Unlock dairy success with expert tips on nutrition and comfort. Boost productivity and profits. Are your cows thriving?
Did you know that improving nutrition and keeping cows comfortable can increase milk production by up to 20%? Every drop of milk counts in today’s fast-paced dairy industry. Nutrition and keeping cows comfortable are critical for increasing productivity and overall profitability on dairy farms. If you get these components correctly, you’ll have healthier cows and higher yields. However, achieving this balance can be challenging. Dairy producers face various issues, including shifting market demands and increased need to be sustainable while managing their finances. So, how can we navigate this complex scenario so that our herds and companies thrive?
As we delve into unlocking the secrets behind dairy profitability, it becomes crucial to highlight the potential returns various investments in nutrition and cow comfort can yield. Understanding these figures empowers farmers and paves the way for informed decision-making in fostering a thriving dairy environment.
| Investment | Type | ROI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| High-Quality Forage | Nutrition | 20% |
| Feed Efficiency Technologies | Nutrition | 30% |
| Comfort Bedding Systems | Cow Comfort | 15% |
| Ventilation and Cooling Systems | Cow Comfort | 25% |
| Automated Feeding Systems | Nutrition | 18% |
The Power of Nutrition: Elevating Dairy Success
Nutrition is essential in dairy production, affecting milk yields and herd health. Any competent dairy farmer will tell you that a healthy diet is more than simply food; it is the foundation of a profitable dairy operation. So, how can nutrition indeed increase milk production?
- Balanced Diets and High-Quality Forage: To maximize milk production, it’s crucial to craft balanced diets rich in high-quality forage. This is not just a theory but a practical strategy that can be implemented on your farm. Cows operate at their peak when fed a diet tailored to their nutritional needs. Providing cows with good pasture ensures they receive the necessary nutrition without harmful pollutants, significantly enhancing milk output and maintaining cow health. This is a tangible step you can take to improve your dairy operations.
- Importance of Fiber Digestibility: Remember to consider the importance of fiber digestibility! Fiber digestibility refers to the cow’s ability to efficiently break down and utilize the nutrients in their feed. Due to high fiber digestibility, cows can make the most of their feed, which increases output. According to the Journal of Dairy Science, making fodder easier to digest can increase dry matter intake and milk production by 2 to 3 pounds per cow daily. This statistic emphasizes the genuine benefits of paying attention to fiber quality in feed.
- Clean, Contaminant-Free Forages: In addition to what you offer your herd, it is essential to keep forages pure. This prevents health concerns from interfering with the milk supply. Mycotoxins, for example, can seriously disrupt cow milk production and potentially impact the herd’s overall health. Regular testing and proper storage of forages, such as alfalfa and clover, can keep things clean and prevent costly health issues in the future.
Dairy farms may increase milk production and keep operations running smoothly by incorporating these ideas into feeding techniques.
Fueling the Future: The Cow Comfort Revolution
Imagine a world where dairy cows thrive instead of just surviving. The key to this vision is keeping cows comfortable, crucial for boosting dairy production. Why is cow comfort so important? It’s simple: A stress-free cow is a productive cow. When cows are comfortable, they spend more energy producing milk than managing stress.
