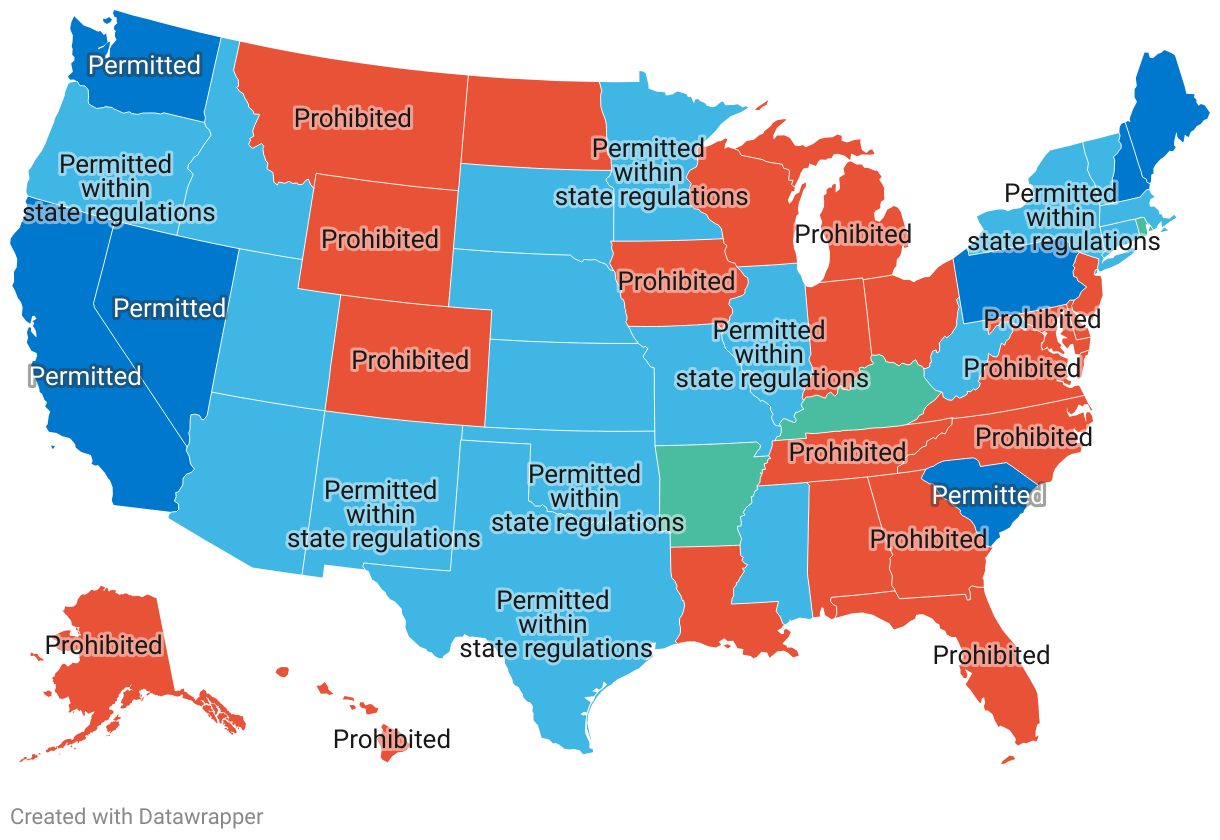
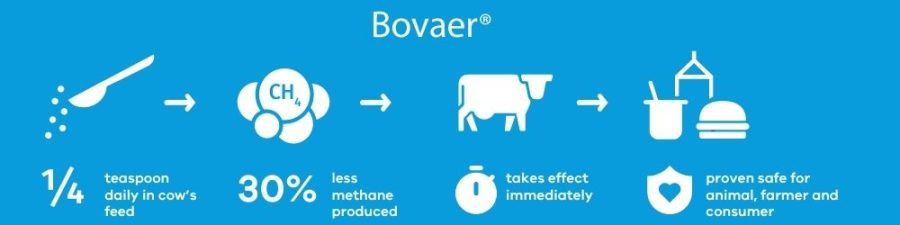
See how 3-Nitrooxypropanol can slash methane emissions by 27% and ramp up milk production. Want to know what this means for your farm? Keep reading.
Summary: Methane emissions in dairy farming significantly contribute to greenhouse gases. Reducing these emissions without compromising milk production has been a challenge—until now. Recent research has investigated using a feed additive called 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) in Holstein-Friesian cows over a year. “The supplementation of 3-NOP led to a 27% decrease in methane production, accompanied by a 6.5% increase in both energy-corrected milk and fat- and protein-corrected milk,” according to the study findings. Enhanced milk fat and protein levels, improved feed efficiency, and the ability to significantly impact environmental sustainability make 3-NOP a valuable addition to dairy farming—3-NOP targets methanogens in the cow’s rumen, thus decreasing methane released into the atmosphere. A ruminant nutrition expert, Dr. Alex Hristov, notes that 3-NOP can reduce enteric methane emissions by up to 30% without negatively impacting milk yield or quality. A study involving 64 late-lactation Holstein-Friesian dairy cows showed that careful management and regular monitoring are necessary to reap the full benefits of 3-NOP, which regulatory bodies like the EFSA and FDA have approved.
