4.2 million on GLP-1 drugs just shifted dairy demand. Yogurt up 3x. Cheese down 7%. Your protein premiums won’t last past 2027.
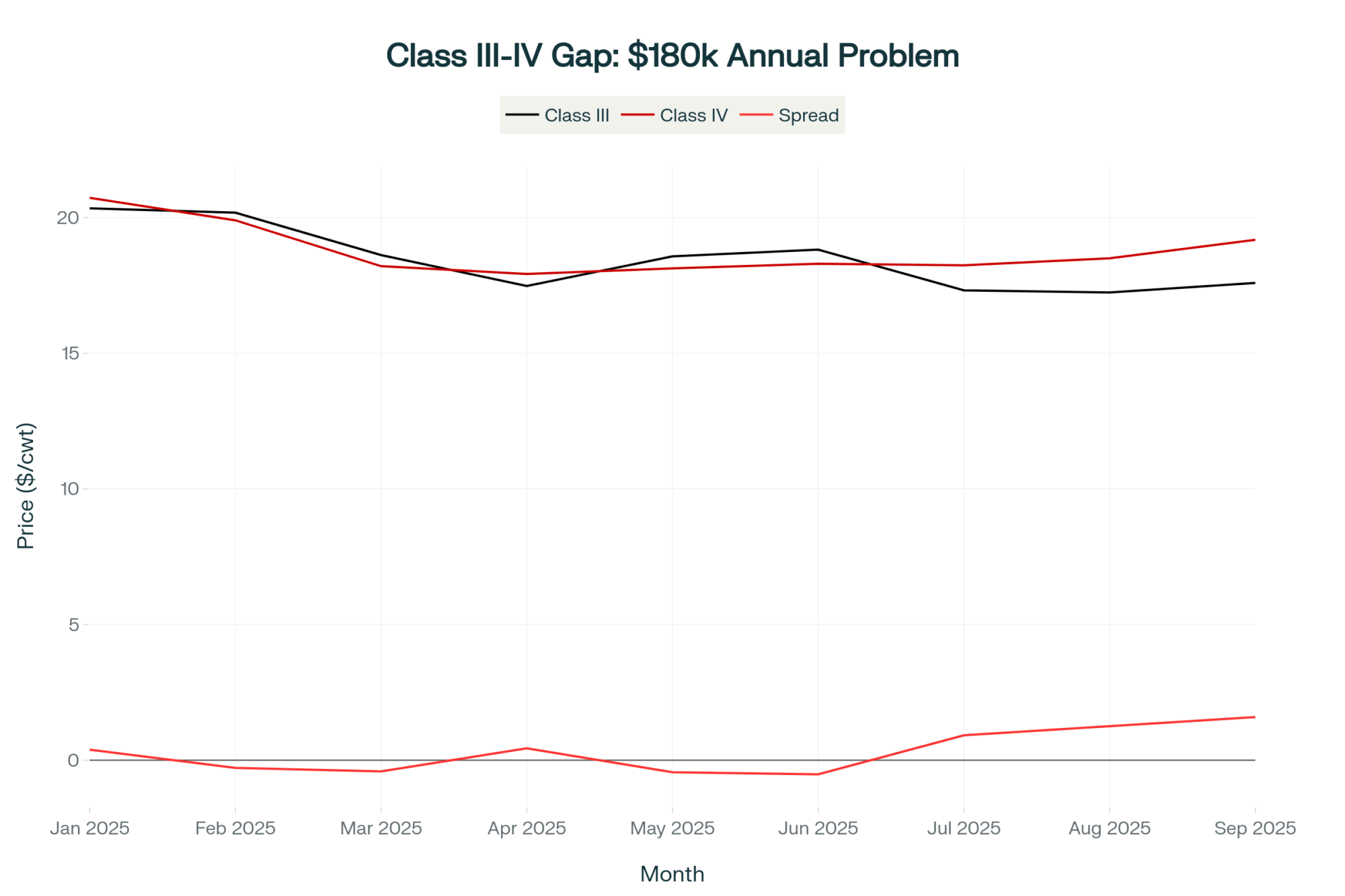
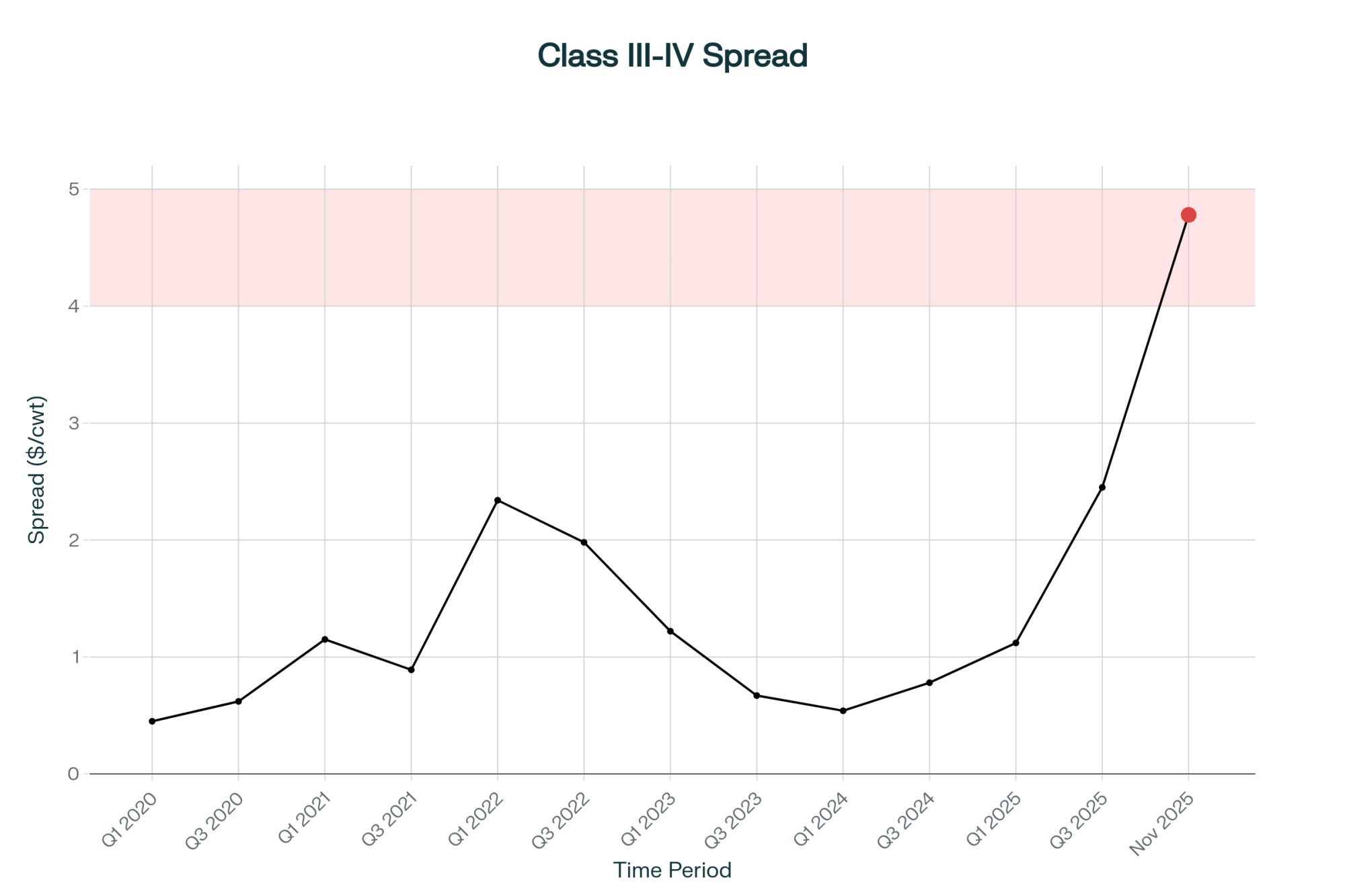
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Right now, the same tanker of milk earns $10,755 more monthly at a cheese plant than a butter plant—that’s the historic $4.78 Class III-IV spread talking. Here’s why it matters: processors invested $10 billion in capacity designed for 3.35% protein milk, but they’re getting 3.25%, forcing them to import protein at $6.50/lb while offering domestic producers $3-5/cwt premiums. Smart farms are already cashing in through amino acid programs (paying back in 60 days), beef-on-dairy breeding ($950 extra per calf), and direct processor contracts. Add 4.2 million new GLP-1 patients needing triple the yogurt, and this protein shortage has legs through 2026. But genetics will catch up by 2027, making this an 18-month window. Your first move: enroll in DMC by December 20th—$7,500 buys up to $50,000 in margin protection when Class III corrects.

Monday morning’s USDA Milk Production Report delivered some surprising news that I think reveals one of the most significant opportunities we’ve seen in years. You know how September production hit 18.99 billion pounds—up 4.2% from last year? Well, our national herd expanded by 235,000 head to reach 9.58 million cows, which is the largest we’ve had since 1993.
