Understand the impact of the recent avian influenza outbreak in California’s dairy farms. Discover steps to protect your herd and ensure safety.
Summary: The detection of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) in three dairy herds in California’s Central Valley has led to immediate quarantine measures and heightened biosecurity protocols. While no human cases have been reported, health authorities emphasize the importance of protective equipment for dairy workers. The state’s milk supply remains safe for consumers, with pasteurization effectively neutralizing the virus. The California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) and the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) assure the public that the risk to human health is low, focusing their efforts on monitoring and assisting affected farms. The outbreak underscores the need for continued vigilance and preparedness among dairy farmers. For ongoing updates and resources, stakeholders must visit the CDFA’s official website.
- Immediate quarantine measures and enhanced biosecurity protocols are in effect for affected dairy farms.
- No human cases of HPAI have been reported in California linked to this outbreak.
- Health authorities stress the importance of protective equipment for dairy workers to prevent infection.
- California’s milk supply remains safe, with pasteurization effectively neutralizing the HPAI virus.
- CDFA and CDPH assure the public that the risk to human health is low.
- Affected farms receive continuous monitoring and assistance from state health authorities.
- Ongoing vigilance and preparedness are vital for dairy farmers to combat potential outbreaks.
- Stakeholders are advised to visit the CDFA’s official website for regular updates and resources.

Imagine the unsettling news that highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI), a virus typically associated with birds, has breached your dairy herd. This alarming reality has now struck three dairy farms in California’s Central Valley. CDFA Secretary Karen Ross, with her eloquence, reassures, “We have been ready for this possibility since earlier this year when HPAI cases were confirmed on dairy farms in other states. Our extensive experience with HPAI in poultry has equipped us to handle this issue, with a primary focus on workers and public health. The confirmed presence of HPAI in cows in these locations is a pivotal moment for dairy producers, necessitating swift and decisive action. The agricultural community, already grappling with economic pressures, now faces an even greater sense of urgency due to this looming threat. While rare, the occurrence of HPAI in cattle underscores the importance for dairy producers to be vigilant and prepared.”
A Wake-Up Call for Dairy Farmers: HPAI Detection in California’s Central Valley
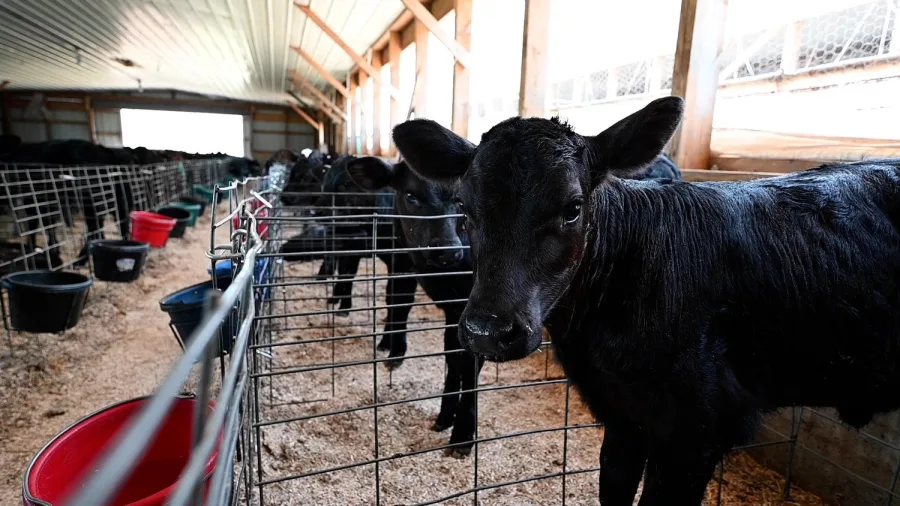
The highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) epidemic has substantially affected dairy producers in California. On August 25, 2024, cows at three dairies in the Central Valley started to exhibit HPAI symptoms. This is especially serious since it might jeopardize dairy production and worker safety.
The California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) quarantined the impacted farms. Authorities are working with local health agencies and the Centers for Disease Control (CDC) to undertake thorough testing and implement biosecurity measures. They also provide personal protection equipment (PPE) and assistance to concerned farmers and workers.
Urgent Quarantine Measures and Biosecurity Protocols: Keeping Dairy Safe Amid HPAI Outbreak
Detecting highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) in three Central Valley dairy herds has immediate and severe consequences for dairy producers. The afflicted farms are now under tight quarantine, with ill cows separated and treated on-site to prevent the virus from spreading. Despite these challenging conditions, the CDFA has promised that healthy cows may continue transporting milk since pasteurization successfully inactivates the virus.
Despite the HPAI epidemic, the milk supply is stable and unaffected. Dairy producers may continue to operate with confidence that their products are safe for customers. However, adherence to biosecurity standards is critical. Farmers must collaborate closely with veterinary authorities to maintain isolation zones and avoid cross-contamination of healthy and sick livestock. These early efforts are essential to ensure public health and the dairy industry’s economic viability.