- 3-NOP reduces methane emissions in dairy farming by up to 27%.
- Milk production metrics, including energy-corrected and fat- and protein-corrected milk, improved by 6.5% with 3-NOP.
- Enhanced milk fat and protein levels were observed.
- Feed efficiency improved significantly.
- 3-NOP targets methanogens in the cow’s rumen, lowering methane release.
- Dr. Alex Hristov states that 3-NOP can cut methane emissions by up to 30% without affecting milk yield or quality.
- A study involving 64 Holstein-Friesian cows showed that careful management and monitoring are vital to maximizing 3-NOP’s benefits.
- 3-NOP has received approval from regulatory bodies like the EFSA and FDA.
Imagine a single supplement that could revolutionize your dairy farm, making it more sustainable and productive. It may sound too good to be accurate, but it’s not. Introducing 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP), a game changer for dairy producers worldwide. A recent study has shown that 3-NOP can reduce methane emissions from dairy cows by up to 27% while increasing milk output by 6.5%. This means significant environmental and economic benefits for farmers, as the Dairy Science Journal confirmed.
Why Reducing Methane in Dairy Farming Matters More Than Ever
Methane emissions are critical in dairy production, and their environmental impact cannot be overstated. According to Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) research, methane contributes to about 44% of total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from dairy production, with enteric fermentation accounting for 92%. This process occurs when cows digest their food and produce methane as a byproduct.
Why is this important? Methane is about 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide in trapping atmospheric heat over 100 years (EPA). Thus, lowering methane emissions has the potential to halt climate change considerably.
Traditionally, farmers have used several methods to mitigate methane emissions:
- Improving forage quality: Better-quality fodder may result in more effective digestion and less methane generation.
- Diet reformulation: Introducing various forage and feed concentrates to change the fermentation process in the cow’s stomach.
- Supplementing lipids: Adding fat to the diet may help lower methane emissions but can also impact milk composition and cattle health.
- Rumen manipulation: Feed additives suppress methanogens, bacteria that produce methane directly.
Despite these attempts, conventional approaches are limited. For example, boosting forage quality may only sometimes result in reduced forage quality, diet reformulation is typically expensive, and lipid supplementation might harm milk production and animal health. Furthermore, altering the rumen environment with feed additives can provide short-term results.
Ever Wondered How You Could Significantly Reduce Methane Emissions from Your Herd Without Compromising Milk Production?
Enter 3-nitrooxypropanol, sometimes known as 3-NOP, an innovative feed ingredient creating waves in dairy production. But what precisely is 3-NOP, and how does it function?
3-NOP is a chemical that targets and interrupts the last stage of the methane-formation process in a cow’s rumen. It inhibits the action of methyl coenzyme M reductase, which rumen microbes require to create methane gas. By preventing this phase, 3-NOP significantly decreases the methane released into the atmosphere by cows.
So, how does this operate in the real world? When cows ingest feed containing 3-NOP, the substance operates in their stomachs by targeting methanogens, which are bacteria that produce methane. Consider 3-NOP, a specialized instrument that accurately removes vital gear in the methane-production machine while leaving the cow’s digestive tract functioning normally.
Dr. Alex Hristov, a well-known ruminant nutrition expert, puts it into perspective: “Our studies show that 3-NOP can reduce enteric methane emissions by up to 30% without negatively impacting milk yield or quality” [source: Hristov et al., 2022]. This implies that you may take proactive steps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining or even increasing agricultural output.
A Year in the Life: How 3-NOP Transformed Methane Emission and Milk Yield in Holstein-Friesian Dairy Cows
The study included 64 late-lactation Holstein-Friesian dairy cows and lasted one year. The cows were separated into pairs and randomly allocated to a diet containing 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) or a placebo; the experimental design sought to determine the long-term effects of 3-NOP on methane emissions and milk production. Throughout the trial, the cows underwent many lactation phases, including late lactation, dry period, early lactation, and mid-lactation, and their meals were modified appropriately. Among the critical indicators assessed were methane emissions, body weight, dry matter intake (DMI), milk output, and dairy components such as fat and protein. The study was conducted in a controlled environment to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
A Dramatic Impact on Methane: Key Findings You Can’t Ignore
The long-term study on 3-Nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) revealed significant reductions in methane emissions across various lactation stages:
- Late Lactation: 26% reduction in methane yield
- Dry Period: 16% reduction in methane yield
- Early Lactation: 20% reduction in methane yield
- Mid Lactation: 15.5% reduction in methane yield
The chart below depicts these reductions visually, showcasing the effectiveness of 3-NOP over different stages of lactation.
Boost Your Profits and Quality: ECM, Fat, Protein Yields, and Feed Efficiency
- Energy-Corrected Milk (ECM): A 6.5% increase in the yields of energy-corrected milk was observed, making milk production more efficient and profitable.
- Fat Yields: Adding 3-NOP resulted in more excellent milk fat yields, increasing milk richness and quality.
- Protein Yields: Protein yields also saw a notable increase, enhancing the nutritional value of the milk produced.
