Dairy farms slash $457/head costs via beef-cross breeding: 20% faster growth, 37% methane cuts, and $900+/calf premiums. The feed revolution is here.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Dairy producers are leveraging beef-on-dairy crossbreeding to combat soaring feed costs, with crossbred calves finishing 20% faster than pure Holsteins and delivering $457/head in feed savings. Backed by Texas Tech research and global precedents like the Netherlands’ methane-efficient programs, this strategy boosts sustainability through reduced emissions and unlocks premium pricing via quality carcasses. However, risks like extended Wagyu-cross gestations and genetic diversity loss require balanced breeding via the 60/30/10 rule. With 7.9 million beef semen units sold to dairies in 2024, the approach is reshaping profitability while aligning with climate-smart incentives.
KEY TAKEAWAYS:
- Feed efficiency pays: Crossbreds cut feed costs by $457/head with 7:1 conversion ratios vs. Holsteins’ 8:1.
- Global proof: Dutch operations achieve 19.8% lower feed costs; NZ crosses hit 57.8% dressing percentages.
- Strategic balance: The 60/30/10 rule (60% beef semen, 30% sexed dairy, 10% elite dams) safeguards herd genetics.
- Sustainability premium: $20/head carbon credits and Prime-grade beef growth (9.6% of production) boost ROI.
- Mitigate risks: Manage gestational trade-offs and genetic diversity through targeted Limousin/Angus pairings.

The dairy industry’s shift toward beef-on-dairy crossbreeding has unlocked unprecedented feed efficiency gains, slashing costs and reshaping profitability. With 7.9 million beef semen units sold to dairies in 2024 – nearly tripling since 2017 – this strategy is proving a game-changer for producers navigating volatile feed markets. Let’s dissect the verified science driving this transformation.
FEED EFFICIENCY: THE $457/HEAD ADVANTAGE

Beef-on-dairy crossbreds outperform pure Holsteins across key metrics, delivering measurable savings for dairy farms. The numbers tell a compelling story: while Holstein steers typically require 407 days to reach slaughter weight, their beef-cross counterparts finish in just 326 days – a 20% faster timeline, dramatically reducing feed inputs. This accelerated growth translates to improved feed conversion ratios of 7:1 compared to the Holstein standard of 8:1, representing a 12.5% efficiency gain that compounds throughout the feeding period.
The financial impact is substantial. With crossbreds consuming 3,807 fewer pounds of feed per animal, operations save approximately $457 per head at current feed prices of $0.12 per pound. Texas Tech research confirms these advantages, documenting average daily gains of 1.82 kg for crossbreds versus 1.50 kg for Holsteins – a 21% improvement that creates cascading benefits throughout the production cycle.
This efficiency revolution isn’t limited to American operations. The Netherlands’ “Double Dairy Beef” programs demonstrate real-world success, with 38% of dairy births now using beef genetics, focusing mainly on methane-efficient Limousin crosses. Dutch producers report 19.8% lower feed costs per kilogram of beef produced than pure Holstein steers. Similarly, New Zealand’s pasture-based systems achieve 57.8% dressing percentages from Piedmontese x Friesian calves, outperforming native beef breeds by 3.8 percentage points.
COST IMPACT: BEYOND THE FEED BUNK

The economic advantages extend well beyond direct feed savings. Dairy producers implementing crossbreeding strategies report significant labor and overhead reductions. Due to their hardier constitutions, crossbred animals require 5.3 fewer hours per head in health management. This translates to approximately 14% lower veterinary costs from reduced stress-related issues typically plaguing purebred dairy steers.
Sustainability premiums represent another growing revenue stream. Cargill’s RegenConnect program offers $20 per head in carbon credits for qualifying crossbred operations, while research documents a 37% methane reduction per pound of gain compared to pure dairy systems. These environmental benefits create marketable advantages as consumers and retailers increasingly prioritize climate-friendly production methods.
Carcass quality improvements further enhance the value proposition. Beef-dairy crosses demonstrate 24-hour more extended color stability in retail cases, improving shelf life and reducing waste throughout the supply chain. This quality advantage has contributed to the remarkable growth in Prime-grade carcasses, which now constitute 9.6% of U.S. beef production – more than double the 4.4% seen in 2014.
THE COUNTERARGUMENT: FEED EFFICIENCY TRADE-OFFS

