At an ever increasing rate new equipment and information becomes available that dairy farmers can use to advance the way in which they manage their herds. The early adopters often go out on a limb and install systems on their farms that they hope will make their operations more profitable. Making better decisions or having information that gives advance notice of potential cow problems is critical to increased herd profit.
New on the Scene
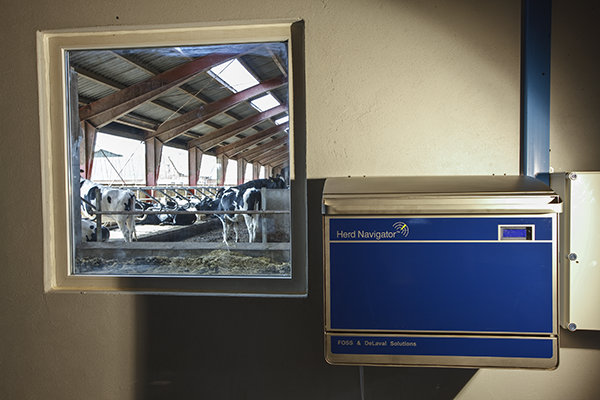
Recently the Bullvine took the opportunity to get close-in on a new piece of equipment by visiting two reference farms. This equipment is called Herd Navigator™ (HN), a product of DeLaval/FOSS, and it has just completed verification in Canada using four Ontario dairy farms. It had been developed, field tested and implemented in Europe and at the present time it is being installed commercially in additional farms in Canada.
In brief what it does is take milk samples from selected cows on selected days and, based on the analysis of the milk, provides reports for herd managers to use. As one would expect, this requires equipment for sampling (a sampler and a sorter) and testing (on-farm mini lab), computer software and linkage to the herd management software used on the farm by the herd manager, the nutritionist or the veterinarian.
![VMSFullCow[1]](data:image/svg+xml,%3Csvg%20xmlns='http://www.w3.org/2000/svg'%20viewBox='0%200%20300%20200'%3E%3C/svg%3E) Designed as the next tool for top herds
Designed as the next tool for top herds
The focus of HN is cows in robotic and parlour herds from calving to being pregnant again. (Read more: Robotic Milking: More than just automation it’s a new style of herd managment) Nancy Charlton DVM (Nutrition & Herd Management Specialist, DeLaval Canada) started her explanation and demonstration of HN by saying that “…. lets start with the basics. A herd must have an effective cow and heifer transition program. That is a well proven fact. HN is then a tool to make very good managers even better at their job.” That made me want to listen even harder to Dr Charlton as she very adeptly went through the various procedures and reports for HN.
 Multi-Purpose Tool
Multi-Purpose Tool
HN takes a milk sample at prescribed times and provides information on four areas important to herd management and profitability. Users of the HN™ system set up Standard Operating Procedures for all four areas, reproduction, mastitis, ketosis and urea level in the milk. When results for metabolic conditions exceed owner determined levels an alarm sounds (more correctly a report is generated) notifying the herdsman. Acting before a cow becomes a problem means less cost, more production and more profit.
It is a well known fact that managing REPRODUCTION takes detailed recording, considerable staff time, is a significant expense and reduces the average revenue per cow per year. For the time period starting 30 days before the voluntary waiting period until 55 days pregnant progesterone levels are monitored on critical days. Herd managers have access to detailed reports including: changes in progesterone levels; heats and the best time to breed; prolonged post partum anestrous; follicular cysts; luteal cysts; potential pregnancy; and early embryonic loss or abortion.
Life for herd managers would be much simpler if MASTITIS did not occur. But that would be a perfect world. HN uses the milk sample to measure the enzyme Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) which is released into the milk in an affected quarter during inflammation. Increasing LDH levels are highly correlated with the increased presence of somatic cells and the early stage of subclinical mastitis. The herd manager can choose to monitor the situation or to treat the cow immediately. At the very least the manager can look the cow up and make a visual or hands-on assessment. The creators of HN see using LDH as a more accurate way of determining the presence of mastitis. The frequency of testing cows for LDH is recommended as once per day for the first thirty days of lactation and after that it depends on the cow’s history and the herd’s standard operating practice.
The metabolic disease KETOSIS can be a thief of profit for cows by causing the loss of milk, lowering peak milk yield and cost of treatment. HN monitors the concentration of ketone bodies in a cow’ milks early in lactation. Measurements start on day four of lactation and continue until readings indicate there is a small chance of ketosis occurring. It is significant that HN reports on subclinical ketosis. Thus alerting the herd manager to take action before full blown ketosis occurs, either by altering the fresh cows diet or by treating the cow. Recent research indicates that subclinical ketosis is much more prevalent than dairymen are aware of. Potentially all herds are losing production due to subclinical ketosis and do not know it.