- Feed Efficiency: 3-NOP supplementation significantly improved feed efficiency, improving overall productivity per unit of feed consumed.
Maximizing the Benefits of 3-NOP: Tailoring Its Use for Optimal Results
Understanding why 3-NOP performs well in specific settings but not in others will allow you to make the most of this intriguing feed addition. Let’s break down the main factors:
- Diet Composition: What your cows consume considerably influences 3-NOP’s effectiveness. Diets strong in fiber, such as those heavy in straw, may diminish 3-NOP’s ability to cut methane. On the other hand, high-quality meals rich in readily digested nutrients may enhance the effectiveness of 3-NOP. The kind of forage and concentrate mix in the feed also impacts.
- Lactation Stage: The stage of breastfeeding influences how well 3-NOP works. Cows have excellent metabolic rates and variable dietary requirements during early lactation compared to later stages. This may lead to variations in how efficiently 3-NOP lowers methane emissions. The research found that effectiveness fluctuated throughout time, becoming less effective after a lactating stage.
Understanding these aspects allows you to personalize your use of 3-NOP better to optimize its effects. For example, adjusting the meal composition to the breastfeeding stage may help maintain or improve its methane-reducing benefits.
Let’s Dive Into Some Practical Advice.
So, you’re interested in 3-NOP’s ability to reduce methane emissions while increasing milk production. But how do you apply it on your farm? Let’s look at some practical recommendations.
- Start with a Plan: Develop a clear strategy before you begin. Determine your goals: methane reduction, increased milk output, or both. Document your objectives to keep track of your development. If you’re interested in exploring the potential of 3-NOP for your dairy farm, consider consulting with a nutrition expert or a veterinarian to develop a tailored plan for your herd. Choose the
- Right Dose: Utilizing the right amount of 3-NOP is critical. Studies have shown that outcomes vary depending on how much is used, so strictly adhere to the manufacturer’s instructions. Including around 80 mg/kg DM in the entire diet has had excellent outcomes.
- Consistency is Key: Ensure that 3-NOP is continuously included in your cows’ diet. Mix it well with their regular feed to ensure each cow receives the appropriate quantity. If feasible, employ an automatic feeder to standardize distribution.
- Monitor Feed Intake: If using a feed monitoring system, monitor how much each cow eats. This will allow you to confirm that the supplement is being taken as intended.
- Adjust for Lactation Stages: Adapt the feed content to the cows’ lactation phases. For example, early lactation diets may need more energy-dense foods than late ones. To ensure optimal effectiveness, tailor the 3-NOP dose to these modifications.
- Regularly Assess Diet Quality: Monitor your forage quality and overall food composition. Changes in forage may impact 3-NOP’s efficacy. Examine the chemical composition regularly to make any required changes.
- Track Performance: Monitor critical variables such as milk output, composition, and methane emissions. This information will allow you to assess the efficacy of 3-NOP and make any necessary modifications.
- Consult Experts: Consult your dietician or extension officer regularly. They may give valuable data relevant to your business, allowing you to adapt the diet and 3-NOP inclusion efficiently.
Implementing 3-NOP may be transformative, but careful management and regular monitoring are necessary to fully reap the benefits. Maintain your commitment to your objectives and refine your strategy as you collect additional facts.
Frequently Asked Questions About 3-NOP
Is 3-NOP Safe for My Cows?
3-NOP has been carefully investigated and proven safe for dairy cows. Research indicates it does not harm cow health, milk output, or quality. Long-term research, including a one-year study, has shown its safety.
Have Regulatory Bodies approved 3-NOP?
Absolutely. 3-NOP has been approved by major regulatory organizations worldwide, including the EFSA and FDA. Its safety and efficacy have been carefully tested.
Will 3-NOP Affect the Quality of the Milk I Produce?
No, 3-NOP has no adverse effects on milk quality. Studies have shown that it does not affect the composition of milk fat, protein, or other vital components. You may securely utilize 3-NOP without fear of harming the quality of your milk.
Are There Any Side Effects I Should Be Aware Of?
Long-term investigations of 3-NOP, including its impact on dairy cow health and production, have shown no adverse side effects. The supplement efficiently minimizes methane emissions without causing injury or pain to the cows.
How Does 3-NOP Benefit My Dairy Farm?
In addition to considerably lowering methane emissions, 3-NOP has been proven to enhance energy-corrected milk (ECM) and fat- and protein-corrected milk (FPCM) yields, improve feed efficiency, and benefit overall herd health.
Is 3-NOP Easy to Implement in My Current Feeding Program?
Yes, 3-NOP can be added to current feeding regimens. It combines nicely with regular dietary components and requires no substantial changes to existing feeding procedures.
The Bottom Line
3-Nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) has established itself as a revolutionary feed ingredient for dairy producers. Adding 3-NOP to your feeding regimen may lower methane emissions by up to 27% while increasing critical milk production indices such as ECM, fat, and protein yields. With these twin advantages, 3-NOP improves your farm’s environmental sustainability and increases production and profitability. Are you prepared to take the next step in creating a more sustainable and profitable dairy farm?