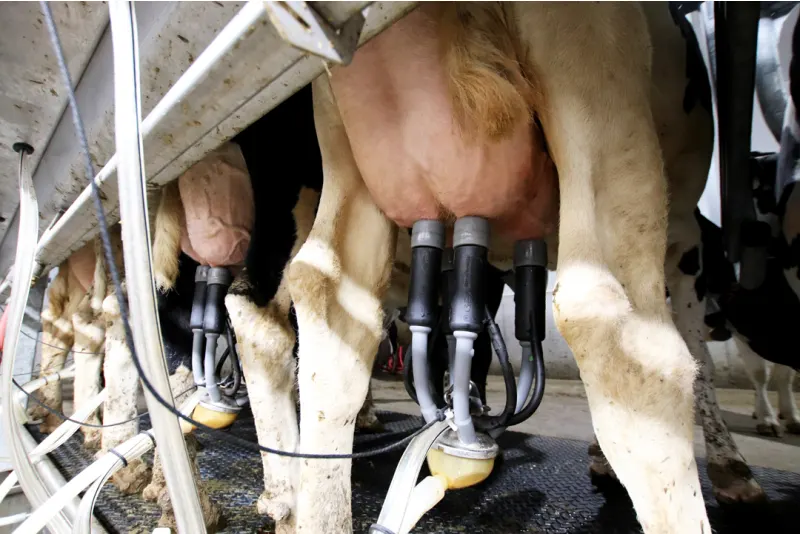
Struggling with flies and heat in the milking parlor? Discover effective strategies to keep your cows comfortable and productive during the summer months.

The heat of summer transforms the milking parlor into a battleground of discomfort. Temperatures can reach near 100 degrees Fahrenheit, making it unbearable for both cows and farmers. The eight stanchions, filled with large Holsteins, amplify the sweltering conditions, causing cows to become grumpy and disrupting their usual demeanor. This affects their well-being and challenges farmers striving to maintain productivity and animal health. As readers, your role in addressing these summer challenges is crucial for efficient milk production, cow comfort, and farm profitability. Finding practical solutions is necessary for the sustainability and success of dairy farming.
High Temperatures: A Multi-faceted Challenge for Dairy Cows
The impacts of high temperatures on dairy cows are multifaceted, reaching well beyond physical discomfort. Physiologically, cows are highly susceptible to heat stress, absorbing more heat than they can dissipate. This leads to elevated heart and respiratory rates as they try to cool down through increased panting and sweating. Their feed intake also drops, lowering energy levels and reducing milk production.
Behaviorally, cows seek shaded or cooler areas, become more agitated, and show less activity. This discomfort is well-documented and significantly impacts their health and productivity. A stressed cow produces less milk, and the quality can suffer with higher somatic cell counts, indicating mastitis—a painful udder infection. Heat stress also weakens their immune function, making them more prone to diseases and illnesses.
Effective management practices are crucial to mitigate these effects. Providing shade, ensuring access to cool, clean water, and using cooling systems like fans and misters can significantly reduce heat stress. Farmers should monitor feed intake and adjust nutritional plans to ensure cows receive enough energy despite reduced appetites. These measures can mitigate the adverse effects of high temperatures on cow behavior and milk production, supporting both the animals’ health and the viability of dairy operations. With these practices, success in dairy farming is not just a possibility but a potential reality.
Robust Heat Management Strategies to Maintain Cow Comfort and Productivity
The escalating heat of summer demands effective heat management to ensure cow comfort and productivity. Fans are crucial, strategically placed in the milking parlor and resting areas to create continuous airflow that dissipates body heat. This reduces barn temperature and stress on cows, allowing them to stay healthy and productive.
Another effective technique involves misters. These systems spray a fine mist over the cows, cooling them through evaporation. Combined with fans, the cooling effect is amplified, providing relief during the hottest parts of the day.
Shade structures are also vital. Whether from natural trees or constructed shelters, shade provides a refuge from direct sunlight, preventing heat stress and maintaining a comfortable environment.
Fans, misters, and shade structures form a comprehensive approach to heat management. These methods ensure that cows remain content and productive, even during summer’s peak.
Fly Infestations: A Persistent and Pervasive Issue on Dairy Farms
Fly infestations during the summer are persistent for dairy farms, driven by warmth and humidity, which serve as ideal breeding grounds. Stable flies, horn flies, and face flies thrive in decomposing organic matter and cattle dung, causing nonstop discomfort and stress for cows. This results in decreased milk production as cows, driven to irritation, display restless behaviors and frequent tail flicks to fend off these pests.
The fight against flies demands a multifaceted approach, balancing immediate measures like misting fly sprays and bug zappers with longer-term treatments. Organic dairy producers face additional challenges due to limited fly control options that meet organic standards. Strict sanitation to eliminate breeding sites is essential, but maintaining these practices adds to the labor burden.
Innovative strategies for pastured cattle, such as using low-hanging dust bags or oilers, help treat animals as they move. Despite these efforts, farmers endure a relentless struggle, with mixed results, until cooler winter months provide some relief. The resilience of fly populations ensures that dairy farmers remain engaged in a continuous battle to protect their herds and sustain productivity.
Efficient Management of Fly Populations: A Multifaceted Approach
Effectively managing fly populations in dairy farms demands a multifaceted approach, blending chemical, natural, and technological methods. Chemical sprays are a direct option, with knockdown sprays for immediate relief and residual sprays for longer-term protection. Correct application is vital to maximize their effectiveness and minimize adverse impacts on livestock and the environment.
