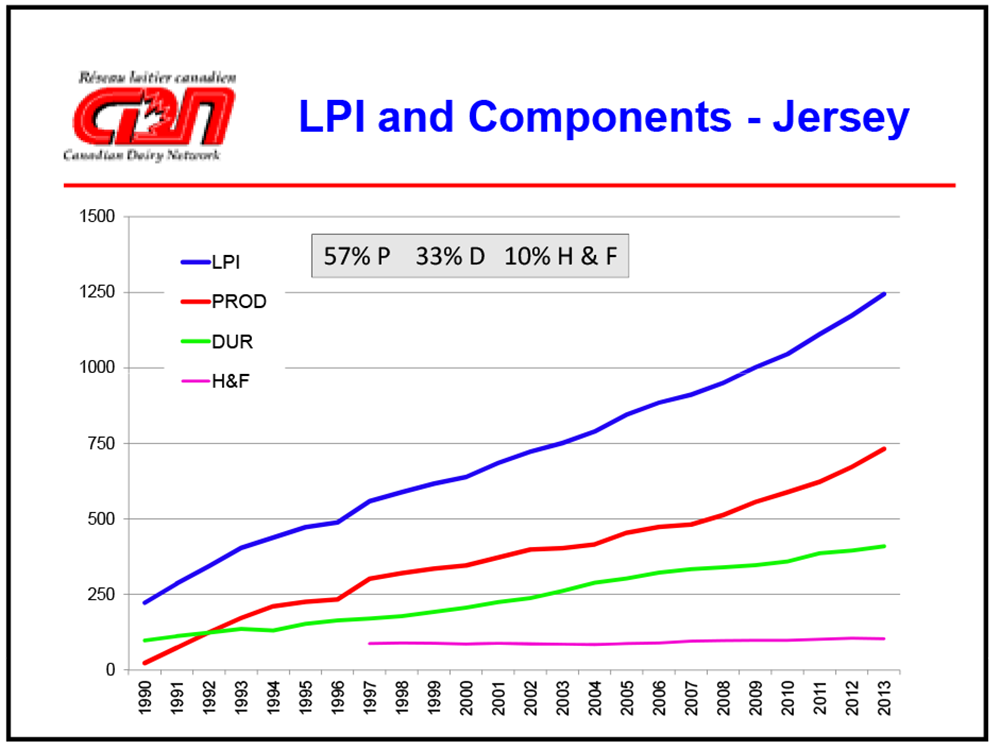
- Jerseys often have better conception rates than Holsteins. Studies in the Western US show Jerseys’ conception rates are around 37.5% with regular semen and 35.5% with sexed semen, compared to about 34% for Holsteins.
- Crossbreeds: Due to their hybrid vigor, crossbreed calves may benefit most from male-sexed beef semen. They can also add significant value, fetching 50% to 200% more per kg at auctions than purebred calves.
Understanding these breed-specific traits is crucial for farmers to select the most effective breeding strategies for their herds strategically.
Real-World Success Stories
Case Study: Easom & Sons, Broom House Farm
The Easom family manages a 340-cow Holstein herd near Buxton, known for its dairy farming heritage. They’ve had success using male-sexed semen. Eric Easom says, “We use British Blue sexed semen on our cows and Limousin on heifers. British Blue bulls at 12 months make approximately $305 more than Holstein bulls, boosting our profits.”
Testimonial: Talfan Farm, South Wales
Kevin Jones and his son Steffan from Talfan Farm have used sexed semen since 2013 with excellent results. They have a 170-cow herd. Kevin shares, “We switched to Cogent sexed semen for its benefits. Our conception rates are the same as regular semen, and our Cullard Charolais X beef calves sell for more than Holstein bulls, raising our profits.”
This should motivate dairy farmers to consider these technologies for their operations.
Economic Considerations
| Technology | Initial Cost ($) | Annual ROI (%) | Payback Period (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Embryo Transfer | 1,000-1,500 | 15-20 | 3-5 |
| Sexed Semen | 20-40 per dose | 10-15 | 2-3 |
| Genomic Testing | 40-100 per animal | 25-30 | 1-2 |
Return on Investment
While embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen necessitate an initial investment, they can yield substantial returns. A recent study revealed that herds employing embryo transfer experienced a 15% enhancement in genetic quality over five years, leading to increased milk production and improved health traits.
| Herd Size | Estimated ROI for Embryo Transfer (5-year period) | Estimated ROI for Male-Sexed Beef Semen (annual) |
|---|---|---|
| 100 cows | 120% | 35% |
| 500 cows | 150% | 40% |
| 1000+ cows | 180% | 45% |
Note: ROI figures are estimates based on industry averages and may vary depending on individual farm management and market conditions.
Cost Breakdown
When thinking about using embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen, knowing the costs is key:
Embryo Transfer Costs (per donor cow)
- Superovulation drugs: $232-$330
- Veterinary services: $280-$462
- Embryo freezing (if needed): $23-$33 per embryo
- Recipient cow synchronization: $18-$28 per cow
Male-Sexed Beef Semen Costs
- Semen straw: $18-$37 (compared to $14-$23 for normal semen)
- Extra insemination cost: $5-$10 per cow due to lower conception rates
These costs give a better idea of the upfront money for both methods. Although these costs seem high, they should be compared to the possible long-term gains and better profits mentioned earlier.
It’s important to remember that costs vary depending on herd size, location, and service providers. However, with careful planning and expert advice, dairy farmers can make informed decisions about these technologies.
Challenges and Considerations
Although embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Embryo transfer costs can range from $500 to $1500 per donor cow. This includes medications, vet services, and handling embryos.