Essential Safety Measures: Protecting Dairy Workers from HPAI
The recent identification of HPAI in dairy cows emphasizes the crucial significance of solid health and safety procedures. Experts advise adopting extensive personal protective equipment (PPE) to safeguard dairy workers. Masks, gloves, hats, face shields, and safety goggles are required while dealing with animals or materials contaminated with avian influenza. Adopting these precautionary measures protects the workers and helps to avoid future viral transmission.
The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) has encouraged safety precautions. Earlier this summer, CDPH provided safety equipment to dairy farm workers and anyone who handled raw dairy products. The campaign, which included slaughterhouse and commercial poultry farm workers, substantially influenced public health.
The CDPH continues to provide PPE assistance to farms with verified HPAI incidences. This endeavor is supported by a USDA grant, which provides financial help to growers who provide PPE to their workers. These materials are helpful to dairy producers during these difficult times.
Monitoring workers’ health is critical. Public health authorities collaborate with dairy owners to provide farm workers with the tools and information they need to preserve their health and safety. Regular evaluations and PPE are critical in reducing the risk of infection and maintaining a safe working environment. By putting workers’ health first, the sector protects its workforce and helps dairy operations remain stable throughout health emergencies.
Public Health Assurance: HPAI Poses Low Risk to Humans, Authorities Take Proactive Measures
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) have both said that the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) virus offers no significant public health risk. The danger to humans is modest, particularly affecting dairy workers who have direct contact with affected animals. CDPH, in partnership with the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) and local health agencies, is actively monitoring the situation. These agencies collaborate to provide timely clinical and public health responses, if necessary, and effective management and minimization of possible human exposure. Rest assured that the collaboration between these health agencies is intended to maintain strict safety and health regulations that protect both the public and dairy sector personnel.
Expert Voices on HPAI Preparedness: A Unified Front Against Emerging Threats
“We have been preparing for this possibility since earlier this year when HPAI detections were confirmed at dairy farms in other states,” Karen Ross, secretary of the CDFA, said. “Cheat vast experience with HPAI in poultry has provided us with adequate preparedness and expertise to handle this issue, with workers’ and public health being Cheat’s top concerns. Given the economic constraints they face in a volatile market, this is a difficult moment for our dairy farmers. Therefore, I want to tell them that we are handling this event with the greatest haste.”
Renowned virologist Rick Bright shared similar concerns: “The convergence of avian and human flu viruses poses a real threat as we approach the colder months.” We have carefully observed the situation and worked with several authorities to ensure that we are prepared to react quickly and efficiently.
These expert viewpoints show the collaborative efforts and thorough planning that underline the urgency with which authorities address the HPAI epidemic.
Understanding HPAI: The Ongoing Battle Against a Deadly Avian Threat
HPAI, or Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza, is a significant issue for wild and domestic bird populations. Since 2022, wild birds in North America have been infected with the H5N1 virus. These migratory birds disseminate the virus across areas, sometimes causing spillover occurrences in domestic poultry and animals such as cattle.
In terms of history, the United States has had multiple HPAI epidemics. Because of the virus’s high fatality rate in poultry, early detections in wild birds raised worries. Domestic chicken farms suffered severe consequences, necessitating extensive regulatory and biosecurity precautions. Quarantines, killing diseased birds, and strict flock monitoring are among the procedures used.
Federal and state authorities worked closely together to address this issue. The USDA and CDC are critical players in monitoring and response initiatives. They collaborate with state agencies such as the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA) to conduct regular testing and develop biosecurity measures to prevent and manage outbreaks.
Wild birds continue to be closely monitored as a main HPAI reservoir. Farmers, veterinarians, and public health authorities continue to install sophisticated biosecurity measures, especially in high-risk locations. These collaborative efforts aid in the early detection and mitigation of the virus, protecting both animal and public health.
Preventive Measures for Dairy Farmers: Practical Steps to Mitigate the Spread of HPAI
As a responsible dairy farmer, I know that the threat of HPAI demands your full attention and proactive measures. Here are essential strategies to safeguard your herd and farm against this potentially devastating virus:
Enhance Biosecurity Measures:
- Restrict Farm Access: Limit farm access to essential personnel only. Implement strict visitor protocols and maintain a visitor log.
- Sanitize Equipment and Vehicles: Clean and disinfect all farm equipment and vehicles before they enter and leave your property.
- Protective Gear: Ensure all workers wear appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including masks, gloves, and coveralls.
Conduct Regular Health Checks for Livestock:
- Monitor Symptoms: Train staff to recognize signs of illness in cattle, such as reduced milk production, lethargy, and respiratory issues.
- Health Screenings: Implement regular veterinary health check-ups to catch and address potential infections early.
Implement Rigorous Sanitation Practices:
- Disinfect Common Areas: Regularly clean and disinfect barns, feeding areas, and milking equipment.
