One generation instead of twenty. That’s what gene editing offers for heat tolerance—and Europe just accelerated the timeline. The dairy producers paying attention now will be the ones leading in five years.
Executive Summary: Twenty generations through traditional breeding—or one with gene editing. That’s the new math for traits like heat tolerance, disease resistance, and polled genetics, and it’s not hypothetical: heat-tolerant cattle are FDA-approved, Brazil has gene-edited Holsteins in commercial herds, and Europe’s December 4 agreement just accelerated the global timeline. The economic stakes are clear. U.S. dairy loses up to $1.6 billion annually to heat stress alone, with hot-climate operations absorbing several hundred dollars per cow each summer. What sharpens the urgency is the compounding effect—genetic advantages multiply over generations, which is why producers who moved early on genomic selection built leads their competitors are still chasing a decade later. This analysis covers where regulations stand, what’s available today, legitimate concerns that deserve honest consideration, and practical steps for positioning strategically. The technology is proven. The producers paying attention now will shape the next decade of dairy genetics—not spend it catching up.

I was talking with a producer in central Texas last month who told me something that stuck with me. He’d calculated his heat-related losses across the past summer: reduced milk production, reproduction failures, increased health events, and the energy costs of running cooling systems around the clock for four straight months. His number came to several hundred dollars per cow—losses he could measure but couldn’t fully prevent, no matter how much he invested in fans and sprinklers.
That conversation was fresh in my mind when news broke from Brussels on December 4, 2025. After all-night negotiations and years of fierce debate, EU policymakers reached a provisional agreement allowing gene-edited crops to bypass the bloc’s strict GMO regulations. The immediate focus is on plants—wheat, tomatoes, that sort of thing. But here’s why that Texas conversation matters: among the dairy cattle applications currently working through research pipelines is gene-edited heat tolerance. The kind that could fundamentally change that producer’s math.
The question isn’t really whether gene editing will become part of dairy cattle breeding. The science is proven, commercial animals already exist in some markets, and regulatory doors are opening. The real question is how individual operations position themselves as these tools become available—or whether they’ll spend years trying to catch up with competitors who moved earlier.
The Global Regulatory Landscape: Where Things Stand

Before diving into the science and economics, it helps to understand the regulatory patchwork that will determine when and how gene-edited genetics reach your market. Here’s where major dairy regions currently stand:
| Region | Regulatory Status | Livestock Included? | Current Availability |
| European Union | NGT regulation provisionally agreed December 4, 2025; formal adoption expected early 2026 | Plants only initially; livestock framework to follow | Not yet available |
| United Kingdom | Precision Breeding Act in full force as of November 13, 2025 | Yes—includes cattle | Framework ready; commercial products developing |
| United States | Case-by-case FDA review via “low-risk determination” process | Yes | Heat-tolerant cattle approved March 2022; other traits under review |
| Canada | Guidance for gene-edited livestock is still developing under Health Canada and CFIA | Pending | Not yet available |
| Brazil | CTNBio approved gene-edited cattle for breeding and food use | Yes | Heat-tolerant Holsteins approved 2023 |
Sources: European Parliament (December 2025), Morrison Foerster regulatory analysis (November 2025), FDA Risk Assessment Summary (March 2022), CTNBio public records (2023)
What Brussels Actually Decided (And Why It Creates Precedent)
Let me walk you through what the EU agreement actually does, because the details matter for understanding where this is heading.
The new framework creates two categories for plants developed using what regulators call “New Genomic Techniques,” or NGTs:
- Category 1: Plants with genetic changes that could theoretically occur through natural mutation or conventional crossbreeding. These skip the GMO approval process entirely—no mandatory safety assessments for each generation, and final food products won’t need special labels (though seeds will be marked).
- Category 2: Plants with more complex modifications that go beyond what conventional breeding could achieve. These still face the full regulatory process.
That’s according to the European Parliament’s official announcement from December 4. The European Commission’s press release emphasized the regulation’s potential to develop plant varieties more resilient to climate change while requiring fewer pesticides. Copa-Cogeca, representing EU farmers and agricultural cooperatives, expressed strong support. Thor Gunnar Kofoed, chair of their working party on plant breeding, called it “a turning point for European agriculture.”
