Nine days changed everything—US dairy faces $6B loss. Your farm ready for what’s next?
Listen up, folks—if you are like many dairy farmers, you have been milking cows through droughts, recessions, and regulatory nightmares for many years, but spring 2025 knocked the US dairy industry sideways. If you haven’t felt it in your milk check yet, buckle up. Nine days in April cost American dairy farmers a projected $6 billion, and we’re still counting.
Look, I’ll cut to the chase. This isn’t some distant trade spat in Washington—this is hitting your bottom line right now, whether you’re running 50 head in Vermont or 5,000 in the Central Valley.
When Politics Became Your Biggest Risk Factor
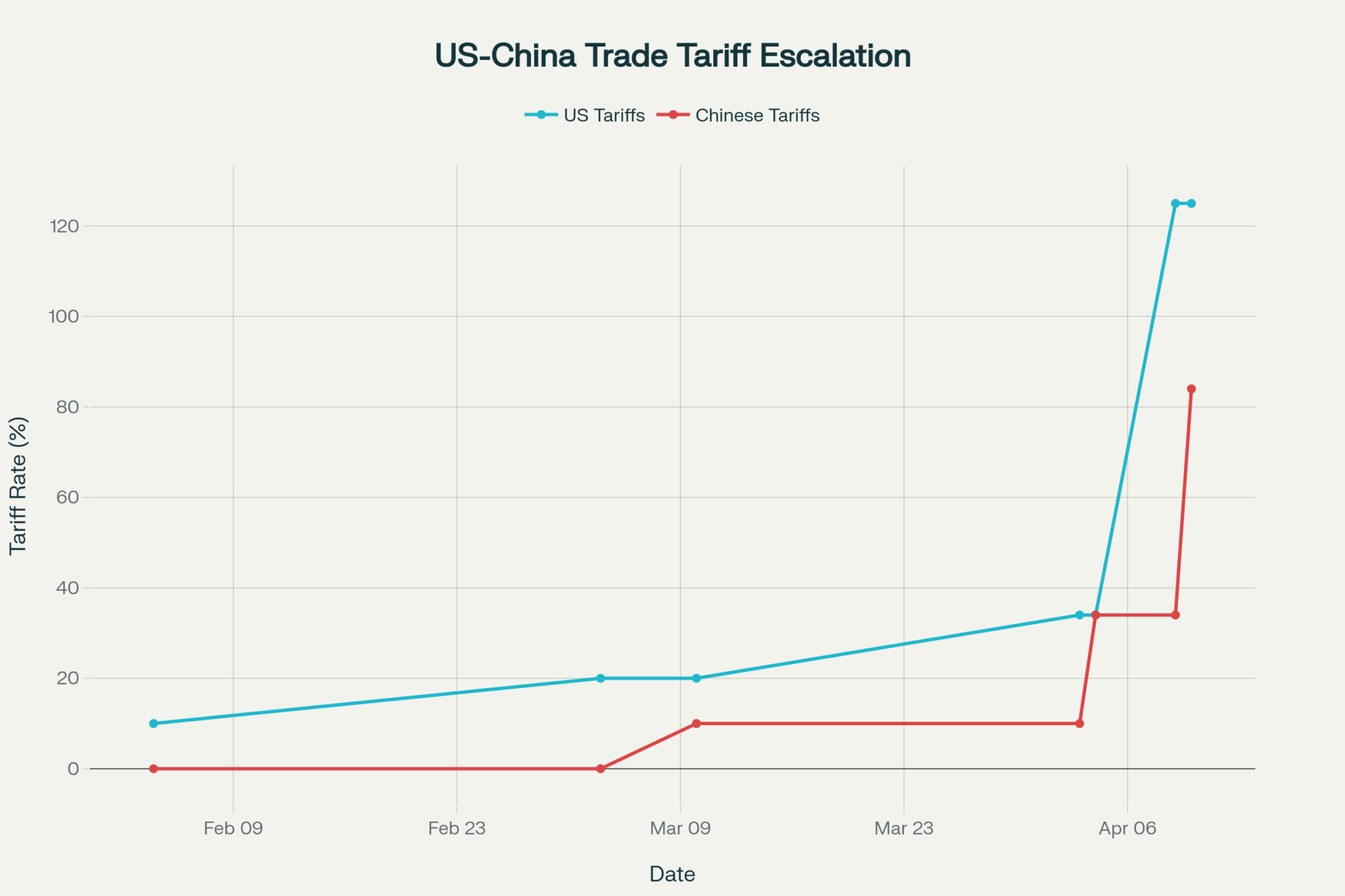
Nine Days That Changed Everything
| Product Category | Export Market | Year-over-Year Change (May 2025 vs. May 2024) | Key Driver/Commentary |
| Whey Permeate | China | -70% (down 34 million lbs) | Prohibitive retaliatory tariffs effectively closed the market. |
| WPC 80 | China | -83% | High-protein whey caught in the same tariff escalation. |
| Lactose | China | -59% (plunged in May) | U.S. price advantage was erased by the 125% tariff. |
| Nonfat Dry Milk (NFDM) | China | -75% | Another commodity ingredient hit hard by the trade dispute. |
| Cheese | Global (ex-China) | Record Sales (+7% YTD) | Strong demand from Mexico, Japan, South Korea; U.S. price competitiveness. |
Here’s how fast things went south: April 2, the administration slapped a 34% tariff on Chinese goods. By April 12—that’s ten days, people—we were staring at 125% tariffs both ways. China matched us move for move, hour for hour.

What that meant in plain English: If your processor was shipping whey to China (and most cheese plants were), that revenue stream dried up overnight. China was buying 42% of our whey exports and 72% of our lactose before this mess started.