For a more eco-friendly alternative, natural repellents use botanical extracts and essential oils to deter flies. Though less immediate, they are instrumental in organic farming, where pesticide use is restricted. Bug zappers can also help by using ultraviolet light and electric grids to attract and kill flies. Their strategic placement around the milking parlor boosts their effectiveness and enhances cow comfort.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an increasingly popular tactic that combines various control methods for sustainable fly management. IPM focuses on sanitation to remove breeding grounds, biological controls like parasitoids and predators to reduce larvae, and mechanical controls such as fly traps and sticky tapes. This holistic approachreduces fly populations and limits chemical reliance, supporting long-term environmental and economic sustainability.
Each method has pros and cons, so dairy farmers must evaluate their needs. Farmers can effectively manage fly infestations and maintain a healthier, more productive dairy operation by using a tailored combination of these techniques.
Stepping into the Milking Parlor: Navigating the Heat and Maintaining Operations
Stepping into the milking parlor during peak summer reveals an intense heat and bustling activity as the team gears up for the day. The routine starts at dawn to capitalize on cooler temperatures, which is vital for cows and staff. Each day begins with meticulous cleaning, ensuring all milking equipment is sanitized to prevent bacterial contamination. Floors and walls, often laden with stray feed and manure, are scrubbed clean.
Cow handling during these hot months requires patience and skill. Cows, already irritable from the heat, are moved calmly into stanchions to minimize stress. Handlers use soothing voices and gentle prods to guide them. Each cow’s udder is inspected before the milking machines are attached to ensure comfort and optimal milk flow.
The oppressive heat necessitates regular checks on milking equipment, including vacuum pumps, pulsation systems, and cooling mechanisms. Fans and ventilation systems are cleaned and serviced to provide airflow, reducing heat stress for cows and staff. Misting systems might also be employed to maintain a bearable temperature.
Managing the fly population is a constant battle. Fly traps and repellents are strategically positioned around the parlor and holding areas. Farmers always seek innovative solutions to keep the fly menace at bay, ensuring cow comfort and steady milk production despite the summer heat.
Innovative Solutions from the Field: Farmer Success Stories
Numerous success stories have emerged throughout my discussions with dairy farmers, showcasing how resilience and ingenuity can overcome the challenges of summer heat and fly infestations. Tracey, for instance, improved cow comfort and boosted milk production by incorporating additional fans and a misting system in her milking parlor. Erickson’s experience underscores the importance of proactive heat management through technology and infrastructure adjustments.
A seasoned dairy farmer, John recounted his battle with fly populations using strict sanitation protocols and knockdown and residual sprays. He drastically reduced fly breeding grounds by promptly removing manure and organic matter. His meticulous adherence to product application instructions enhanced the effectiveness of his fly control plan.
Moreover, an organic dairy producer, Linda, highlighted the unique challenges of adhering to organic practices. With fewer chemical options, she relied on physical barriers and biological controls. Dust bags and oilers at pasture entry points effectively mitigated fly issues, demonstrating the potential of alternative methods in an organic fly management plan while maintaining animal welfare standards.
The Bottom Line
As summer’s sweltering days press on, addressing issues in the milking parlor is essential. The relentless heat, nearing 100 degrees, and persistent fly infestations demand robust strategies. Effective heat management—fans, misting systems, and proper ventilation—is crucial for cow comfort and operational efficiency. Equally important is combating fly populations with misting sprays, bug zappers, and insecticides. Weekly applications can significantly reduce flies, thus improving livestock health and productivity. Perseverance through these trials embodies the resilience of dairy farming. Implementing well-designed management plans based on successful practices helps navigate extreme weather. As seasons change, dairy producers must adopt these strategies, maintain vigilance, and seek out advancements in farm management. This collective effort boosts productivity and strengthens the bond between farmers and their animals, allowing both to thrive despite challenging conditions.
Key Takeaways:
- Summer heat significantly impacts cow comfort and behavior, making them grumpy and harder to manage in the milking parlor.
- Fly infestations pose a persistent challenge, causing stress and discomfort to cows, which affects their productivity.
- Effective fly management requires a multifaceted approach including misting sprays, bug zappers, fans, and new treatment methods.
- Even gentle cows can become unpredictable when disturbed by flies, emphasizing the need for constant vigilance and fly control.
- Proactive fly control and consistent application of treatment products can lead to improved milk production and financial savings for dairy farmers.
- Farmers must balance the extreme heat of summer and cold of winter with strategies to maintain cow comfort and productivity.
Summary:
Summer heat in dairy farms can cause cows to become grumpy and disrupt their behavior, affecting their well-being and posing challenges for farmers. High temperatures are highly susceptible to heat stress, leading to elevated heart and respiratory rates, decreased feed intake, and reduced milk production. Cows seek shaded or cooler areas, become more agitated, and show less activity, significantly impacting their health and productivity. Heat stress weakens their immune function, making them more prone to diseases and illnesses. Effective management practices, such as providing shade, access to cool water, and using cooling systems, are crucial to mitigate these effects. Farmers should monitor feed intake and adjust nutritional plans to ensure cows receive enough energy despite reduced appetites. Robust heat management strategies, such as fans, misters, and shade structures, are essential to maintain cow comfort and productivity during the escalating heat of summer.