Now here’s what I find interesting for livestock producers: this regulation specifically covers plants, not animals. But the product-based framework being established—evaluating what a genetic change does rather than reflexively restricting how it was made—creates a template. When gene-edited livestock applications eventually reach European regulators, there’s now a philosophical precedent for how to approach them.
Key Regulatory Dates to Watch
- November 2025: UK Precision Breeding Act takes full effect, including livestock provisions
- Early 2026: EU NGT regulation expected to receive formal adoption
- Ongoing: FDA continues case-by-case “low-risk determination” reviews for gene-edited livestock traits
- TBD: Health Canada and CFIA guidance for gene-edited livestock expected to develop further
The Climate Challenge That Traditional Breeding Can’t Solve Fast Enough
Here’s where this discussion gets personal for many operations, especially if you’re farming in areas where summers are becoming more difficult for your herd.

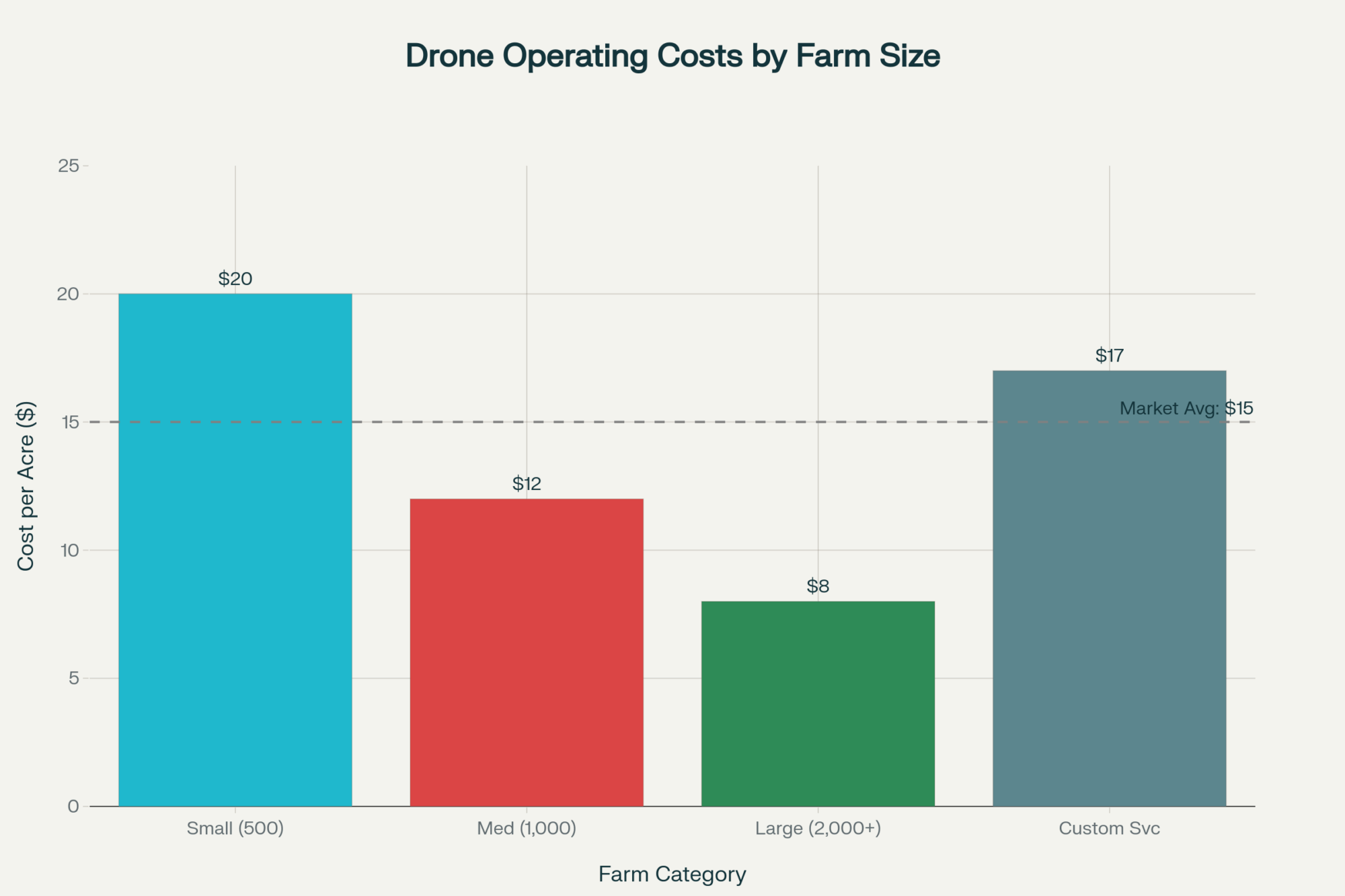
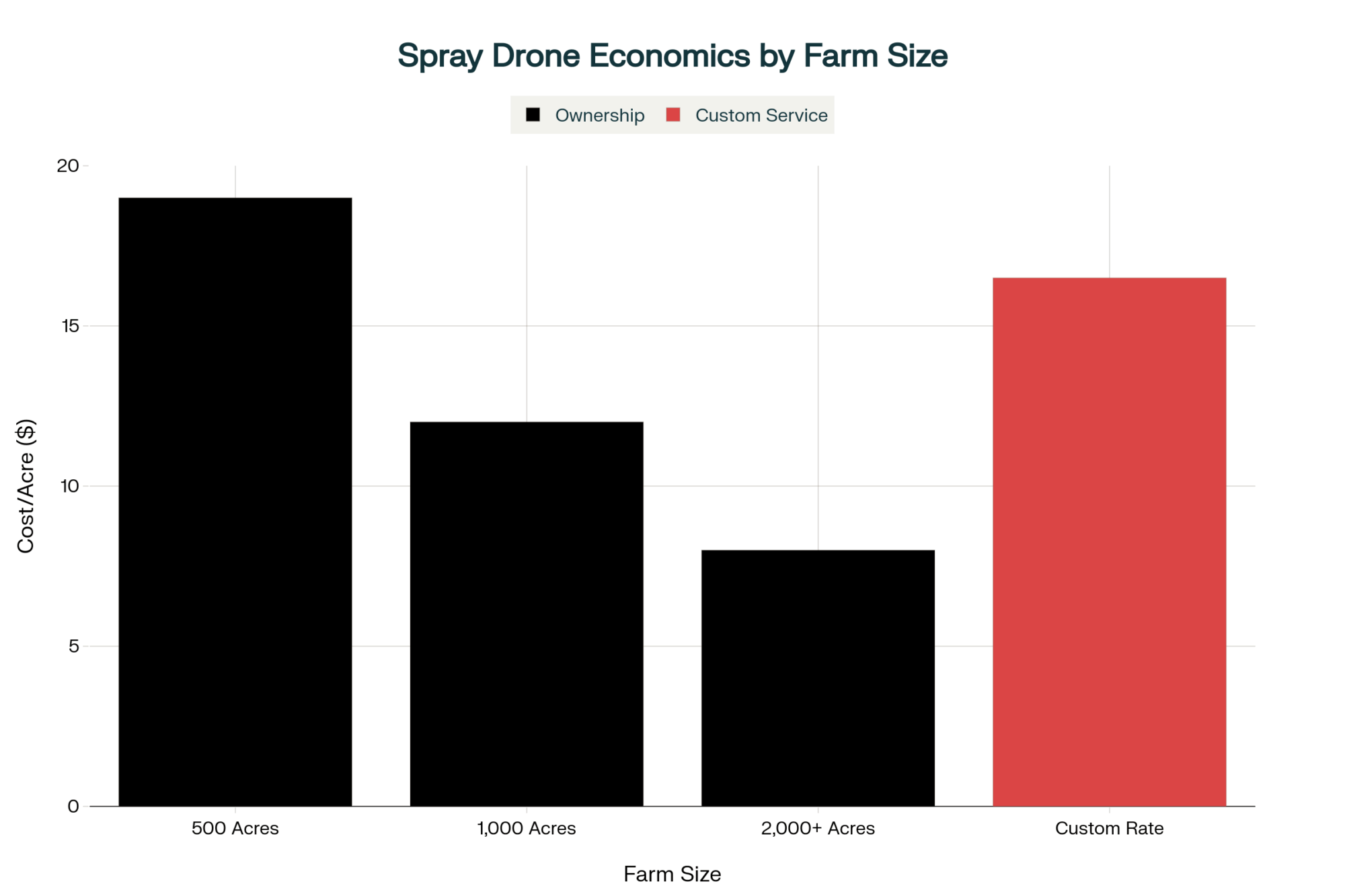
The economic impact of heat stress on U.S. dairy is substantial—and probably larger than many producers fully account for. The foundational study by St-Pierre and colleagues, published in the Journal of Dairy Science in 2003, estimated annual industry-wide losses between $897 million and $1.5 billion. More recent work from Ohio State University researchers suggests losses can reach $1.6 billion annually as summer conditions have intensified across much of dairy country.