Despite these advantages, it’s essential to acknowledge that crossbreds aren’t universally superior to straightbred beef genetics. Purebred beef cattle still demonstrate marginally better feed efficiency metrics when adjusted for mature size. They also produce more consistent carcasses with predictable frame sizes, which can simplify processing and marketing.
Texas Tech research reveals an interesting fact: straight-bred beef calves from dairy dams via IVF technology outperform crossbreds in feed efficiency when adjusted for mature size. This suggests that as reproductive technologies advance, the advantages of crossbreeding may evolve. However, the current economic reality still strongly favors the crossbred approach for most commercial dairy operations seeking to maximize returns on non-replacement animals.
The days-on-feed advantage remains firmly with crossbreds, which typically finish 20% faster than their straightbred counterparts. This accelerated timeline creates operational flexibility and reduces exposure to feed price volatility – critical considerations in today’s uncertain agricultural markets.
BREEDING STRATEGY: THE 60/30/10 RULE
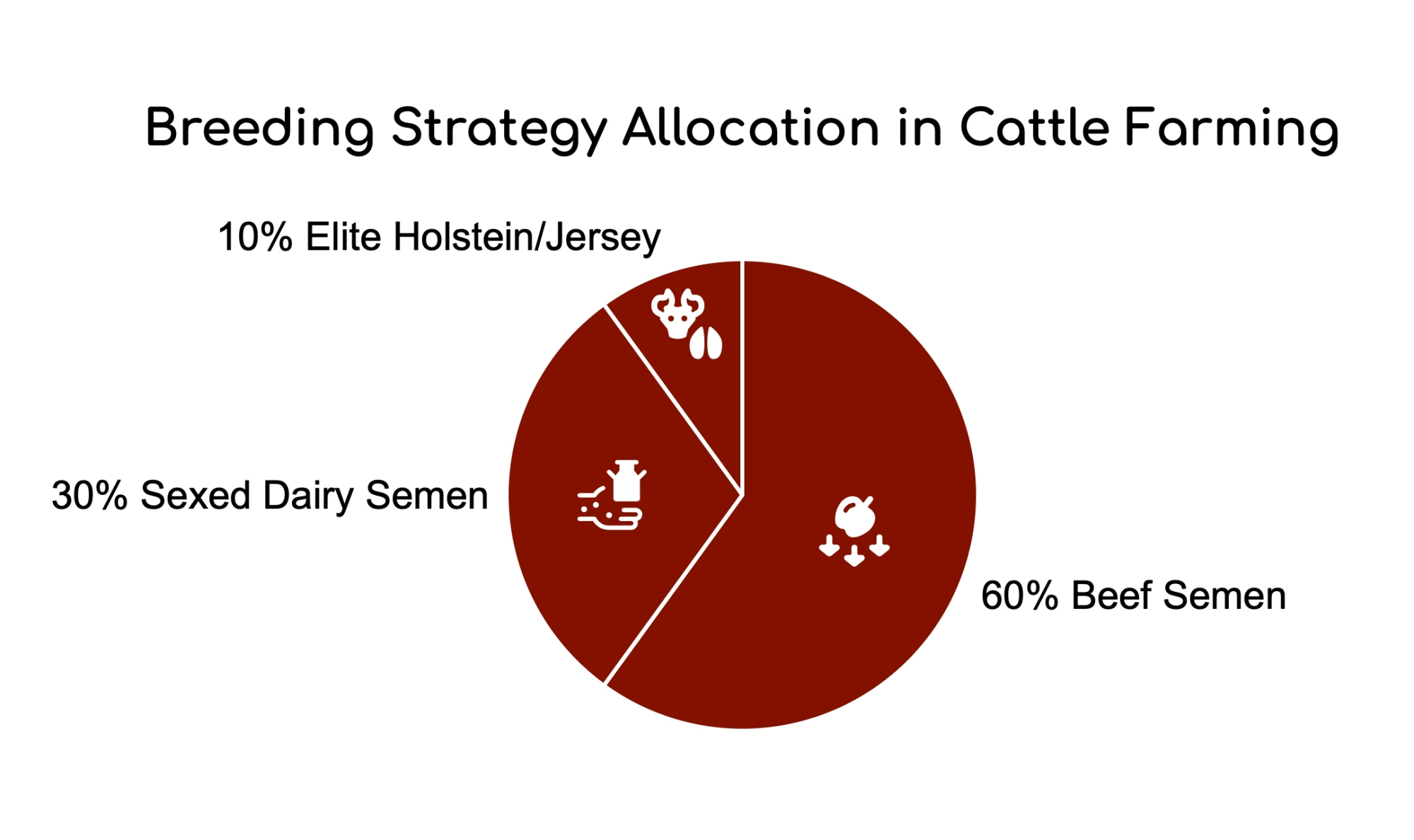
Strategic sire selection maximizes efficiency gains while maintaining herd integrity. Industry leaders recommend allocating 60% of breeding decisions to beef semen, prioritizing Continental breeds like Limousin and Charolais for feed efficiency and red meat yield while incorporating Angus genetics to enhance marbling potential. This approach has demonstrated a 12% higher likelihood of achieving Prime grade at slaughter.
The remaining breeding decisions should be carefully balanced, with 30% dedicated to sexed dairy semen used exclusively on the top genetic merit cows to maintain replacement heifer supplies. Genomic testing helps identify marbling gene carriers and other desirable traits complementing the crossbreeding program. The final 10% should preserve elite Holstein or Jersey cows with superior fertility and milk solids production to safeguard the herd’s genetic foundation.
This balanced approach prevents the common pitfall of over-aggressive crossbreeding, which can lead to replacement heifer shortages and force operations to purchase $3,000+ replacements on the open market. Producers create a self-sustaining system that captures crossbreeding benefits without compromising long-term herd development by maintaining sufficient purebred dairy genetics.
THE SUSTAINABILITY DIVIDEND

