Get expert advice on solving and treating heifer mastitis infections. Looking to keep your herd healthy and productive? Keep reading to find out more.
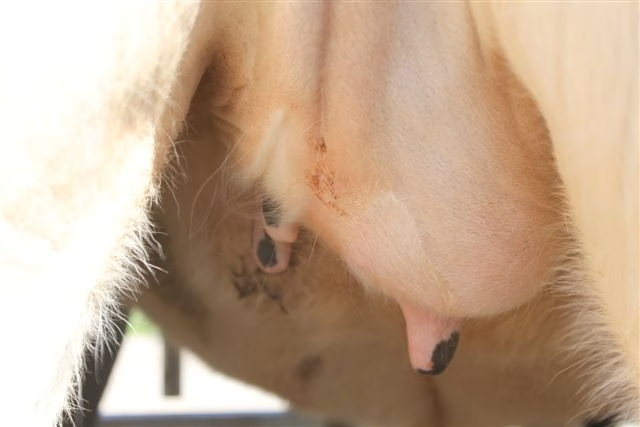
Imagine waking up to discover one-third of your heifers suffering from mastitis, which is both avoidable and curable. This is more than a minor setback; it is a substantial economic burden that will impact your dairy herd’s overall health and production. Understanding heifer mastitis is critical for protecting your investment and maintaining your enterprise. Sometimes undiscovered until too late, mastitis influences milk output and quality while raising veterinary expenditures. Addressing this problem immediately is critical, given the apparent correlation between heifer health and future dairy cow performance. Mastitis in heifers significantly influences young stock health and farm profitability. Why should dairy producers care? Effective management minimizes losses and lays the groundwork for healthier, more productive dairy cows. Investing in preventive and prompt treatment promotes a healthy herd and economic sustainability.
| Mastitis Impact | Effect on Heifer | Economic Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Milk Production | -20% to -50% | Losses ranging from $150 to $300 per heifer annually |
| Poor Milk Quality | Increased somatic cell count (SCC) | Penalties for milk quality issues; reduced market value |
| Increased Veterinary Costs | Frequent treatments and interventions | Additional expenses from $50 to $150 per heifer |
| Long-term Health Impacts | Potential for recurring infections | Higher culling rates and replacement costs |
| Future Productivity | Compromised udder health | Reduced lifetime milk yield |
Unique Challenges in Preventing and Treating Heifer Mastitis
Heifer mastitis, an udder infection affecting young female cows that have not yet given birth or begun breastfeeding, offers distinct issues compared to lactating cow mastitis. Unlike the apparent signs in nursing cows, heifer mastitis usually starts gradually, with mild swelling or redness of the udder, which may progress to discomfort, fever, or abscesses. Common pathogens include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis, and Escherichia coli. Environmental factors like inadequate bedding cleanliness, close closeness to diseased animals, and stress enhance infection risk.
Effective prevention requires regular health screenings and a focus on early intervention. Strategies vary significantly from those used for lactating cows, emphasizing prevention rather than therapy. Maintaining clean, dry bedding, regulating social contacts, and managing diet are all critical. Implementing vaccination procedures and pre-breeding health exams ensures that heifers are healthy and ready for milk production.
| Cost Component | Estimated Cost per Incidence |
|---|---|
| Treatment (antibiotics, veterinary care) | $100 – $250 |
| Reduced milk yield | $50 – $150 |
| Discarded milk | $20 – $75 |
| Labor costs (additional management) | $30 – $80 |
| Potential long-term productivity loss | $200 – $400 |
The Multifaceted Nature of Heifer Mastitis: Navigating the Web of Risk Factors
Heifer mastitis is a complicated disease with several risk factors impacting susceptibility. Environmental factors are critical; wet, unclean, and overcrowded dwelling settings serve as breeding grounds for bacteria, dramatically boosting illness rates. Adequate cleanliness, ventilation, and dry bedding are critical in minimizing these dangers. Management strategies also influence the occurrence of heifers. Infection risk might increase due to inconsistent milking procedures, incorrect equipment usage, and inadequate post-milking teat cleaning.