Regional heat stress impacts vary significantly:
- Upper Midwest (Wisconsin, Minnesota): University of Wisconsin researchers measured costs at roughly $74 per cow based on milk yield losses alone—relatively moderate but still meaningful
- Southeast (Florida, Georgia): Losses several times higher; some Florida operations have spent decades working with Senepol and Gir crossbreeding programs to introduce natural heat tolerance, with real success—but also real tradeoffs in production genetics that take years to breed back
- Southwest (Texas, Arizona): Producers report losses of several hundred dollars per cow when factoring reproduction failures, health events, and cooling costs
- California Central Valley: Compounding the challenge of water constraints alongside rising temperatures, affecting both cooling capacity and irrigated feed production
A study published in Science Advances this past July really crystallized the scope of the problem. The research, led by Claire Palandri at the University of Chicago’s Harris School of Public Policy, analyzed production data from over 130,000 cows across 12 years of Israeli dairy records—one of the most comprehensive datasets ever assembled on heat-stress impacts.
Key findings from the Palandri study:
- A single day of extreme heat can reduce milk production by 10 percent
- That suppression can persist for more than 10 days after temperatures return to normal
- Even with cooling systems in place, mitigation effectiveness dropped to around 40 percent during extreme heat events
- Cooling “cut losses in half” at moderate temperatures, but became progressively less effective as conditions worsened
There appears to be a ceiling to what management interventions can accomplish when ambient temperatures push into truly dangerous territory.
So what’s the traditional breeding alternative? You could crossbreed with heat-adapted cattle—Senepol, Gir, or Carora breeds that carry what’s called the “slick coat” gene naturally. The challenge, as anyone who’s tried it knows, is the timeline.
Timeline Comparison: Traditional Breeding vs. Gene Editing

Traditional approach to adding heat tolerance to elite Holsteins:
- Initial crossbreeding + 20 generations of backcrossing
- Approximately 5 years per generation
- Total timeline: 80-100+ years to recover elite genetics with a new trait
Gene editing approach:
- Direct introduction of the slick coat allele to elite genetics
- Single generation
- Timeline: Available for breeding in current genetic lines
Dr. Appolinaire Djikeng, Director of the Centre for Tropical Livestock Genetics and Health at the Roslin Institute in Scotland, has explained that gene editing can accomplish in one generation what would otherwise take 20 generations through conventional breeding.
One generation versus twenty. For operations facing mounting heat pressure right now, that’s not an incremental improvement—that’s a fundamentally different approach to the problem.
What’s Actually Available Today

This isn’t all laboratory work and future promises. Commercial gene-edited cattle exist today, though availability depends significantly on where you’re located and what regulatory frameworks apply.
Heat-Tolerant Genetics
The U.S. FDA issued its first “low-risk determination” for PRLR-SLICK cattle back in March 2022. The FDA’s risk assessment confirms that these were cattle developed by Acceligen, primarily beef animals initially, but the regulatory pathway has since been opened for dairy applications.