Crossbreds deliver substantial environmental benefits that increasingly translate to market premiums. The reduced greenhouse gas emissions from shorter feeding periods represent a quantifiable climate advantage, while lower water usage per pound of beef produced enhances the resource efficiency narrative. These environmental credentials are increasingly valuable as consumers and retailers prioritize sustainability metrics.
The economic upside is equally compelling. Midwest feedlots now pay $900+ premiums for Angus x Holstein calves with ribeye measurements exceeding 14.5 square inches. These premiums reflect the superior performance and carcass characteristics these animals deliver. Additionally, USDA Climate-Smart Commodity grants are increasingly available to operations demonstrating methane-efficient production methods.
The social dimension completes the triple-bottom-line advantage. Dairy’s robust recordkeeping systems provide unparalleled traceability throughout the production chain, addressing growing consumer demands for transparency. The high-touch calf management typical in dairy operations also aligns with welfare expectations, creating a compelling narrative for retailers and consumers.
CRITICAL RISKS TO MITIGATE

Despite the compelling advantages, several risks require careful management. Gestational trade-offs can impact operational efficiency, particularly with certain breeds. While delivering exceptional marbling, Wagyu crosses typically extend pregnancies by 8 days, increasing dam feed costs by $18-22 per gestation. Similarly, premium Continental breed semen costs $12-18 more per straw than conventional options, requiring careful cost-benefit analysis.
Genetic diversity represents another consideration. Over-emphasizing feed efficiency metrics may inadvertently reduce fertility resilience and other valuable traits. This is particularly evident in Jersey-dam crossbreds, which face approximately 14% carcass discounts at slaughter due to their smaller frames and lighter finished weights.
Market consistency challenges also exist. The variable size distribution between crossbreds can complicate feedlot pen uniformity, potentially reducing overall system efficiency. The current market dominance of Holstein x Angus calves limits breed diversity, potentially constraining genetic progress and creating vulnerability to disease or market shifts.
THE BEEF-DAIRY PLAYBOOK