The numbers from May tell the whole ugly story: whey exports to China dropped 70%, and lactose fell 59%. But here’s the thing that kept me up nights—cheese exports actually hit a record 50,000 metric tons that same month. Markets outside China are hungry, and our product is still competitive. The problem isn’t demand; it’s politics.

Where the Pain Hit Different
Wisconsin: Cheese Capital Under Siege
Wisconsin’s $52.8 billion dairy economy took it on the chin hard. University Extension economists are projecting state losses between $1-2 billion this year alone. That’s real farms going under, not some abstract number.
If you’re milking in Wisconsin:
- Eastern counties (Kewaunee, Brown, Manitowoc): Large operations tied to export-heavy processors got hammered the worst
- Driftless region (Grant, Crawford): Smaller operations and grazing dairies showed more resilience—they weren’t hanging their hat on China to begin with
- Central counties (Marathon, Wood): Mixed bag, depending on your co-op’s export exposure
Your homework: Get on the phone with your field rep today. Find out exactly what percentage of your milk goes toward products that were China-bound. That’s your pain percentage.
California: Getting Hit from Both Ends
Central Valley dairies are facing what UC Davis economists call a “compound crisis.” Feed costs jumped $18-22 per ton for imported concentrates. Water costs are adding another buck-twenty-five per hundredweight. Energy up 12% year-over-year.
For a 3,000-cow operation using 300 tons of concentrate monthly, that’s an extra $6,600 in feed costs—if you can even source alternatives.
Smart operators are: Locking Q1 2026 feed pricing now. Diversifying suppliers. Looking at longer-term hay contracts while they’re still available.
Pennsylvania: Border Uncertainty
Pennsylvania farms exported $364 million in dairy products last year, mostly to Canada and Mexico. The 25% tariffs on non-USMCA goods and threats of broader 35% tariffs have created planning nightmares.