Potential benefits:
- Improved heat dissipation without crossbreeding tradeoffs
- Maintained elite production genetics (butterfat, protein, yield)
- Single-generation trait introduction
- Reduced cooling infrastructure dependence
Current status: Commercial animals exist in the U.S. and Brazil; they are not yet widely distributed in North American dairy markets.
Disease Resistance (BVD)
USDA researchers at the U.S. Meat Animal Research Center have produced calves with dramatically reduced susceptibility to Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus. The approach, published in PNAS Nexus in May 2023, used CRISPR editing to modify just six amino acids in the CD46 gene.
Potential benefits:
- Reduced BVD infection severity and transmission
- Fewer secondary bacterial infections in calves
- Decreased antibiotic dependence
- Improved calf survival and performance
Verification data: After 20 months of monitoring, researchers found no off-target effects anywhere in the genome. The edited calf showed minimal clinical signs and no detectable viral infection in white blood cells when challenged.
Current status: Research stage; not yet commercially available.
Polled (Hornless) Genetics
Gene editing allows the naturally occurring polled allele to be introduced directly into elite dairy genetics without production tradeoffs.
Potential benefits:
- Eliminates the need for dehorning/disbudding
- Reduced calf stress and pain
- Labor and medication cost savings
- Improved welfare optics for retail markets
Important caveat: In 2019, FDA scientists discovered that Recombinetics’ gene-edited polled bulls contained bacterial DNA that had been accidentally introduced alongside the intended edit. MIT Technology Review broke that story, and it set the field back years. Verification protocols have since improved substantially.
Current status: Approaching commercialization; enhanced screening is now standard.
Methane Reduction
UC Davis and the Innovative Genomics Institute announced a $70 million, seven-year project in 2023 using CRISPR to re-engineer rumen microbial communities.
Potential benefits:
- One-time calf treatment (not daily feed additives)
- No ongoing compliance or costs
- Targets methane-producing archaea directly
- Potential carbon credit value
Current status: Early research stage; commercial availability likely 5+ years out.
The Economics: Understanding What’s Actually at Stake
Let me work through the financial picture, because this is ultimately where the decision-making happens for most operations.
Direct heat stress recovery potential:
For a 1,000-cow herd in a hot climate, recovering even a portion of heat-related losses could translate to:
- Tens of thousands of dollars annually in recovered milk production
- Improved reproduction rates that compound over time
- Fewer fresh cow challenges are cascading through the transition period
- Reduced cooling infrastructure and energy costs
Emerging carbon/sustainability value:
A typical dairy cow emits roughly 100-125 kg of methane annually (based on Canadian research and IPCC modeling), which translates to about 2.5-3.5 tonnes of CO₂-equivalent. If gene-based solutions achieve the 30-50 percent reductions researchers are targeting, that represents meaningful potential value. Several major cooperatives and processors—including initiatives from organizations such as Dairy Farmers of America and various state-level sustainability programs—are beginning to develop premium structures for verified emissions reductions. These markets are still developing and vary considerably by region and processor, but the trajectory is clear.

The compounding factor:
Here’s the economic dynamic that I think deserves more attention than it typically gets: genetic advantages compound over generations.
Think back to what happened with genomic selection. According to CDCB data and a comprehensive review published in Frontiers in Genetics in 2022:
- Genomic selection roughly doubled the rate of genetic gain for many traits
- Annual net merit increases jumped from around $40 to approximately $85
- Producers who moved early built advantages that compounded with every breeding cycle
- The cautious crowd found themselves years behind on the genetic curve—a gap that proved surprisingly difficult to close
Will gene editing follow the same pattern? Early indications suggest it might. Once gene-edited traits are integrated into elite genetics and multiplied through AI, the same compounding dynamic kicks in.
What Consumers Actually Think
One concern I hear regularly from producers: “This all sounds interesting, but consumers will never accept milk from gene-edited cows.”
The research tells a more nuanced story.