- Maintain Clean Facilities: Clean and dry bedding to minimize bacteria and virus proliferation.
Isolate and Test New Animals:
- Quarantine New Arrivals: Isolate new animals for at least two weeks before integrating them into the herd. This helps to identify any potential illness before it can spread.
- Screen for Diseases: Conduct thorough health checks and diagnostic tests on new animals during quarantine.
By rigorously applying these preventive measures, you will protect your herd and contribute to the broader effort of controlling HPAI in the dairy industry. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and take proactive steps to secure the future of your farm.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can HPAI spread to other livestock?
HPAI typically affects birds, although it may sometimes spread to other species, including animals like cattle, under certain situations. While less prevalent, the virus may be transmitted by contaminated equipment, humans, or intimate contact with infected animals. Dairy producers should be cautious and follow strict biosecurity protocols to reduce cross-species transmission.
What should I do if I suspect my herd is infected?
If you suspect HPAI in your herd, notify your veterinarian and the California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA). Isolate any ill animals and increase biosecurity measures to prevent further spread. Quick action and coordination with authorities are critical for managing and controlling epidemics.
How can I apply for financial assistance or PPE grants?
Dairy producers may apply for financial assistance and personal protective equipment (PPE) subsidies from the US Department of Agriculture (USDA). These subsidies may help them pay the expenses of obtaining PPE, adopting biosecurity measures, and compensating for losses caused by disease outbreaks. To learn more about eligibility and application procedures, visit the USDA’s official website or contact your local USDA office.
Is the milk from infected cows safe to consume?
Yes, milk from diseased cows is safe to consume after pasteurization. Pasteurization efficiently kills the virus, and long-standing norms remove diseased cow milk from the supply chain. Dairy products, including pasteurized milk, continue to be safe for consumption.
What are the signs of HPAI in cattle?
Cattle with HPAI may exhibit reduced milk production, thicker, concentrated colostrum-like milk, decreased feed intake, atypical feces, lethargy, dehydration, and fever. If you see any of these signs, call your veterinarian and the CDFA immediately.
Where can I find more information about HPAI in livestock?
Dairy producers may get the most up-to-date information on HPAI in cattle by visiting the CDFA’s official website, especially the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) section. This website contains detailed information on monitoring, epidemic response, and preventative measures.
Resource Round-Up: USDA and CDPH Support for Dairy Farmers Navigating HPAI Challenges
Dairy producers, critical resources, and assistance can assist you during this difficult time. The USDA offers several initiatives to help distressed dairy farms. These include:
- Dairy Herd Status Program: This project offers critical information regarding your herd’s health status and guarantees that diseased animals are treated correctly.
- Financial Assistance: The USDA provides financial assistance for heat treatment and disposal of milk, veterinary charges, personal protective equipment (PPE), milk loss offset, biosecurity planning and execution, and shipping cost offset for H5N1 testing.
Effective HPAI management requires tight biosecurity precautions and suitable PPE. The California Department of Public Health (CDPH) has been crucial in supplying protective equipment. Earlier this summer, the CDPH funded a one-time personal protective equipment (PPE) delivery to dairy farm workers. They continue to support farmers with verified cases by providing further PPE distribution while supplies persist. Affected farmers could also use USDA programs to help personnel purchase PPE.
For more comprehensive guidance, you can consult the following resources:
- CDC Guidance for Employees and Employers
- Preventing Bird Flu Outbreak on Your Farm: Essential Actions for Dairy Farmers
- US Dairy Farmers’ Guide: Navigating Bird Flu Outbreak – Permits, Quarantines and Beyond
Stay informed and leverage these resources to protect your herd and your livelihood.
The Bottom Line
Discovering highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) in three Central Valley dairy cows has resulted in swift quarantine measures and cooperation efforts between local and national health authorities. Dairy workers are protected by essential safety measures, such as using personal protective equipment (PPE) and periodic health monitoring. Public health experts have guaranteed that the milk and dairy supply is safe since pasteurization efficiently inactivates the virus.
Dairy producers are asked to be attentive, keep updated on the latest developments, and regularly follow biosecurity rules to protect their cattle and personnel. Farmers may stay ahead of developing hazards by communicating regularly with veterinarians and health authorities.
Learn more:
- Preventing Bird Flu Outbreak on Your Farm: Essential Actions for Dairy Farmers
- Bird Flu Hits Michigan Dairy Herd—Farmers Brace for Impact
- US Dairy Farmers’ Guide: Navigating Bird Flu Outbreak – Permits, Quarantines and Beyond
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Bullvine Daily is your essential e-zine for staying ahead in the dairy industry. With over 30,000 subscribers, we bring you the week’s top news, helping you manage tasks efficiently. Stay informed about milk production, tech adoption, and more, so you can concentrate on your dairy operations.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!














![7733001[1]](https://www.thebullvine.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/05/77330011.jpg)







