Every breeding decision you’ll make next year connects to lessons buried in this year’s best journalism. A $260,000 gamble from 1926 that critics called insanity. A bankruptcy that produced three generations of World Dairy Expo champions. A bull whose daughters added $6,500 per head in today’s dollars, while his modern genomic evaluation shows negative Net Merit—a $2,117 swing from December 2025’s top bull. These aren’t just stories – they’re the strategic frameworks top breeders reference when everyone else is guessing.
Look, we published over 300 feature articles this year. Breeder profiles, sire spotlights, donor stories, industry investigations. When our editorial team sat down to identify which ones actually mattered—not which got the most clicks, but which ones readers bookmarked, shared with their herd managers, or referenced in breeding meetings—ten articles kept coming up.
These pieces combined a strong readership with lasting impact. Our Elevation story generated over 340 comments and was shared more than 2,800 times across platforms. The Blackrose piece prompted eight separate emails from readers who’d reconsidered their approach to dispersal auctions. The “Death of Get Big” article? At least a dozen producers told us they’d shared it with their lenders.
That’s the standard we used. Months after publication, readers were still emailing about these stories, arguing about them, applying them.
If you’re planning your 2026 breeding strategy, reviewing dispersal auction opportunities, or just trying to understand why certain genetic decisions matter more than others, these articles deserve your attention. Your competitors have probably already read them twice.
Four Bets, Five Legends: The Holstein Visionaries Who Built Everything You’re Breeding Today
Here’s the thing about Holstein history—most of us think we know it. We can name the big bulls, recite a few famous prefixes. But this article did something different. It traced four distinct breeding philosophies through five legendary figures and showed how each remains valid today.
Take T.B. Macaulay’s gamble on Johanna Rag Apple Pabst in 1926. According to Bank of Canada inflation calculations, that $15,000 purchase represents roughly $260,000 in today’s dollars—for one animal, in a post-WWI economy when farmers were still digging out from agricultural depression. The critics thought he’d lost his mind.
And here’s what makes this relevant to your operation right now: Holstein Canada pedigree records confirm that virtually every registered Holstein walking the planet today carries that bull’s blood.
Why Macaulay’s Math Still Works
What made Macaulay different? He came from actuarial science, not cattle breeding. He was doing progeny testing—evaluating bulls by their daughters’ actual performance—decades before Holstein Association formalized the practice in the 1930s. The man treated genetic improvement like a math problem while everyone else bred on gut instinct and show-ring appearance.
The article pairs Macaulay’s data-driven approach against Stephen Roman’s empire-building through marketing muscle, Roy Ormiston’s patient cow-family development, and Heffering and Trevena’s paradigm-shifting partnership at Hanover Hill.
The question worth asking yourself: Are you breeding like Macaulay (data-first), Roman (marketing-first), Ormiston (cow-family-first), or some combination? Your answer shapes every semen purchase you’ll make in 2026. Knowing your bias reveals your blind spots.
Round Oak Rag Apple Elevation: The Bull That Changed Everything
You can’t have a serious conversation about Holstein breeding without talking about Elevation. But this article went beyond the usual tribute piece—it interrogated his legacy while respecting it. That tension is exactly what makes it Editor’s Choice material.
Born in 1965 on a modest Virginia farm from what the article calls “a questionable mating,” this unassuming black-and-white calf became the most significant genetic influencer Holstein breeding has ever seen. His bloodline now runs through nearly 9 million descendants. Almost every glass of milk you’ve ever enjoyed likely came from a cow with some connection to this sire.
His numbers were off the charts for the era: daughters averaging 29,500 pounds of milk during their first lactations—beating their peers by 15%—while sporting picture-perfect udders described by Charlie Will of Select Sires as having “high and wide rear udders with exceptional shape and symmetry”.
Here’s where it gets interesting for your bottom line. Those udders stayed attached for 2-3 lactations longer than average, translating into an extra $1,200 in profit per cow in 1970s dollars. Adjusted for inflation, that’s roughly $6,500 per cow today—the difference between a profitable and breakeven herd on longevity alone.
The Paradox Every Breeder Should Understand
What sets this piece apart is how it handles the tension between Elevation’s historical importance and his modern genomic evaluation. His current CDCB summary shows a Net Merit of -$821. Compare that to December 2025’s #1 Net Merit bull, Genosource Retrospect-ET, sitting at +$1,296 NM. That’s a $2,117 swing—representing six decades of genetic progress built on Elevation’s foundation.