What surveys consistently show:
- Consumer concerns center primarily on transparency and choice—not categorical rejection
- Only about one in five consumers indicate they’d refuse to purchase gene-edited products entirely
- The majority want information and the ability to make informed choices, not outright prohibition
What influences acceptance:
- Framing matters enormously—purchase intent increases substantially when applications are explained in terms of:
- Animal welfare (reduced antibiotic use, disease prevention, and eliminating painful procedures)
- Environmental benefits (lower emissions, reduced resource use)
- The Vermont GMO labeling experiment is instructive: when mandatory labeling was implemented in 2016, researchers Kolodinsky (University of Vermont) and Lusk (now at Purdue) found that opposition to genetically engineered food fell by 19 percent. Their findings, published in Science Advances in 2018, suggest transparency defuses anxiety rather than amplifying it.
What damages acceptance:
- Opacity and perceived deception
- Products appearing on shelves without disclosure, discovered later through media or activist campaigns
- The path to sustained acceptance runs through honesty about what’s being done and why

Engaging with Legitimate Concerns
I want to spend time on criticisms that have genuine substance, because glossing over real challenges doesn’t serve anyone well.
Genetic Diversity

| Concern | Evidence | Counterargument |
| Gene editing could accelerate genetic narrowing | Holstein effective population size has dropped to ~50 (John Cole, CDCB Chief R&D Officer); Lactanet Canada’s August 2025 report shows Holstein heifers approaching 10 percent inbreeding, continuing the +0.26% annual increase from the 8.86 percent recorded for heifers born in 2021 | Gene editing could allow beneficial traits to be introduced into broader genetics—expanding options rather than narrowing them |
| Same elite bulls get edited, concentrating influence further | Valid concern if industry deploys technology narrowly | Whether gene editing helps or hurts diversity depends on how the industry uses it—that’s a choice, not an inherent feature |
Off-Target Effects
| Concern | Evidence | Current Mitigation |
| Unintended genetic modifications are possible | 2019 Recombinetics incident: bacterial DNA discovered in “precisely” edited polled bulls | Whole-genome sequencing now enables comprehensive screening; newer editing technologies offer improved precision |
| Technology isn’t infallible | Valid—the Recombinetics case demonstrated this clearly | BVDV-resistant calf showed zero off-target effects after 20 months of monitoring (PNAS Nexus, 2023); verification protocols have improved substantially |
Patent Concentration
| Concern | Evidence | Potential Solutions |
| Few companies could control critical genetic improvements | Foundational CRISPR patents held by a small number of entities | The EU NGT framework includes a patent transparency database requirement |
| Seed industry consolidation as a cautionary parallel | Valid historical comparison | Most current breakthroughs are happening in public institutions (USDA, UC Davis, Roslin Institute); advocacy is needed for open licensing arrangements |
International Trade Complexity
| Challenge | Implication |
| Regulatory frameworks don’t align across jurisdictions | A bull with FDA approval may face different treatment in Canada, the EU, or export markets |
| Semen from gene-edited animals could face trade barriers | Operations with an international genetics business need to navigate a complex patchwork |
| UK more permissive, EU evolving, North America case-by-case | Creates real operational considerations for genetics suppliers and larger breeding operations |
Insurance and Liability
Insurance coverage, liability for off-target effects, and warranty frameworks for gene-edited animals remain unresolved. Larger operations considering early adoption should have conversations with insurers and legal advisors about how these animals fit into existing coverage structures.
A Dynamic Worth Watching: When the Ethics Shift
Here’s something I’ve been thinking about that doesn’t typically come up in industry discussions, but strikes me as potentially significant.

Currently, gene editing is associated with ethical risks for some audiences—it’s something certain advocacy groups criticize. But as welfare-positive applications mature and prove themselves, the ethical pressure may begin flowing in the opposite direction.
Consider the implications:
- Once polled genetics that eliminate dehorning are commercially available and demonstrably safe, how do you justify continuing to disbud calves?
- Once heat-tolerant genetics exist that meaningfully reduce chronic heat stress, how do you explain choosing not to use them where cows are visibly struggling?
The question shifts from “Why are you using gene editing?” to “Why aren’t you using available tools to prevent avoidable animal suffering?”
In markets with strong welfare audit frameworks—such as premium processors, retailers with animal welfare commitments, and European export channels—gene-edited traits may increasingly align with responsible animal husbandry expectations rather than conflict with them.