Successful implementation requires a comprehensive approach. Depending on market signals and operation goals, genetic prioritization should focus on Holstein dams with marbling EPDs exceeding +1.0, paired strategically with Limousin sires for yield or Angus for marbling. This targeted approach maximizes the value of each breeding decision.
Feedlot partnerships represent a critical success factor. Forward-thinking dairy operations negotiate $900+ contracts for their crossbred calves by guaranteeing minimum birth weights of 84 pounds, providing complete health records, and avoiding Jersey lineage that might compromise carcass value. These partnerships create predictable revenue streams and reduce market volatility.
Enrollment in sustainability programs completes the strategy. Cargill’s Dairy Beef Accelerator offers premium pricing for operations meeting specific quality and environmental metrics, while Walmart’s Project Gigaton provides carbon credit opportunities for documented methane reductions. These programs transform environmental performance into tangible financial returns.
CONCLUSION: FEED EFFICIENCY MEETS FARMER REALITY
Beef-on-dairy crossbreeding isn’t a trend – it’s necessary for dairy farms facing $8+ per bushel corn and volatile milk markets. The economic case is compelling, with verified savings exceeding $500,000 annually for 1,000-cow operations and growing sustainability premiums. As Texas Tech’s Dr. Dale Woerner notes: “This isn’t better nutrition – it’s metabolic reengineering.”
The path forward requires thoughtful implementation. Producers should consult nutritionists to model breed-specific feed plans that maximize efficiency advantages. Regular audits of replacement need to prevent costly heifer shortages, while proactive engagement with feedlot partners secures premium pricing for crossbred calves. Dairy operations can transform feed efficiency into sustained profitability by balancing these considerations.
The feed efficiency revolution represents a rare win-win in modern agriculture – better environmental outcomes, improved animal performance, and enhanced farm profitability. Strategic crossbreeding offers a proven path to resilience and growth for dairy producers navigating challenging economic conditions.
 Download “The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration” Now!
Download “The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration” Now!
Are you eager to discover the benefits of integrating beef genetics into your dairy herd? “The Ultimate Dairy Breeders Guide to Beef on Dairy Integration” is your key to enhancing productivity and profitability. This guide is explicitly designed for progressive dairy breeders, from choosing the best beef breeds for dairy integration to advanced genetic selection tips. Get practical management practices to elevate your breeding program. Understand the use of proven beef sires, from selection to offspring performance. Gain actionable insights through expert advice and real-world case studies. Learn about marketing, financial planning, and market assessment to maximize profitability. Dive into the world of beef-on-dairy integration. Leverage the latest genetic tools and technologies to enhance your livestock quality. By the end of this guide, you’ll make informed decisions, boost farm efficiency, and effectively diversify your business. Embark on this journey with us and unlock the full potential of your dairy herd with beef-on-dairy integration. Get Started!
Learn more:
- Transform Your Dairy Economics: How Beef-on-Dairy Crossbreeding Delivers 200% ROI
Discover how strategic beef-on-dairy crossbreeding programs can unlock 200% ROI through calf premiums, feed efficiency gains, and targeted genetic strategies. - Boosting Feed Efficiency and Metabolic Flexibility for Resilient Dairy Farming
Explore the critical role of feed efficiency in reducing costs, improving sustainability, and enhancing profitability for modern dairy operations. - Everything Dairy Farmers Need to Know About Residual Feed Intake
Learn how optimizing residual feed intake (RFI) can improve herd health, reduce feed costs, and boost milk production for a more competitive dairy business.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Daily for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.








 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!