That seems damning until you understand—as the article carefully explains—that these numbers compare him to a modern Holstein population he helped create. As Will put it: “Elevation’s genes form the baseline against which we measure progress—you can’t delete the foundation of a skyscraper and expect it to stand”.
Six decades after his birth, his DNA still runs through 14.5% of active proven Holstein sires. Understanding why matters when your genetics rep is pushing the latest trendy lineup. Foundation sires created the genetic architecture you’re building on. Ignoring that context leads to concentration mistakes.
READER ACTION: Before your next mating batch, review CDCB’s relationship tools to understand how heavily your current herd relies on Elevation and Chief genetics. Concentration you don’t see is concentration you can’t manage.
When Financial Disaster Breeds Genetic Gold: The Blackrose Story
This is the kind of story conventional dairy media won’t touch—financial ruin, bankruptcy, bull calves sent to slaughter just to keep the electricity on. But it’s also a story about vision, opportunity recognition, and the staying power of superior genetics.
Picture it: mid-80s, brutal January morning. Jack Stookey—once a larger-than-life figure who owned some of North America’s most elite cattle—can’t scrape together payroll. Decades of careful breeding sitting in legal limbo. And Louis Prange looks at that situation and sees a buying opportunity where everyone else sees disaster.
Prange worked out a deal with the bankruptcy trustee: lease the best cows, flush embryos, split proceeds three ways. His vision was what breeders call a “corrective cross”—mating two animals whose strengths perfectly complement each other’s weaknesses. He wanted to breed the red-and-white champion Nandette TT Speckle to To-Mar Blackstar, a production powerhouse who needed help on the structural side.
On March 24, 1990, Stookey Elm Park Blackrose came into this world.
From $4,500 Purchase to Dynasty
Sold as an 18-month-old for $4,500—about $10,400 in today’s money—she grew into a commanding presence that dominated wherever she went. Her numbers: 42,229 pounds of milk at five years old, 4.6% butterfat, 3.4% protein, EX-96 classification. She won All-American honors as both a junior two-year-old and a junior three-year-old, then captured the Grand Champion title at the Royal Winter Fair in 1995, joining an exclusive club of U.S. cows to win Canada’s most prestigious show.
But what really earns this story Editor’s Choice status is tracing Blackrose’s influence forward. Her descendants include Lavender Ruby Redrose-Red, who in 2005 became the first and only Red & White cow ever named Supreme Champion over all breeds at World Dairy Expo. And Ladyrose Caught Your Eye—a Unix daughter born in 2019 who’s won World Dairy Expo three consecutive years (2021-2023) with 16 milking daughters classified VG-87 or higher.
Financial disaster. Genetic gold. Same story, same cow family. If you’re not looking at dispersal auctions and bankruptcy sales as potential genetic opportunities, this article might change your mind.
READER ACTION: Before your next dispersal auction, ask: what second-chance genetics might be available that well-funded operations are overlooking? The Blackrose story suggests financial distress creates buying opportunities—if you know what you’re looking for.
When Giants Fall Silent: The Shore Dynasty’s Century of Excellence
“Have you ever gotten one of those calls that just stops you cold? Mine came the day after Christmas, 2013. Hardy Shore Jr. was gone.”
That opening line sets the tone for something different—not just a breeder profile, but a meditation on legacy, creative genius, and the personal costs of relentless pursuit of excellence.
The Shore story spans four generations, from William H. Shore’s leap into purebreds in 1910 (when most thought he’d lost his mind) to Hardy Jr.’s embryo exports in the genomic era. It’s a century of dairy evolution through one family’s decisions.
Why This History Matters Right Now
What really struck me, rereading this article, is how it mirrors challenges producers face today. Consider William’s decision to buy those first purebred Holsteins from Herman Bollert when mixed farming was safe, predictable, and profitable. Sound familiar? How many of us are weighing similar pivots right now with robotic milking systems, precision nutrition protocols, or carbon-neutral initiatives?
The genetic throughline is extraordinary. Follow it from Hardy Sr.’s twin bulls Rockwood Rag Apple Romulus and Remus, through Shore Royal Duke, to Fairlea Royal Mark—described as “possibly the best bull to come out of Western Ontario”—and you’ll find it leads directly to Braedale Goldwyn. Breeding decisions made in the 1940s shaped the breed through to the 2000s and beyond.
