Learn how 3-NOP and tannins can boost milk production and cut emissions. Ready to improve your herd’s performance? Read more.
Summary: The dairy industry is struggling to balance high milk output with sustainability as regulatory organizations impose stricter limits on methane emissions and nitrogen excretion. 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) is an innovative feed additive that lowers methane emissions by blocking an enzyme required for methane synthesis in microorganisms, thus improving cow digestion and energy utilization for milk production. Research indicates that cows on a 3-NOP-supplemented diet may reduce methane emissions by 16% to 17% while maintaining milk output. The combination of 3-NOP and tannins has the potential to significantly enhance the dairy industry’s feed efficiency and methane emission reduction efforts.
- 3-NOP supplementation led to a significant reduction in methane emissions by 16-17%.
- Brown Swiss and Holstein Friesian cows responded differently to 3-NOP, with Holsteins showing a more significant reduction in methane production.
- Tannins did not affect milk yield but reduced urinary nitrogen while increasing fecal nitrogen, suggesting better nitrogen utilization.
- No adverse effects on feed efficiency were observed for 3-NOP or tannin treatments.
- Combined supplementation of 3-NOP and tannins could offer dual methane mitigation benefits and improved nitrogen management.
- The study highlights the necessity for further research to optimize additive use and understand breed-specific responses.

Are you seeking solutions to increase dairy farm output while lowering hazardous emissions? In today’s world, dairy producers must balance growing milk output with reducing their environmental impact. It’s a delicate balance, but the current study on 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP; Bovaer ®10) and tannin extract (Acacia mearnsii) holds great promise for those prepared to try new things. Imagine the potential of simultaneously improving breastfeeding performance, reducing methane emissions, and optimizing nitrogen utilization. “The dairy industry is at a watershed moment where sustainability and productivity must coexist,” explains Dr. Michael Niu, chief researcher at the ETH Zürich Department of Environmental Systems Science. Ready to embrace a more hopeful future for your farm’s production and environmental impact? Let’s dig in.
Balancing Act: Achieving High Milk Yields with Sustainable Practices in Modern Dairy Farming
One of the most challenging difficulties confronting dairy producers today is reconciling high milk output with the need for sustainability. It’s no longer simply about how much milk your herd can produce; the environmental impact of your enterprise is being closely scrutinized. Regulatory organizations enforce more muscular limitations for methane emissions and nitrogen excretion, encouraging farmers to adopt more environmentally friendly techniques. Meanwhile, customer demand for ecologically friendly dairy products is increasing, placing more pressure on farmers to innovate. The time to strike this balance is now, crucial not just for regulatory compliance and market competitiveness but also for the dairy industry’s long-term survival.
What is 3-NOP?
3-Nitrooxypropanol, or 3-NOP, is an innovative feed additive used in dairy production to reduce methane emissions. But what does it accomplish, and why should you care? This additive, along with tannin extract, holds the potential to revolutionize dairy farming, reducing emissions and improving performance. It’s a game-changer, and it’s time to get on board.
When cows digest food, microorganisms in their rumen create methane, a potent greenhouse gas. 3-NOP comes into play here. It acts by blocking an enzyme required for methane synthesis in these microorganisms. To put it simply, 3-NOP reduces the effectiveness of methane-producing organisms.
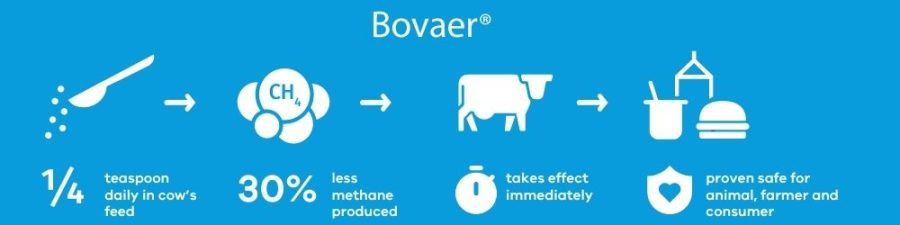
Let us now discuss the positives. Reducing methane emissions benefits both the environment and your farm. Lower methane generation improves the overall efficiency of the cow’s digestive process, allowing more of the feed’s energy to flow into milk production instead of being wasted as gas. According to research, cows fed a 3-NOP-supplemented diet may lower methane emissions by 16% to 17% while maintaining milk output. This is not only excellent news for the environment, but it is also a reassuringly cost-effective solution. It may help you enhance the sustainability of your agricultural methods without breaking the bank.