Furthermore, poor nutrition, rapid feed changes, and physical handling might impair a heifer’s immune system. Genetic predispositions are also important. Some breeds may be more susceptible to mastitis owing to udder conformation difficulties or weakened immune systems. Selective breeding strategies that enhance genetic resistance to mastitis show promise, implying long-term reductions in infection rates.
Early Detection: The Keystone of Effective Heifer Mastitis Management
Early identification of heifer mastitis is critical for optimal management and treatment, avoiding serious health problems and output losses. Clinical indications such as swelling, redness, increased warmth, and soreness in the udder must be observed first to get an accurate diagnosis. These clues, however, need validation using rigorous procedures. Laboratory testing is critical for verifying clinical observations. Somatic cell count (SCC) testing is often employed, and increased SCC levels indicate inflammation and infection, which suggests mastitis. Furthermore, microbiological cultures aid in identifying particular diseases, allowing for more effective antibiotic therapy. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays identify pathogens quickly and precisely, especially when bacterial cultures are inconclusive or many infections are present.
Early detection is critical. Early intervention prevents illness development and lowers the chance of herd spread. Regular monitoring and using techniques such as the California Mastitis Test (CMT) during regular herd health inspections may significantly increase early detection rates. This proactive technique ensures that heifers get early and proper care, preserving their health and productivity.
Strategic Approaches to Prevent Heifer Mastitis: Hygiene, Vaccination, and Nutrition
Preventing heifer mastitis requires a diversified strategy. The most important aspect is to maintain appropriate hygiene. Keep the milking area and equipment clean to avoid pathogen exposure. Disinfect udders and milking instruments before and after each session. This method reduces germs, resulting in a better environment for heifers.
Implementing immunization campaigns is also critical. Vaccines improve heifers’ immunological protection against particular infections. Customize these programs to the microbiological profile of the herd’s habitat and work with veterinary professionals to develop tailored immunization regimens to defend against possible risks.
Nutritional management is also quite important. A well-balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals promotes general health and immunity, lowering the chance of illness. Please pay attention to micronutrients such as selenium and vitamin E for their beneficial impact on udder health. To drastically reduce the risk of mastitis, continuously check and change the food based on the heifers’ developmental phases and health state.
Comprehensive Treatment Strategies for Heifer Mastitis: Integrating Antibiotic Therapy, Alternatives, and Supportive Care
| Treatment Option | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic Therapy | Quickly effective against bacterial infectionsWidely researched and proven treatmentsReadily available | Potential for antibiotic resistanceResidue concerns in milkPossible side effects on animal health |
| Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) | Reduces inflammation and painCan improve animal well-being and productivitySupportive alongside other treatments | Does not directly address infectionMay have gastrointestinal side effectsRequires careful dosage regulation |
| Herbal Medicines | Natural alternative with fewer side effectsCan have immune-boosting propertiesReduced risk of residue in milk | Variable efficacy and dosingLimited research and clinical trialsPotential for allergic reactions |
| Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) | High specificity against pathogensReduces the risk of antibiotic resistanceCan target multi-drug resistant strains | Still under research and not widely availablePotential high cost of developmentUnknown long-term safety profile |
| Bacteriophages | Highly specific to bacterial pathogensEnvironmentally friendlyCan be a valuable tool against antibiotic-resistant bacteria | Limited availability and regulatory approvalRequires precise identification of bacteriaPotential for bacterial resistance to phages |
| Vaccination | Prevents infection before it occursReduces overall incidence of mastitisImproves herd immunity | Requires time for immunity to developNot effective against already infected animalsPossible adverse reactions in some animals |
Addressing heifer mastitis infections requires a complex treatment strategy. Antibiotic treatment is crucial, particularly against harmful germs. However, cautious antibiotic usage is needed to combat antimicrobial resistance. Selecting an antibiotic based on culture and sensitivity data promotes effectiveness while reducing needless exposure.
Alternative therapies are gaining momentum. Intramammary infusions of herbal extracts and essential oils from plants such as eucalyptus, thyme, and oregano have antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making them a viable complement to mastitis therapy.