The article doesn’t shy away from Hardy Jr.’s personal struggles either. “The same creative fire that produced breakthrough genetics also fueled personal demons that few understood”. The industry’s response—celebrating his contributions while acknowledging his difficulties—showed the best of our community.
That’s nuanced, human storytelling. The dairy industry deserves more of it.
The $4,300 Gamble That Reshaped Global Dairy: The Pawnee Farm Arlinda Chief Story
If Elevation changed everything, Chief changed it alongside him. According to CDCB data cited in this article, up to 99% of AI bulls born after 2010 can be traced back to either Round Oak Rag Apple Elevation or Pawnee Farm Arlinda Chief. That’s not influence—that’s near-total genetic dominance of the modern Holstein population.
This piece opens with a pregnant cow traveling 1,152 miles by train from Nebraska to California in 1962, then traces how her calf would revolutionize milk production worldwide. Chief contributed nearly 15% to the entire Holstein genome—a level of genetic concentration unprecedented in livestock breeding.
The Question That Makes This Essential Reading
What earns this story Editor’s Choice status isn’t just the historical account—though that’s compelling. It’s the article’s willingness to honestly interrogate the legacy.
Chief transmitted tremendous production, yes. But he also passed along udder conformation challenges that breeders spent decades managing. The piece asks a provocative question: would Chief still have become the most influential Holstein sire in history if today’s genomic tools had been available? Would we have managed his genetics differently if we’d known what we know now from the start?
That’s not second-guessing history. That’s learning from it. And it’s exactly the kind of uncomfortable question we exist to ask.
READER ACTION: Run your herd through CDCB’s haplotype and relationship tools. Understanding your concentration on foundation sires like Chief helps you make smarter outcross decisions—and avoid repeating mistakes the breed made when we couldn’t see what we were building.
Death of ‘Get Big or Get Out’: Why Tech-Savvy 500-Cow Dairies Are Outperforming Mega-Farms
For years, the industry’s biggest voices told mid-size dairies to expand or exit. This article asked: what if that conventional wisdom was incomplete—and what if the data revealed something more nuanced?
Every decade has its orthodoxy. For the past fifty years, dairy’s orthodoxy has been scale. This piece challenged it directly, examining how mid-size operations leveraging precision technology achieve profitability metrics that compete with operations several times their size in specific market conditions.
Now, to be clear: scale advantages are real. Recent USDA data shows larger operations generally achieve lower per-unit costs, and the correlation between size and overall profitability remains strong in aggregate. The article didn’t dispute that.
What the Article Actually Found
What it documented was more specific: certain 500-cow operations in the Upper Midwest using robotic milking, precision feeding, and intensive management protocols were achieving component yields and margin-per-cwt figures that challenged the assumption that they were simply waiting to be consolidated out of existence.
The key variable wasn’t size—it was technology adoption intensity and management focus. Operations that couldn’t compete on scale were competing on precision.
That’s a different argument than “small is better.” It’s an argument that technology can substitute for some—not all—of the scale advantages when management intensity matches the investment.
The response from readers was telling. At least a dozen producers emailed us about sharing this article with their lenders when justifying technology investments over expansion. One Wisconsin producer credited the piece with helping secure $180,000 in automation financing instead of a $2.4M expansion loan that would have stretched his operation thin.
If you’re running a mid-size operation and feeling pressure to “grow or go,” this article offers a more nuanced framework for evaluating your options.
The Human Stories: Hearts, Tragedy, and Triumph
Not every Editor’s Choice selection centers on breeding decisions and production records. Two articles this year reminded us why the human element matters—and earned their place through reader impact rather than genetic analysis.
Hearts of the Heartland
This Youth Profile documented young dairy farm girls battling extraordinary health challenges while their families remained committed to dairying. What struck readers wasn’t just the adversity—it was the community response. The article traced how neighboring operations stepped in during medical crises, how 4-H networks mobilized support, and how the fabric of rural dairy communities showed its strength when tested.
The piece generated more reader emails than any other youth profile we’ve published. Several readers mentioned sharing it with family members who questioned why they stayed in dairy when the economics got tough. It captured something data can’t measure—the emotional core of agricultural life, the values that keep operations running when spreadsheets say they shouldn’t.
From Tragedy to Triumph: Nico Bons
This profile showed how setbacks can catalyze the kind of focused intensity that produces greatness. Bons’s trajectory—tragedy, rebuilding, excellence—provided both inspiration and a practical framework for breeders facing their own obstacles.
