How can U.S. dairy farmers benefit from Mexico’s rising cheese demand? Will you take advantage of this chance to supply American cheese?
Summary:
Cheese consumption in Mexico is rising, significantly driven by imports from the United States due to domestic demand and a preference for diverse cheese varieties. Mexico is expected to see a 4% increase in cheese consumption by 2024, with an 85% reliance on U.S. imports, prevalent in pizzas with shredded cheeses. This trend offers substantial opportunities for U.S. cheesemakers, bolstered by strategic trade policies enhancing economic collaboration between the two nations. The growing export market prompts innovative farming techniques and investments in higher-quality milk production. U.S. dairy farmers can benefit by forming strategic alliances with Mexican distributors and retailers, conducting joint marketing campaigns, and investing in supply chain efficiencies.
Key Takeaways:
- Mexico’s cheese consumption is rapidly increasing, with expectations of a 4% rise next year.
- The U.S. remains the leading cheese supplier to Mexico, fulfilling over 85% of Mexico’s cheese imports in the first half of this year.
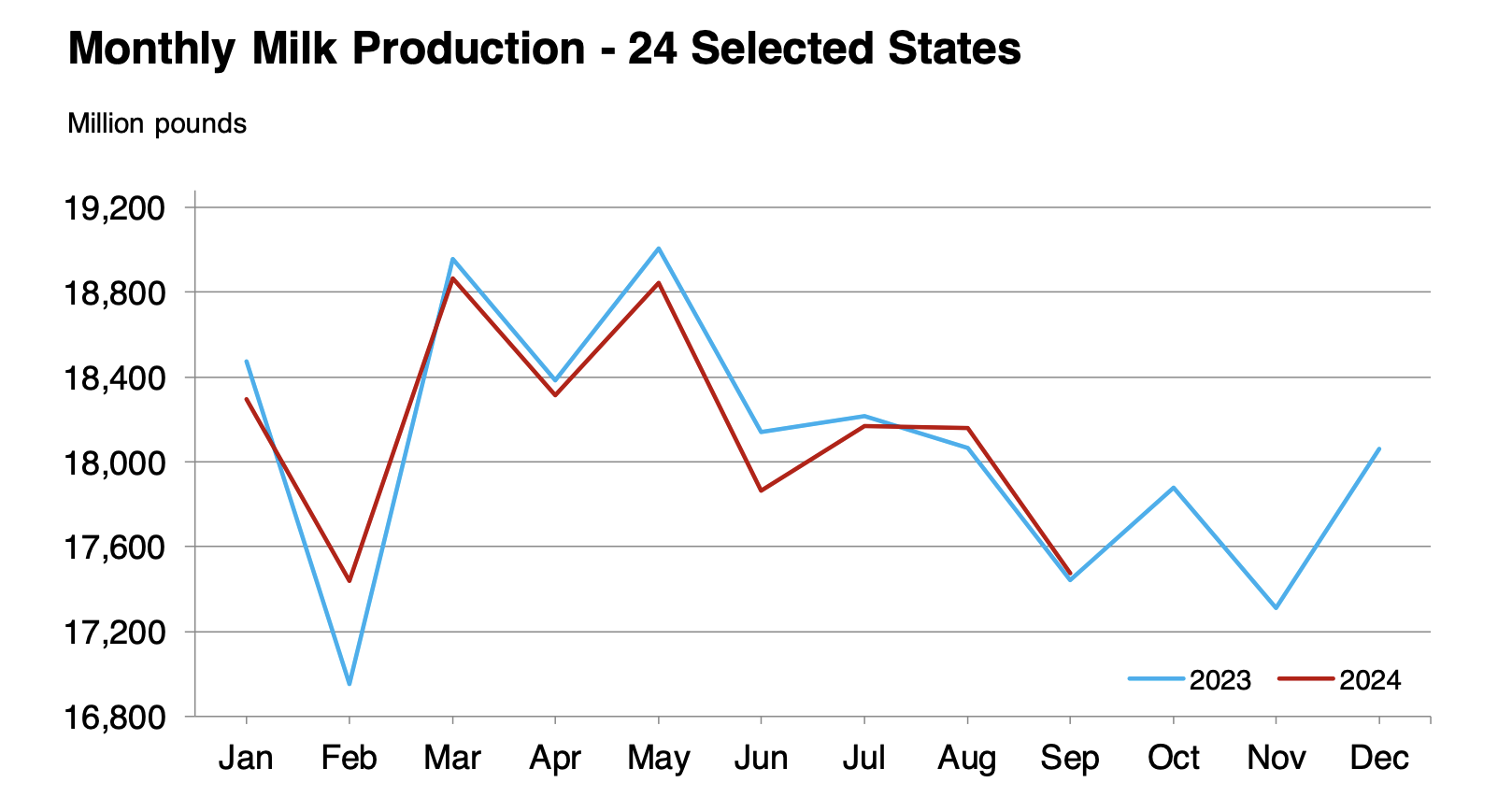
- Despite rising local milk production, Mexico still relies heavily on cheese imports to meet domestic demand.