- Technical Expertise: These methods require special skills. Embryo transfer may require hiring an expert or extensively training farm staff.
- Variable Success Rates: Success rates for embryo transfer vary from 30% to 70%. Factors include embryo quality and the quality and management of the recipient cows.
- Increased Management Intensity: These technologies need precise management. For embryo transfer, recipient cows need close synchronization and monitoring.
- Market Volatility: The value of male beef calves can change with market prices, affecting returns from using male-sexed beef semen.
Labor and Training Requirements
Using embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen often needs more work and training:
- Embryo Transfer:
- Staff may need special training or professional help.
- Each donor cow adds 1-2 extra work hours.
- Training covers hormone treatments and monitoring cow health.
- Courses can cost between $650-$1,300 per person.
- Male-Sexed Beef Semen:
- You might need extra training in heat detection and AI techniques.
- Plan for 10-15% more time for breeding tasks.
- Timing is vital since sexed semen needs precise insemination.
- Consider buying heat detection tools like monitors or tail paint.
- Keeping Records: Both methods need careful record-keeping. Staff might need training on software or apps for tracking breeding and pregnancy.
- Ongoing Learning: Cattle breeding changes frequently. Budget for training to stay current with the latest practices.
Although these extra labor and training efforts are an investment, they are key to maximizing the benefits of these breeding methods. Farmers should consider these costs and efforts when planning to use them.
The Future of Dairy Breeding
| Year | Genetic Potential (kg/year) | Actual Milk Yield (kg/year) |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 8,000 | 9,500 |
| 2015 | 9,500 | 10,800 |
| 2025 | 11,000 | 12,500 (projected) |
The future of dairy breeding is changing as genomic testing becomes more straightforward and accurate. This helps farmers make smarter decisions about their animals, improving productivity and profits.
Embryo transfer with male-sexed beef semen marks a new level of precision in breeding. These methods are expected to become common soon in top dairy farms. The genetic improvements from embryo transfer, along with the higher-value calves from sexed semen, offer a balanced approach for quick financial gains and long-term benefits.
Dairy farmers who embrace these innovative techniques early have a promising future. They will gain a competitive edge and build a strong foundation for ongoing success in the dairy world.
As more data from genomic testing becomes available, it will help improve breeding strategies even further, pushing the limits for farmers who want to be industry leaders.
Environmental Considerations
| Breeding Method | Methane Reduction (%) | Land Use Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional | 0 (baseline) | 0 (baseline) |
| Embryo Transfer | 5-10 | 10-15 |
| Sexed Semen | 3-7 | 8-12 |
| Combined Approach | 8-15 | 15-20 |
Adopting advanced breeding technologies like embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen can significantly help the environment:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Better genetics and productivity mean fewer cows are needed to make the same amount of milk, cutting methane emissions. To illustrate, beef from dairy calves emits 29% fewer greenhouse gases per kilogram than conventional beef.
- Resource Efficiency: Crossbred calves made with male-sexed beef semen eat less for the same weight gain. These calves grow faster and are ready for market in 15 months, using resources more efficiently than purebred dairy calves.
- Methane Reduction: Fewer unproductive cows mean less methane and less land needed. Good breeding can lower methane by over 1% each year.
- Land Use Optimization: More efficient dairy and beef production requires less land, allowing for sustainable land practices.
- Biodiversity Considerations: Maintaining genetic diversity is essential to realize these environmental benefits. Careful breeding management is key to protecting diversity in the future.
These environmental benefits show how advanced breeding can lead to more sustainable dairy farming, supporting efforts to lower the livestock industry’s environmental impact.
Quick Facts
- Embryo transfer can increase genetic gain by up to 300% compared to traditional breeding methods.
- Male-sexed beef semen typically results in 90% male calves.
- The global embryo transfer market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.8% from 2021 to 2028.
- In some markets, beef x dairy crossbred calves can command a 20-30% premium.
- Over 70% of large dairy operations in the US now use some form of sexed semen or embryo transfer.
The Bottom Line
Combining embryo transfer and male-sexed beef semen is a smart choice for dairy farmers who want to keep up in a changing industry. These tools help improve genetics and produce valuable calves while assisting farmers in meeting market demands. Farmers must plan carefully to use these technologies well, focusing on future goals and current benefits. Expert advice and careful planning are crucial to overcoming challenges and achieving results. As the industry changes, those who adopt these tools can gain an advantage and improve their farm’s financial success.
 Download “The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration” Now!
Download “The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration” Now!
Are you eager to discover the benefits of integrating beef genetics into your dairy herd? “The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration” is your key to enhancing productivity and profitability. This guide is explicitly designed for progressive dairy breeders, from choosing the best beef breeds for dairy integration to advanced genetic selection tips. Get practical management practices to elevate your breeding program. Understand the use of proven beef sires, from selection to offspring performance. Gain actionable insights through expert advice and real-world case studies. Learn about marketing, financial planning, and market assessment to maximize profitability. Dive into the world of beef-on-dairy integration. Leverage the latest genetic tools and technologies to enhance your livestock quality. By the end of this guide, you’ll make informed decisions, boost farm efficiency, and effectively diversify your business. Embark on this journey with us and unlock the full potential of your dairy herd with beef-on-dairy integration. Get Started!








 Meet Holstein Canada’s new leaders for 2024-2025. How will President Gilles Côté and his team drive the future of the organization? Discover their strategic vision.
Meet Holstein Canada’s new leaders for 2024-2025. How will President Gilles Côté and his team drive the future of the organization? Discover their strategic vision.