The final area that HN monitors is the UREA level in the milk a cow produces. This is similar to the MUN (milk urea nitrogen) service offered by CANWEST DHI but does not require that the owner wait until a milk recording test day. As yet this part of HN may not get as much use as the three previously mentioned areas. It is important to know if protein level in the diet are too high, just right or too low. Over feeding protein, the expensive part of the ration, costs money while under feeding means a cow’s potential is not being achieved and other feed ingredients are not being fully utilized. From what I heard when speaking with the two herd owners, that I visited, this area has yet to be ‘discovered’ for use by HN owners.
In summary these four areas give herd managers the opportunity to increase the profitability of their herds from just a milk sample.
Information Provided
At any time the herd manager can go to his computer and call up any reports. HN is definitely designed for larger herds that manage cows by groups. It provides information so that individual cows within the groups can have their current problem addressed. Only problem cows need to receive the attention of the herdsman.
Sytse Heeg of Heegstee Farms commented “I only need to give my attention to cows with problems. It would not be possible for my wife and me to manage without HN. We have 110 cows milking on two robots, all the young stock and our family to attend to every day and also the field work during the summer time. We do have assistance from my father part time and a summer student. I am so much more in control of my herd than I was before HN. And I am getting the results (profit) I wanted to get. Already 4 kgs more milk per cow per day with cows back in-calf as well as very low levels of mastitis and ketosis. In non-busy times it is even possible for us to take a vacation. But don’t forget I can remotely watch what is happening back home.”
At Elmwold Farms (Buchner Families), Jennifer is responsible for searching out the details from their 170 cow 3x herd that on the day I visited were producing, on average, 2.8 kgs (6.2 pounds) of fat & protein per day. When I visited Jennifer was on vacation so father (Chris) and brothers ( Greg and Derek) and cousin (Kevin), over a cold ice tea in the shade on a very hot summer day, described the many ways that their farm uses HN to better manage their herd. Chris Buchner provided the details. “Our herd is focused on efficient high fat plus protein yield. That is what we are paid for kgs of fat and protein sold off-farm. But it is more than that. We were having too many cows on holidays, aka in the dry pens, too much of the time. We calve the vast majority of our heifers before two years of age so we give a bit of a break in having them calve back but the herd average calving interval is 12.6 – 12.8 months. We are running a 24% pregnancy rate, we average 2.2 inseminations per pregnancy, our reproductive cull rate has gone from 28% down to 22%, the vast majority of our cows are pregnant by 120 days into lactation and using the urea numbers we have been able to lower our TMR from 18 to 17% protein. We purchased HN to improve our daily management of cows by focusing on cows outside the norm and to use our facilities to their maximum. We will soon build additional cow housing and will give more attention to our fresh cows with one pen for fresh heifers only as we already know that they get pushed out of the feed bunk by older cows in the fresh group. We looked at using pedometers but after seeing how much more HN could do we made the decision to purchase it. We are very happy we decided to go this route. Our family operation is growing and I am proud to say that the next generation is keen to be profitable dairy farmers.”
Cost Benefit
Top notch herd managers always want to know the cost benefit of any input, service or tool. The DeLaval website suggest that using HN a herd can increase revenue by $330 US$ (250 euros) per cow per year with annual material costs of 130 US$ per cow and an equipment cost of 500 US$ per cow for a two hundred cow herd. All of these numbers do not include the savings in feed for fewer cows (milking and dry) as well as the need for less housing facilities. Definitely it does require that a herd be of sufficient size to justify the initial cost of the equipment.
Another thing about the HN system is that it does all the work and testing thus allowing the herd manager to avoid the time to search out cows and do cow side testing. And, best of all, it does it before there is a problem not after the fact.
Muhieddine Labban (Automated Milking Systems Manager at DeLaval) sees the benefits in these ways “I like to call it return on investment with the results being: 1) accurate feeding – lower cost and waste; 2) lower cull rate; 3) lower use of antibiotics; 4) higher production per cow; 5) more effective use of the herd veterinarian; 6) higher pregnancy rate; 7) fewer inseminations lowering costs and semen used; 8) less herd manager frustration; 9) more family time for the dairy producer; and last but not least 10) the use of technology which will encourage the next generation to be dairy farmers”. An impressive list for every herd managers to consider.
The Bullvine Bottom Line
For breeders looking to manage better and increase their per cow profit, more attention to cows needing individual attention is an avenue to pursue. It definitely does pay to have cows reach peak production, avoid mastitis and get back in calf as quickly as possible. Knowing the facts to base decisions on is the way to go.
Get original “Bullvine” content sent straight to your email inbox for free.








![VMSFullCow[1]](https://www.thebullvine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/VMSFullCow1.png) Designed as the next tool for top herds
Designed as the next tool for top herds Multi-Purpose Tool
Multi-Purpose Tool