- U.S. cheesemakers can capitalize on Mexico’s unmet demand with strategic trade policies.
- The versatility of cheese products and the expanding food service sector drive cheese consumption in Mexico.
- Pizza tops the list of popular cheese-based foods, with shredded cheeses from the U.S. favored for toppings.
- Mexico’s continued reliance on imports indicates a booming opportunity for U.S. dairy farmers.

Can you envision a future where Mexico’s love for cheese surpasses its fondness for tacos? This may seem improbable, but the burgeoning cheese consumption in Mexico is turning this into a reality. As cheese becomes a central part of Mexican cuisine, the opportunities for U.S. dairy farmers are vast and promising. The recent GAIN report states, ‘One of the most significant trends in the Mexican cheese market is the increasing consumer preference for a wider variety of cheeses.’ With cheese consumption in Mexico projected to surge by a remarkable 4% next year, driven in part by the popularity of U.S. shredded cheeses on pizzas, the potential for American dairy farmers to benefit from this trend is enormous. As cheese imports from the U.S. escalate, are dairy stakeholders ready to meet this demand? The stakes have never been higher for both nations as the cheese craze unfolds, promising a future of growth and success in the Mexican cheese market.
A Diverse Cheese Revolution: Mexico’s Evolving Palate and the Rise of U.S. Imports
Mexico is experiencing a notable shift in cheese consumption patterns, driven by an increasing consumer preference for diverse cheeses. This trend reflects a broader global palate, where traditional tastes mingle with new, exciting options. The Global Agricultural Information Network (GAIN) report highlights this development, noting a surge in demand for varied cheese types among Mexican consumers.
But what’s catapulting this growing appetite for different cheeses? Look no further than Mexico’s evolving food culture, prominently featuring pizza as a staple. Once just a humble dish, pizza has climbed to become the second-most consumed food item in the country, just behind tacos. As a result, the demand for U.S. shredded cheeses, which pizza makers prefer, has significantly increased.
The GAIN report provides illuminating statistics to showcase this trend. In 2024, cheese consumption in Mexico is forecast to grow by 4%, reaching 649,000 metric tons. This represents a remarkable shift from previous years and underscores the burgeoning demand.
Furthermore, with expanding exports and robust domestic demand, the Mexican cheese industry is poised for continued growth, affirming its significance in the region. As Mexico’s culinary landscape evolves, so does the opportunity for various cheese producers to tap into this vibrant market.
Mexico’s Cheese Boom: A Ripple Effect for U.S. Dairy Farmers
The uptick in cheese consumption in Mexico is a win for cheesemakers and a golden opportunity for U.S. dairy farmers. As the primary supplier, the U.S. stands to gain from this unprecedented boom in Mexican cheese demand. According to recent figures, Mexico imports around 85% of its cheese from the United States, indicating a deep and lucrative relationship.
For U.S. dairy farmers, the rise in cheese exports is a cornerstone in securing economic stability amidst fluctuating domestic demands. By supplying Mexican markets, U.S. farmers can mitigate risks associated with potential downturns in domestic consumption. Furthermore, this growing export market encourages the adoption of innovative farming techniques and boosts investments in higher-quality milk production. This aligns with meeting Mexico’s demand for diverse cheese varieties, further cementing the U.S.’s market dominance.
U.S. dairy farmers hold the key to their success in the thriving Mexican cheese market. They can solidify their position and capitalize on this growing market by forming strategic alliances with Mexican food distributors and retailers. Joint marketing campaigns can boost brand visibility and preference among Mexican consumers. Moreover, investing in improving supply chain efficiencies and building infrastructure that supports seamless exports can ensure that U.S. farmers remain the top choice for Mexican cheese importers. By leveraging these strategies in a burgeoning market like Mexico, U.S. dairy farmers can create more sustainable and profitable futures for themselves, feeling empowered and in control of their market position.
Challenges and Opportunities: Capitalizing on Mexico’s Cheese Demand
Meeting the surge in Mexico’s cheese consumption presents both a thrilling opportunity and a considerable challenge for U.S. dairy farmers. On one hand, an increased demand for imported cheese signifies a potentially lucrative expansion of the American cheese market. However, it also brings forth several hurdles that must be overcome to capitalize on this growing appetite.