The article documented specific decisions Bons made during his lowest points that positioned him for later success: doubling down on cow families he believed in when others suggested selling, maintaining classification standards when cutting corners would have been easier, and building relationships that paid dividends years later.
For anyone dealing with challenges right now—and honestly, between labor pressures, feed costs, and processor consolidation, who isn’t?—this piece offers more than motivation. It offers a model.
The Holstein Genetics War: What Every Producer Needs to Know
Some topics require going beyond surface-level reporting. The competing visions for Holstein breeding’s direction—the economic forces, policy implications, and philosophical tensions shaping the breed’s future—demanded exactly that treatment.
This article examined the battle lines between different approaches to genetic improvement: index-driven selection versus holistic breeding programs; concentration of elite genetics versus diversity; and short-term gains versus long-term sustainability. It named the tensions other publications dance around—including specific industry voices pushing concentration and the researchers warning against it.
Whether you’re navigating US component pricing shifts, EU Green Deal compliance costs, Canadian quota considerations, or NZ emissions regulations, the strategic questions this article raises apply across markets. The breed’s direction isn’t being set in a vacuum. Policy, economics, and genetic decisions interact in ways this piece helped readers understand.
The article generated exactly the kind of productive disagreement we aim for—readers with strong opinions engaging substantively rather than nodding along. When industry professionals argue thoughtfully about something we’ve written, that tells us we hit a nerve worth hitting.
If your genetics rep is pushing hard for one approach, this article gives you a framework for asking better questions and evaluating whether their recommendations align with your operation’s long-term interests.
The Controversial Canadian System That Could Save American Dairy
Trade policy isn’t sexy. We made it essential reading anyway.
By connecting Canada’s supply management debate to real-world implications for American producers, this article transformed dry policy discussion into a story about survival, fairness, and the future of family farming. It examined the evidence honestly—acknowledging both legitimate criticisms of supply management and the genuine problems it addresses that free-market systems struggle with.
The response was polarized. Some readers sent passionate disagreements, arguing that any government intervention distorts markets and punishes efficiency. Others thanked us for finally explaining a system they’d heard criticized but never understood—and pointed to the stability Canadian producers enjoy while American operations ride brutal price cycles.
Both responses tell us the same thing: this was journalism that mattered to people trying to understand their competitive environment.
Whether you think Canadian dairy policy is a model worth studying or a cautionary tale about protectionism, understanding how it actually works—rather than relying on political talking points from either side—makes you a better-informed decision maker.
Articles That Almost Made the List
A few pieces came close and deserve mention for readers looking to go deeper:
Bell’s Paradox: The Worst Best Bull in Holstein History examined a bull who excelled in production traits while transmitting significant type faults—challenging comfortable assumptions about what “best” even means in genetic evaluation. Strong engagement, genuine controversy, but slightly narrower application than our final selections.
The Robot Truth: 86% Satisfaction, 28% Profitability—Who’s Really Winning? found that robotic milking adopters reported high satisfaction rates, but far fewer achieved projected profitability targets within expected timeframes. If you’re considering automation investments, add this to your reading list before signing anything.
The Silent Genetic Squeeze documented inbreeding coefficients in the Holstein population rising steadily over recent decades, with specific data on haplotype frequency changes that affect fertility and calf survival. Important reading for anyone concerned about where genomic selection’s concentration is taking the breed.
The Bottom Line: Your 2026 Reading List
Looking at this collection, patterns emerge. We gravitate toward stories that challenge assumptions rather than reinforce them, connect historical decisions to present-day implications, humanize the industry without losing analytical rigor, and tackle uncomfortable topics when the evidence demands it.
You can read publications that confirm what you already believe, or you can read the ones that make you uncomfortable enough to improve. These ten articles fall in the second category. That’s why they earned Editor’s Choice.