Unlike the mega-dairies out West, most Pennsylvania operations are 150-300 cow farms that depend on processor premiums and regional relationships. When that gets disrupted, there’s no cushion.
| Scenario | Likelihood | China Market Access | U.S. Dairy Industry Impact | Recommended Producer Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trade Détente | ~25% | Partial access restored | Some market recovery; ongoing challenges | Diversify markets; maximize efficiencies |
| Protracted Stalemate | ~60% | Chinese market remains closed | Permanent loss to China; shift to ASEAN and Latin America | Expand new markets; optimize operations |
| Escalation | ~15% | Market worsens; broader conflict | Severe industry disruption; economic downturn risk | Enhance resilience; increase financial buffers |
What Your Co-op’s Actually Doing:
- DFA: Implementing Southeast Asia marketing strategy by Q4. Managing the risk of a domestic cheese surplus from blocked exports. Enhanced feed purchasing programs through regional teams.
- Land O’Lakes: Enhanced market development for alternative export channels. Accelerating domestic protein ingredient programs. Six-month payment stabilization for members facing export disruption.
- Northeast cooperatives: Optimizing Canadian TRQ utilization. Enhanced quality bonus programs for members facing margin pressure. Expanded forward contracting options.
Component Focus: December Changes You Can’t Ignore
The Federal Milk Marketing Order updates taking effect on December 1 make component optimization critical. New manufacturing allowances: cheese jumps to $0.2519/lb (up from $0.2003), butter to $0.2272/lb (up from $0.1715).
Current industry trends:
- National average butterfat: 4.41% (up from 4.36% last year)
- National average protein: 3.42% (up from 3.38% last year)
Real talk: University Extension calculations show increasing protein content by 0.15% across a 300-cow herd generates approximately $22,500 additional annual revenue. That’s not pocket change.
How to get there:
- Focus genetics on bulls with high protein potential
- Maximize nutrition programs for rumen-undegradable protein
- Implement management systems that improve milk quality premiums
Technology That Actually Pays Back
Margin pressure is forcing real decisions. Here’s what works:
- Automated Feeding Systems: $150,000 investment, 18-month payback verified at multiple Wisconsin operations. Requirement: minimum 500 cows for economics to work.
- Rumination Monitoring: $75/cow for quality systems. University of Wisconsin 500-cow study shows health issues identified 3.2 days earlier. Pays for itself in reduced vet bills and improved reproduction.
- Robotic Milking: $250,000/unit, 70+ cow minimum for economics. Reality check: labor savings only work if you can actually reduce staff.
Your DMC Lifeline
| Month (2025) | All-Milk Price ($/cwt) | Average Feed Cost ($/cwt) | Calculated DMC Margin ($/cwt) | Indemnity Payment? | Reasoning |
| March | ~$23.00 (implied) | ~$11.45 (implied) | $11.55 | No | Strong milk price and moderate feed costs kept margin >$2.00 above trigger. |
| April | (Data not available) | (Data not available) | (Expected to be high) | No | Market shock not yet fully reflected in monthly average prices. |
| May | $21.30 | ~$10.90 (implied) | $10.40 | No | Margin tightened but remained nearly $1.00 above the trigger. |
| June | ~$22.00 (implied) | ~$10.90 (implied) | $11.10 | No | Margin widened again due to price rebounds in some categories. |
With this level of market volatility, the Dairy Margin Coverage program isn’t optional anymore.
2025 performance so far:
- May margin: $10.40/cwt
- June margin: $11.15/cwt
- July margin: $10.85/cwt
Producers enrolled at the $9.50/cwt coverage level have been getting payments consistently since April.
2026 enrollment opens January 29. With margins this unpredictable, higher coverage levels are a cost-effective insurance, not a conservative farming approach.
What’s Coming Next
Trade experts see three scenarios, and frankly, none of them get us back to where we were:
- Scenario 1: Trade Deal (25% probability) – Tariffs drop to a 15-25% range, partial Chinese market recovery. However, Brazil and New Zealand retain most of the market share gains. Even with a deal, the trust is broken.
- Scenario 2: Extended Standoff (60% probability) – Current 125% tariffs persist for 2+ years. This becomes the new normal. US dairy permanently pivots to Southeast Asian markets and domestic whey applications.