Challenges Ahead
First and foremost, the U.S. dairy industry could face significant logistical and supply chain pressures. The infrastructure must adapt rapidly to meet the heightened demand, ensuring that quality and delivery timelines are not compromised. Any disruptions or inefficiencies might lead to missed opportunities and increased competition from other countries eager to cater to Mexico’s expanded cheese needs.
Moreover, American farmers must adapt their production to align with the diverse preferences of the Mexican market. Cultural and culinary differences could necessitate changes in production techniques, cheese varieties, and even branding strategies to effectively capture Mexican consumers’ hearts and taste buds.
Opportunities for Innovation and Expansion
The current market dynamics present a golden opportunity for dairy farmers to innovate. Are there unexplored cheese technologies or processes that could optimize production? Consider including sustainable farming practices that boost efficiency and resonate with the growing global demand for eco-friendly products. This is a chance to lead by example and set new industry standards. By embracing innovation, U.S. dairy farmers can feel inspired and forward-thinking, ready to meet the challenges and opportunities of the evolving Mexican cheese market.
Furthermore, expanding into the Mexican market could pave the way for introducing American technology in cheese production. Cutting-edge advancements like automation and AI in dairy farming might streamline processes, ensuring reliability and consistency in supplying to international markets.
As we stand on the precipice of this cheese consumption revolution, U.S. dairy farmers and industry leaders must strategize effectively. The question is more than how to meet this demand; it is how the industry can reimagine itself. How will you leverage current trends to fortify your market position? The future holds immense promise, waiting for those ready to innovate and adapt.
Strategic Alliances and Economic Potential: The Role of Trade Policies in the U.S.-Mexico Cheese Boom
Trade policies and international relations are crucial in the booming cheese trade between the U.S. and Mexico. It’s essential to understand how free-market principles and astutely negotiated trade agreements can unlock immense economic potential for our dairy farmers. The cheese trade isn’t just a business deal; it’s a strategic alliance with our southern neighbor. Historically, policies have aimed at minimizing trade barriers and forming strong agreements that benefit American farmers. How do these policies support and expand this cheese boom? The key lies in maintaining robust, mutually advantageous economic bonds that support the interests of both nations while bolstering states like Wisconsin’s and California’s dairy sectors.
In an era where protectionism is rising, it’s essential to assess how isolationist policies could disrupt this thriving market. Would imposing tariffs or reworking trade deals affect the continuous cheese flow to the South? The trade relationship with Mexico isn’t just about dairy products; it teaches how interconnected geopolitical strategies can boost or hinder our economic well-being. Additionally, consider the broader effects of this trade connection. How might political climates and policy shifts influence agriculture and areas like the automotive and tech industries? Mexico is a trading partner, and even slight policy changes can impact various economic sectors.
This surge in cheese consumption in Mexico presents a golden opportunity for U.S. dairy farmers, a chance built on years of effective dialogue and diplomatic relations. As strategists and policymakers plan for the future, the focus should be crafting policies reinforcing international relations and ensuring these lucrative trade avenues remain strong.
The Bottom Line
As Mexico’s cheese consumption flourishes, the U.S. dairy industry is in a favorable position, poised to meet this burgeoning demand for further growth. Cheese imports from the United States constitute a substantial portion of Mexico’s cheese market, setting the stage for significant potential benefits to U.S. cheesemakers, as evidenced by the forecasted increase in production and imports.
However, it’s crucial to recognize the challenges and opportunities within this thriving market. The expanding palate of Mexican consumers, the prominence of cheese in both traditional and global cuisines, and the robust trade policies between the two nations all contribute to a complex yet promising landscape for American dairy exports.
As we look to the future of the cheese trade between the U.S. and Mexico, the question remains: How can American dairy producers continue to innovate and adapt to meet and exceed Mexico’s growing appetites? Join the conversation and share your insights and thoughts on this dynamic market shift.
Learn more:
- Why Mexico is Essential to the U.S. Cheese Markets: A Comprehensive Analysis
- How Cheese Exports and China’s Demand are Powering the US Dairy Economy in 2024
- US and Mexico Dairy Industries Strengthen Ties for Mutual Growth and Advocacy
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Bullvine Daily is your essential e-zine for staying ahead in the dairy industry. With over 30,000 subscribers, we bring you the week’s top news, helping you manage tasks efficiently. Stay informed about milk production, tech adoption, and more, so you can concentrate on your dairy operations.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!