Practical Steps: What Makes Sense Right Now

If you’ve followed this discussion, you’re probably wondering what concrete actions are warranted. Here’s my perspective:
Immediate actions:
- Track regulatory developments through breed associations and genetics suppliers
- Understand what’s already cleared or approaching availability in your market
- Assess your operation’s specific climate and disease vulnerabilities honestly
Conversations to start now:
Engage your genetics suppliers with these questions:
- What gene-edited traits are you actively developing or licensing?
- What’s your realistic timeline for commercial availability in my market?
- How will gene-edited genetics be positioned and priced relative to conventional offerings?
- What performance data do you have from trial herds or early commercial use?
- How are you approaching genetic diversity considerations in your edited lines?
- What are the implications for international semen sales or genetics trade?
Mental model to adopt:
Think about this as infrastructure, not just another product decision. Gene editing isn’t a discrete product to evaluate in isolation—it’s potentially foundational infrastructure that could reshape how genetic merit is defined, measured, and transmitted. The producers who recognized genomics as infrastructure back in 2010-2012 generally feel that perspective served them well.
The Bottom Line
The EU’s December decision didn’t resolve every question about gene editing in dairy cattle. Significant regulatory, commercial, and practical questions remain across multiple jurisdictions. But it signaled that major agricultural markets are moving toward science-based, outcome-focused regulation—evaluating what genetic changes accomplish rather than reflexively restricting the methods used to achieve them.
The underlying technology is proven and continuing to advance. Commercial animals exist in approved markets. Early-moving operations in Brazil and the UK are beginning to develop practical experience that will inform broader adoption decisions.
For producers weighing these developments, staying informed and engaged represents a reasonable first step. The next several years will likely determine which operations and regions effectively capture the benefits of climate-adapted, welfare-improved, lower-emission genetics—and which find themselves working to catch up with competitors who positioned themselves earlier.
These are decisions worth approaching thoughtfully. And honestly? They’re worth getting excited about, too. The technology is coming—the opportunity is in being ready for it.
Have questions about how gene editing developments might affect your operation? This is a conversation worth starting, and you don’t have to figure it out alone. Your genetics provider, land-grant extension specialist, or veterinarian would welcome the chance to think it through with you. Reach out, ask questions, and stay curious. That’s how the best producers have always stayed ahead.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Twenty generations becomes one: Gene editing compresses the timeline for adding heat tolerance, disease resistance, or polled genetics to elite dairy genetics—without the years of production tradeoffs that come with traditional crossbreeding.
- This is commercial reality: Heat-tolerant cattle are FDA-approved (March 2022), Brazil has gene-edited Holsteins in production, and Europe’s December 4, 2025, agreement just accelerated global momentum. The technology works.
- $1.6 billion in recoverable losses: That’s what U.S. dairy loses annually to heat stress alone. Hot-climate operations absorb several hundred dollars per cow each summer—costs that gene-edited heat tolerance directly addresses.
- Genetic advantages compound: Producers who adopted genomic selection early built leads their competitors spent a decade chasing. Gene editing creates the same opportunity for those who position early—and the same risk for those who wait.
- Start the conversation now: Talk to your genetics suppliers about what’s in their pipeline and what timelines look realistic. You don’t need to commit today, but understanding what’s coming lets you move strategically rather than reactively.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Top Feeding Practices to Cool Down Your Cows and Combat Heat Stress This Summer – While gene editing offers a long-term solution, this tactical guide provides immediate nutritional strategies you can deploy now. Learn specific TMR adjustments and feeding schedules to protect milk yield and maintain intake during peak heat events.
- Genome Editing in Dairy Cattle: Ethical Concerns and Breeding Standards Explored – Go beyond the headlines with this deep dive into the CRISPR technology and ethical considerations shaping the industry. This analysis is essential for understanding the consumer landscape and regulatory hurdles that will dictate how fast these tools reach your farm.
- Understanding the Polled Gene in Dairy Cattle: A Boon for Farming Practices – Master the mechanics of polled genetics and their impact on herd welfare. This breakdown explains the dominant/recessive inheritance patterns and provides the economic business case for why eliminating dehorning is becoming a competitive advantage.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!