Unlocking the Power of Tannins: A Game Changer for Dairy Farming
Let’s discuss tannins, especially the extract from Acacia mearnsii. This extract has received a lot of interest in dairy farming because of its many advantages. Tannins are naturally occurring chemicals that bind and precipitate proteins. In dairy production, they are critical in nitrogen control.
One of the most noticeable impacts of tannins is their influence on nitrogen partitioning. When cows eat feed containing tannins, these chemicals may bind to proteins in their diet. This interaction lowers protein breakdown in the rumen while shifting nitrogen excretion from pee to feces. As a consequence, urinary nitrogen excretion has decreased by around 23.5%. This adjustment benefits the environment by reducing nitrogen’s contribution to groundwater pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Additionally, tannins in the diet have been shown to improve milk composition. Tannins, in particular, have been linked to higher levels of milk-accurate protein content and, in certain circumstances, yield. This not only benefits dairy producers but also meets consumer demand for high-protein dairy products. Furthermore, by enhancing nitrogen consumption inside the cow, tannins help to promote more sustainable and effective dairy production operations. This potential for improved milk quality should make you feel optimistic about the future of your product.
The ETH Zürich Study: Harnessing 3-NOP and Tannins for Optimal Dairy Cows Performance and Sustainability
The researchers at ETH Zürich investigated how the combination of 3-nitrooxypropanol (3-NOP) and Acacia mearnsii tannin extract (TAN) impacts lactational performance, methane emissions, and nitrogen partitioning in Brown Swiss and Holstein Friesian cattle. The experiment included sixteen cows, split evenly between Brown Swiss and Holstein Friesian breeds. Researchers used a split-plot design, dividing cows into a repeated 4 × 4 Latin square with a 2 x 2 factorial design across four 24-day periods.
Cows were fed four diets: a baseline total mixed ration (TMR), TMR with 3-NOP, TMR with TAN, and TMR with both 3-NOP and TAN. Milk output, methane emissions, and nitrogen excretion were among the measurements taken. The study found that TAN lowered milk urea nitrogen and urinary nitrogen without affecting milk output, but 3-NOP substantially reduced methane emissions across diets. Although no significant interaction between 3-NOP and TAN was found for any variable, the combination supplementation showed potential methane reduction and nitrogen management advantages.
Three Key Takeaways: 3-NOP, Tannins, and Their Synergy in Dairy Farming
The research presents three key results. First, 3-NOP decreased methane emissions by 16-17%, demonstrating its promise as a methane mitigator. Second, tannins reduced MUN concentration and urinary nitrogen by 23.5% without affecting milk output or efficiency. Finally, although there was no significant interaction between 3-NOP and tannins, their combination supplementation may provide a potential for methane reduction and enhanced nitrogen management in dairy cows.
The Breed Factor: Unearthing Varied Methane Reductions in Holstein Friesian vs. Brown Swiss Cows
One of the most notable findings when investigating breed-specific impacts is the considerable difference in methane reduction between Holstein Friesian (HF) and Brown Swiss (BS) cows. The research found that methane emissions were significantly reduced in HF cows, with a 22% drop compared to a 13% reduction in BS cows. This divergence highlights the need to study breed-specific responses to nutritional treatments such as 3-NOP.
Why does this variation exist across breeds? While the research provides valuable information, it also raises essential problems requiring additional investigation. Physiological variations, digestive efficiency, and hereditary factors might all influence these results.
More study is needed to determine the underlying processes governing these breed-specific responses. This allows us to adapt mitigation methods better, ensuring that all breeds gain the most from these interventions. As we aim for sustainability in dairy farming, understanding and maximizing breed-specific impacts becomes more critical.
Practical Steps to Embrace 3-NOP and Tannins in Your Dairy Farm
When contemplating using 3-NOP and tannin supplements in your dairy operations, practical actions may help you get the most significant outcomes. Consult a livestock nutritionist to determine the appropriate dose and mix for your herd’s requirements. 3-NOP at 60 mg/kg DM has been demonstrated to be helpful, whereas tannins may be injected at 3% DM. However, these numbers may need to be adjusted depending on your cows’ nutritional needs and current feed mix.
- Integration into Existing Feeding Regimens:
Incorporating these vitamins into your cows’ meals may be simple. To ensure equitable distribution, you may include 3-NOP straight into total mixed rations (TMR). Consider tannins from natural sources, such as Acacia mearnsii extract, which may be added to the diet. Ensure that the supplements are well-mixed to prevent selective feeding. - Monitoring and Adjustments:
After you’ve introduced these vitamins, keep a watchful eye on your cows. Monitor feed intake, milk output, and general health. To determine the advantages, monitor methane emissions and nitrogen excretion. Use essential, accessible tools or work with academics for more sophisticated analysis. - Potential Challenges and Solutions:
One problem may be the initial expense of incorporating supplements into your food routine. To mitigate this, the supplements should be introduced gradually, and the cost-benefit evaluated over time. Another possible concern is the heterogeneity in methane reduction among breeds. Address this by customizing dosages to breed-specific responses, beginning with the suggested quantities and modifying as data is gathered.