- Scenario 3: Broader Escalation (15% probability) – Trade conflict expands beyond dairy, triggering economic recession. Nobody wants this scenario.
Your Action Plan for Fall 2025
Right Now (September-November)
Assess Your Risk: Call your processor today. Get specific answers:
- What percentage of your milk goes to China-bound products?
- How has your pay price formula changed since April?
- What’s their backup plan for whey marketing?
Lock Down 2026:
- DMC enrollment (January 29 deadline)
- Feed contracts for Q1 2026
- Banking relationships for operating credit
Strategic Moves Through Year-End
Component Optimization: Focus genetics on higher protein potential. Audit nutrition programs for protein maximization. Implement milk quality monitoring systems.
Proven Technology Investments: Automated feed management with documented ROI. Health monitoring equipment with verified payback periods. Reproductive management platforms that actually work.
The Bottom Line
This isn’t weather or disease—it’s political volatility that makes long-term planning nearly impossible. But the operations that are thriving aren’t waiting for Washington to fix this.
Three things successful producers are doing right now:
- Maximizing efficiency through technology with proven ROI
- Optimizing components for December’s pricing changes
- Building financial reserves for continued volatility
The era of single-market optimization is over. Feed efficiency isn’t a nice-to-have anymore—it’s survival. Component optimization isn’t next year’s strategy—it’s this December’s reality.
The rules changed in nine days back in April. Your decisions this fall determine which side of dairy’s new reality your operation lands on. Stay sharp, stay flexible, and keep your eyes on the next move.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Diversify your export channels now — with whey down 70% to China, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, which are hungry for US products; get your processor talking to these markets today
- Push that protein percentage — even a 0.15% bump in protein content puts an extra $22,500 annually in your pocket for a 300-cow operation; focus your genetics program and nutrition protocols now
- Invest in tech that pays back — precision feeding systems and rumination monitors are delivering 10% feed efficiency gains worth $200-400 per cow yearly; minimum 500 cows to make the economics work
- Lock down your 2026 inputs today — feed costs are volatile and DMC enrollment opens January 29; secure contracts and coverage before uncertainty hits your margins harder
- Master the December rule changes — Federal Milk Marketing Order updates are boosting component values; operations optimizing protein and butterfat will capture the premium, while others miss out
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY:
Alright, let me lay this out straight—we’re looking at a potential $6 billion hit to US dairy farmers over the next four years, and it all started with nine crazy days in April when tariffs exploded from 34% to 125%. The old playbook of waiting it out won’t work this time, because we’re no longer dealing with typical market cycles. Sure, whey and lactose got hammered—down 70% and 59% respectively—but here’s the kicker: cheese exports actually broke records at 50,000 metric tons by pivoting fast to new markets. Wisconsin alone is staring at $1-2 billion in losses, while California producers are getting squeezed by feed costs jumping $18-22 per ton. The farms that’ll survive and thrive? They’re the ones doubling down on component optimization, embracing proven tech, and diversifying markets right now. Don’t wait—the new dairy reality is here, whether you’re ready or not.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Maximizing Dairy Margins in 2025: Why Precision Genetics, Nutrition, and Tech Are Your Best Bets Amid Market Volatility – This article provides the tactical blueprint for the component strategies discussed above. It details specific genetic selection criteria and nutritional protocols you can use to immediately begin boosting butterfat and protein, directly impacting your milk check under the new FMMO rules.
- 2025 Dairy Market Reality Check: Why Everything You Think You Know About This Year’s Outlook Is Wrong – Go beyond the immediate trade war crisis with this strategic market analysis. This piece unpacks the underlying supply, demand, and global competition factors shaping 2025, helping you build a more resilient long-term business strategy beyond a single political event.
- The Fully Automated Dairy: Is It The Future Or A Fantasy? – Explore the next frontier of dairy innovation with this deep dive into full automation. It moves beyond individual technologies to examine the economics and operational realities of a fully integrated smart farm, helping you plan your long-term technology roadmap.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!