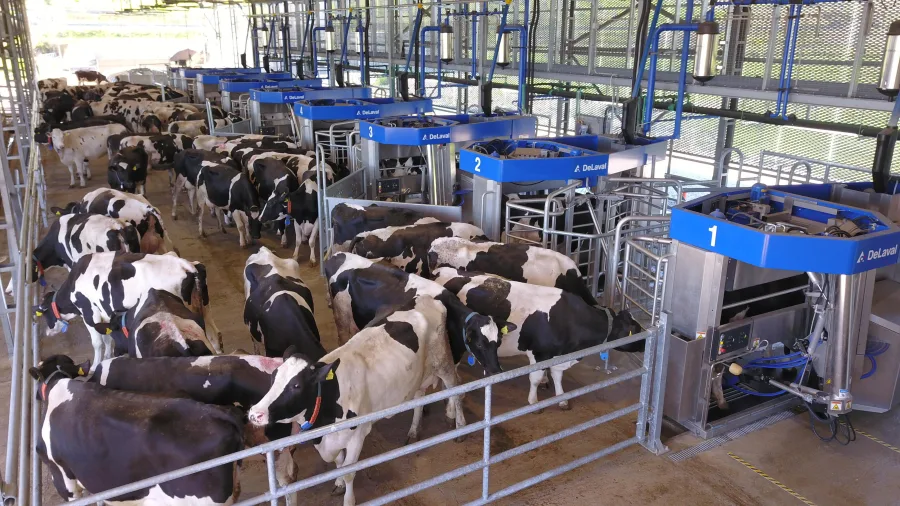
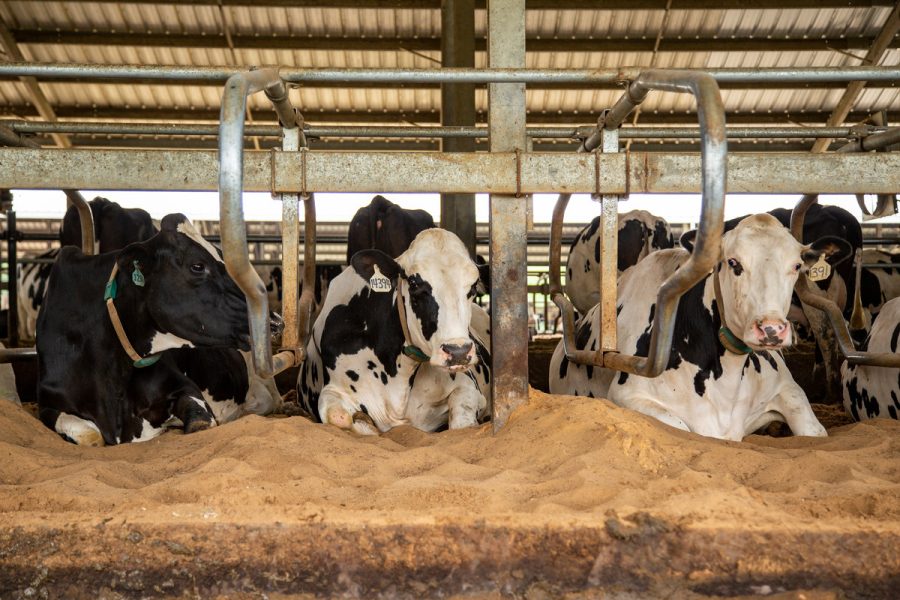
Space is vital. Like us, cows need room to relax, move, and behave naturally. Overcrowding leads to stress and competition, which hinders milk production. A well-structured barn that offers ample space encourages a peaceful environment among the herd. Features such as adjustable bedding, improved ventilation, and softer floors can prevent hoof issues, boosting cow health and milk output. Modern farms focus on reducing stress with better cow handling and humane practices. These improvements can lead to a productivity jump of 20%.
Dairy research shows that cows in top-notch conditions can increase milk production by up to 300% compared to less ideal settings. However, reaching these conditions requires effort, underscoring the importance of cow comfort for profitability. Dairy farmers face many challenges, from shifting productivity needs to sustainability and economic pressures. Prioritizing cow welfare by balancing nutrition, comfort, and sustainability can help farmers succeed in today’s competitive industry.
Smart Investments: The Key to Dairy Profitability and Sustainability
Today, money plays a significant role in dairy farmers’ success. Managing costs is vital for making a profit. Quality forage can make a huge difference. Farmers can save money on buying extra feed by investing in top-notch, clean forage. This cuts costs and leads to healthier cows and more milk.
But for this to work, you must also invest in cow comfort. Happy cows are productive cows. Therefore, spending on good barn designs, cooling systems, and plenty of space is essential. These factors boost cow health and milk production.
Dairy farmers are learning to manage the economy’s highs and lows by making smart investments. They must weigh the initial costs of making cows comfortable and improving forage against the potential earnings. Remember, every dollar spent on better cow welfare and feed quality leads to a more profitable and sustainable dairy farm.
Embrace Innovation: Harnessing Technology for Dairy Excellence
Technology is making dairy farming easier and better for the environment. Farmers now use tools to monitor cow health and eating habits closely. By noticing data changes, they can detect health issues before they become serious. That’s what modern tech can do!
Great software helps create diet plans and feeding methods tailored to your needs. These tools manage info on feed types and costs, giving you the best nutrition without spending too much. This boosts milk production and maintains herd health, increasing profits.
Tech is growing fast, so staying updated is necessary. Farmers who use new technology have an edge, making better products and lowering their carbon footprint. Embracing new ideas in this changing world helps farmers succeed and meet efficiency and environmental goals.