To summarize, including 3-NOP and tannins in your dairy business with appropriate planning and monitoring may result in long-term improvements. Despite the early obstacles, the potential for increased feed efficiency and lower methane emissions makes these supplements worthwhile. Consult with specialists, begin with trial stages, and keep adjusting for the best outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are 3-NOP and tannins, exactly?
3-NOP, or 3-Nitrooxypropanol, is a feed additive that decreases methane emissions from cows by blocking a critical methane-producing enzyme. Tannins, especially those derived from Acacia mearnsii, are plant chemicals that increase protein consumption in cow diets by binding to proteins and other nutrients in the rumen.
Are 3-NOP and tannins safe for my cows?
Both 3-NOP and tannins are safe when used in the prescribed dosages. Extensive research, including a study by ETH Zürich, shows the safety and usefulness of these supplements in lowering methane emissions and improving nitrogen utilization while preserving milk supply.
Will these additives affect my cows’ milk production?
No substantial detrimental influence on milk production has been detected. According to the research, tannin-fed cows produce the same amount of milk, possibly improving the accurate protein percentage. 3-NOP aims to reduce methane emissions, with no observed negative impacts on milk yields.
How much can I expect methane emissions to decrease?
The research found that 3-NOP may cut methane emissions by 16% to 17%. Further decrease varies by breed, with Holstein Friesian cows exhibiting a 22% drop and Brown Swiss cows showing a 13% reduction. The combination of 3NOP with tannins provides additional environmental advantages.
What about other environmental impacts?
Tannins reduce methane emissions while decreasing urinary nitrogen excretion by 23.5%, which may help reduce nitrogen pollution in the environment. This dual advantage contributes to more sustainable dairy production operations.
How do I integrate these additives into my cows’ diet?
The study recommends adding 60 mg of 3-NOP per kg of dry matter (DM) and 3% tannin extract by DM to the total mixed ration (TMR). Appropriate dose and diet formulation are critical for the best outcomes. Consultation with a nutritionist or veterinarian may help you adjust these supplements to your herd’s requirements.
Are there cost implications?
While the initial costs of acquiring these additives may be more significant, the long-term advantages, such as increased sustainability, improved nitrogen usage, and less environmental effect, often surpass the expenses. The improved operational efficiency and possibility for premium market positioning may potentially offer a financial offset.
Where can I source 3-NOP and tannin extracts?
These chemicals are available from specialist agricultural suppliers and nutritional firms. Use high-quality, research-backed goods to guarantee safety and effectiveness. Consulting with industry professionals might also help you locate trustworthy suppliers.
Future Research: Unveiling Untapped Potentials and Answering Pressing Questions
These results represent a big step toward sustainable dairy production but raise several issues for further study. One crucial need is to investigate the long-term effects of 3-NOP and tannin supplementation on cow health and production in different dairy breeds. While the study found differences between Holstein Friesian and Brown Swiss cows, further research might help determine the ideal breeds or genetic lines that respond well to these supplements.
Furthermore, understanding the processes driving differential methane decrease is critical. Why do Holstein Friesian cows produce less methane than Brown Swiss cows? Answering this question might lead to more focused and effective methane mitigation methods.
Another promising area for future study is determining the economic sustainability of broad deployment. While environmental advantages are vital, dairy producers must understand the costs and possible financial gains. Studies assessing cost-effectiveness and environmental benefits will be critical in building a compelling case for adoption.
Furthermore, combining 3-NOP and tannins with additional dietary supplements might provide even higher effects. Could there be a synergistic impact with other methane inhibitors or feed efficiency increases? These are questions that need investigation.
In the long run, combining 3-NOP and tannins might transform dairy production, making it more sustainable while maintaining productivity. Farmers who keep aware and adaptive will be at the vanguard of this shift, possibly benefiting both economically and environmentally.
Staying up to speed on new research and industry advancements is critical as we anticipate future investigations. Participating in the future of dairy farming has the potential to impact the industry significantly.
The Bottom Line
The combined use of 3-NOP and tannins represents a substantial advancement in dairy production. Using these supplements, you may reduce methane emissions by up to 17%, increase nitrogen usage, and refine milk quality indicators. Such advancements boost your herd’s production while promoting a more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural method.
Consider how 3-NOP and tannins might improve your dairy business. Are you prepared to move toward a more sustainable dairy farm?