Supportive treatment is critical. Optimal udder health achieved via diligent milking procedures and clean, dry living circumstances may considerably reduce symptoms. Anti-inflammatory medications alleviate pain and swelling, improving general well-being.
Advances in immunomodulatory therapies, such as bovine lactoferrin and cytokine therapy, may improve the heifer’s immunological response. These cutting-edge innovations have the potential to alter mastitis treatments.
Heifer mastitis is managed comprehensively, which includes antibiotic medication, alternative therapies, and supportive care. This technique treats the illness and strengthens the heifer’s resistance to future occurrences, eventually contributing to sustainable dairy farming operations.
Holistic Herd Management: The Cornerstone of Heifer Mastitis Prevention
Effective herd management is vital for minimizing heifer mastitis. Proper milking methods reduce the risk of infection. To reduce bacterial exposure and improve hygiene, ensure that udders are clean and dry before utilizing milking equipment. Using separate towels for each cow reduces cross-contamination.
Housing circumstances have a tremendous influence on heifer health. Dry, clean, and well-ventilated shelters reduce pathogen exposure. To avoid the accumulation of hazardous germs, clean bedding regularly and guarantee good waste drainage. Adequate space for each animal decreases stress and aggressive interactions, which improves immune function and lowers infection risks. Investing in pleasant bedding materials, such as sand or straw, improves animal well-being and creates a cleaner environment.
The Bottom Line
Vigilance against heifer mastitis is critical for maintaining and improving dairy herd health. Understanding the disease’s complicated nature allows dairy producers to develop practical prevention efforts rather than just treating symptoms. To control heifer mastitis, rigorous herd management measures must address symptoms and underlying causes. This proactive strategy results in healthier and more productive heifers, benefiting the dairy company. Managing heifer mastitis is a continuous commitment to dairy farming efficiency. Implement the recommended measures, be vigilant, and seek ongoing breakthroughs in illness management. This allows dairy producers to create healthier, more productive herds. Invest in prevention now to ensure a sustainable future.
Key Takeaways:
- Heifer mastitis poses unique prevention and treatment challenges due to the distinct physiological and environmental factors affecting heifers.
- Effective management of heifer mastitis requires a dynamic understanding of the multifactorial risk factors, including genetic predisposition, husbandry practices, and microbial exposure.
- Early detection through vigilant monitoring and diagnostic practices is critical in minimizing the impact of mastitis in heifers and initiating timely treatment.
- Preventive strategies should encompass a broad spectrum of practices, including stringent hygiene protocols, targeted vaccination programs, and optimized nutritional plans.
- Comprehensive treatment protocols for heifer mastitis should integrate antibiotic therapies with innovative alternatives and supportive care to ensure robust recovery and milk production.
- Holistic herd management underpins successful mastitis prevention, necessitating a cohesive approach that combines individual animal care with overall herd health strategies.
- A multifaceted action plan, supported by ongoing research and real-world application, is essential for addressing and mitigating the complex issue of heifer mastitis effectively.
Summary:
Heifer mastitis is a disease affecting young female cows who have not yet given birth or started breastfeeding. It is preventable and curable, impacting milk output and quality while increasing veterinary costs. Addressing this problem immediately is crucial as it significantly impacts young stock health and farm profitability. Common pathogens include Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis, and Escherichia coli. Environmental factors like inadequate bedding cleanliness, close proximity to diseased animals, and stress increase infection risk. Regular health screenings and early intervention are essential for effective prevention. Strategies vary from those used for lactating cows, emphasizing prevention rather than therapy. Risk factors include environmental factors, management strategies, poor nutrition, rapid feed changes, and physical handling. Genetic predispositions also play a role, with some breeds being more susceptible due to udder conformation difficulties or weakened immune systems. Early detection is critical for optimal management and treatment, and comprehensive treatment strategies include antibiotic therapy, alternative therapies, and supportive care. Holistic herd management is vital for minimizing heifer mastitis, including proper milking methods, separate towels for each cow, well-ventilated shelters, regular cleaning, waste drainage, and adequate space for each animal.