Bridging the Gap: Aligning Dairy Farming Realities with Public Perceptions
Many people think dairy farming is just about cows relaxing in fields. But running a productive and eco-friendly farm isn’t so simple. The challenge is to use green farming methods while maintaining high production. Efficient farms can lower emissions per milk produced, but that doesn’t always match what consumers think farms should look like.
Dairy farmers need to balance being green and running their farms well. Investing in energy-saving tools and better nutrition is essential, but it can be expensive. With tight budgets, farmers might struggle without clear financial help.
Open about farming practices can help close the gap between people’s thoughts and the truth. Farmers should share how they use new technology and methods to reduce emissions. Hosting farm visits, sharing learning materials, and collaborating with green groups can improve understanding and trust. The dairy industry’s future relies on balancing green practices with making a profit, allowing farmers to meet public expectations and stay successful in the long run.
Empowering Your Workforce: The Backbone of Dairy Productivity
The success of today’s dairy business hinges on a skilled workforce. Is your team equipped with the knowledge to ensure that cows are comfortable and well-fed? Understanding cow behavior and nutrition can significantly boost farm productivity. When employees manage cattle calmly and efficiently, cows are more likely to thrive and produce more milk.
Nutritional expertise in your team is invaluable. Well-trained staff can precisely follow feeding protocols, producing better milk yield and quality. Regular training in new techniques and technologies prepares your crew to enhance farm outcomes. This ongoing learning is crucial for staying competitive in the dairy industry.
Continuous development creates a thriving work culture that benefits animals and boosts your profitability. Investing in your team sets a foundation for sustained growth and success in your dairy operations. Are you ready to elevate your farm’s potential?
The Bottom Line
Our discussion highlighted the importance of nutrition and cow comfort in boosting dairy farm productivity. Ensuring high-quality forage, innovative feeding management, and stress-free environments are key to increasing milk yield and achieving economic and environmental sustainability. By using technology and enhancing management practices, dairy farmers can tackle market challenges and meet customer expectations. Consider how you might enhance your farm’s nutrition and cow comfort to ensure long-term success in modern dairy farming.
Key Takeaways:
- Nutrition and cow comfort are crucial for maximizing dairy productivity, with a focus on both fed diets and managing stress-free environments.
- Improving forage quality and controlling contamination can reduce external feed costs and increase farm profitability.
- Innovations in technology and management practices allow for more accurate monitoring and feeding, enhancing cow health and production efficiency.
- The dairy industry faces a conflict between sustainable practices and economic constraints, with a need for balanced integration.
- Employee training and understanding cow behavior contribute significantly to operational success and animal welfare.
- Aligning dairy farming practices with public expectations while maintaining efficiency remains a key challenge.
- Continued research and development are essential for evolving feeding strategies and achieving optimal dairy outcomes.
Summary:
Unlocking dairy success hinges on nutrition and cow comfort, critical factors for elevating dairy productivity. Dairy producers. They can realize substantial gains in milk production, fat yield, protein content, high-quality forage, and stress-free living conditions. Effective management strategies, innovative technologies, and comprehensive approaches are crucial for sustainable and profitable dairy farming. This involves blending cost-effective feed ingredients, understanding cow comfort for stress reduction, and integrating advanced systems that bridge farm realities with public expectations. Addressing challenges like productivity demands, market pressures, and sustainability requires balancing nutrition, comfort, and economic constraints. Producers can enhance operations by prioritizing high-quality forage, proper storage, and intelligent investments in foraging while minimizing off-farm feed costs. Technology, including real-time monitoring tools, customizes diet plans for dairy excellence. Farmers can further bridge the sustainability gap by being transparent about cutting-edge practices and emphasizing technological and eco-friendly approaches. Empowering the workforce through cow handling and nutrition management training is vital for maintaining productivity and staying updated with industry advancements.
Learn more:
- Transition Cow Facilities: The Golden Investment for Dairy Farm Profitability
- Maximize Your Dairy Farm’s Profit: Insights from the 2021 Nutrient Requirements Report
- Boosting Dairy Farm Profits: 7 Effective Strategies to Enhance Cash Flow
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Bullvine Daily is your essential e-zine for staying ahead in the dairy industry. With over 30,000 subscribers, we bring you the week’s top news, helping you manage tasks efficiently. Stay informed about milk production, tech adoption, and more, so you can concentrate on your dairy operations.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!