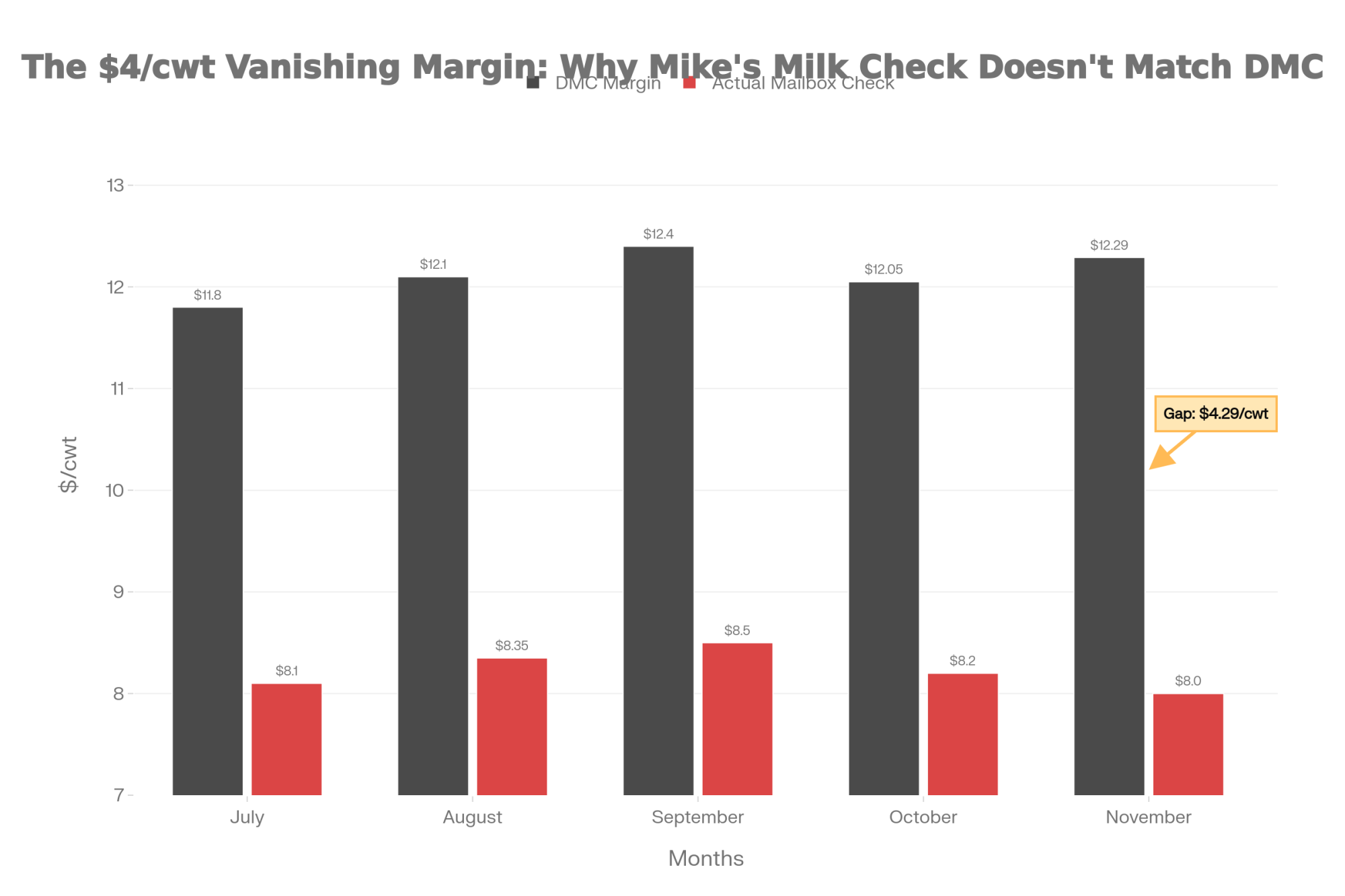
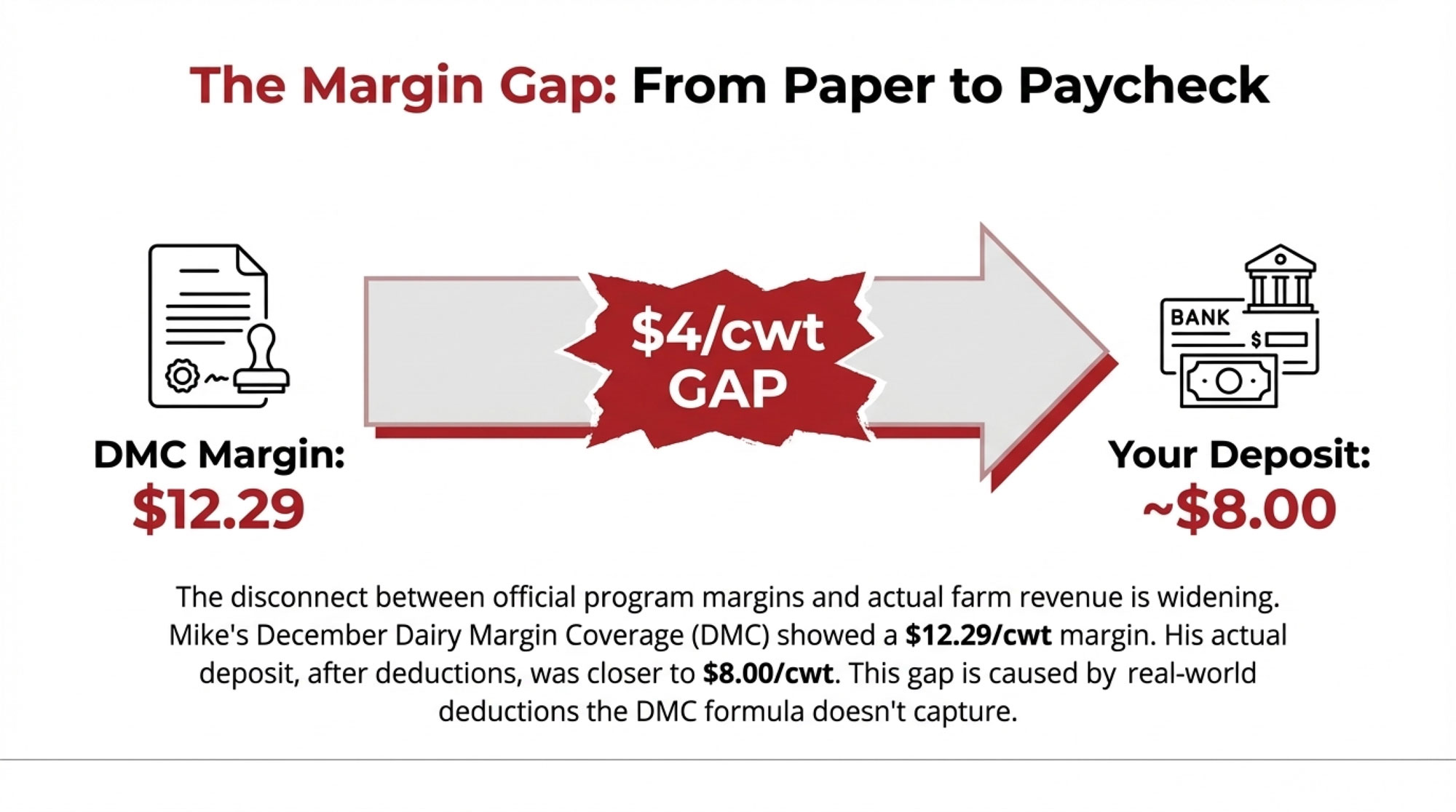
The conversations these articles started aren’t finished. Genomic selection keeps evolving—as the December 2025 proofs showed, with Genosource capturing 22 of the top 30 Net Merit positions and reshaping the competitive landscape overnight. The tension between consolidation and resilience intensifies. Component pricing shifts and processor relationships tighten. And the human stories—the triumphs, the setbacks, the stubborn persistence of people who believe in this industry—keep unfolding.
We’ll be here to cover them. Starting in January with our deep-dive into what the December 2025 proof run means for your spring matings—and why three bulls everyone’s talking about might not deserve the hype.
With data. With nuance. And with the same commitment to making you think rather than just nod along.
That’s what these ten articles delivered in 2025. That’s what we’re aiming for in 2026.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY:
‘We published 300 articles in 2025—these ten are the ones readers bookmarked, argued about, and shared with lenders and genetics reps months later. Inside: the $260,000 gamble that put one bull’s blood in every registered Holstein alive today, a bankruptcy that spawned three consecutive World Dairy Expo champions, and data showing tech-savvy 500-cow dairies beating mega-farms on margin-per-cwt. You’ll find Elevation’s $6,500/cow longevity advantage explained against his -$821 Net Merit—a $2,117 swing from today’s #1 bull representing sixty years of progress built on his foundation. Each piece delivers actionable breeding frameworks for 2026, not just history. One Wisconsin producer used our scale article to secure $180,000 in automation financing instead of a $2.4M expansion loan. Your competitors already read these twice—have you?
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!




















































![dairy farming, solar leases, milk yield, agrivoltaics, dairy profitability]](https://www.thebullvine.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/Whisk_89eec22d14.avif)