And here’s what caught my attention: within 48 hours of that report, December through February Class III contracts on the CME dropped toward $16 flat, yet whey protein concentrate is holding steady at $3.85 per pound according to the latest Dairy Market News.
What I’ve found, analyzing these component value spreads and the processing capacity situation, is that we’re looking at opportunities worth hundreds of millions of dollars across the industry. The farms recognizing these signals over the next year and a half… well, they could find themselves in much stronger positions than those who don’t.
When Component Values Don’t Make Sense Anymore
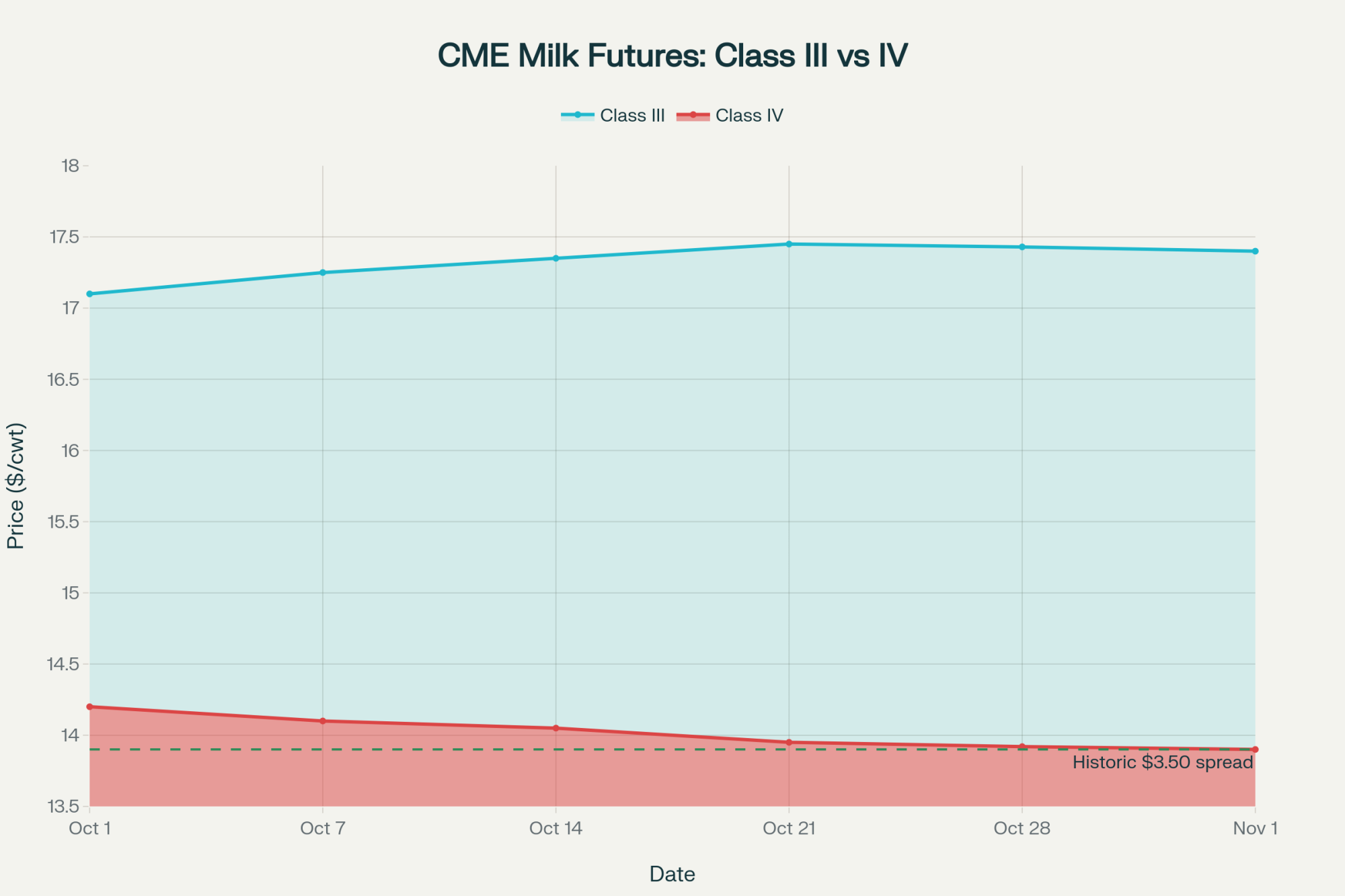
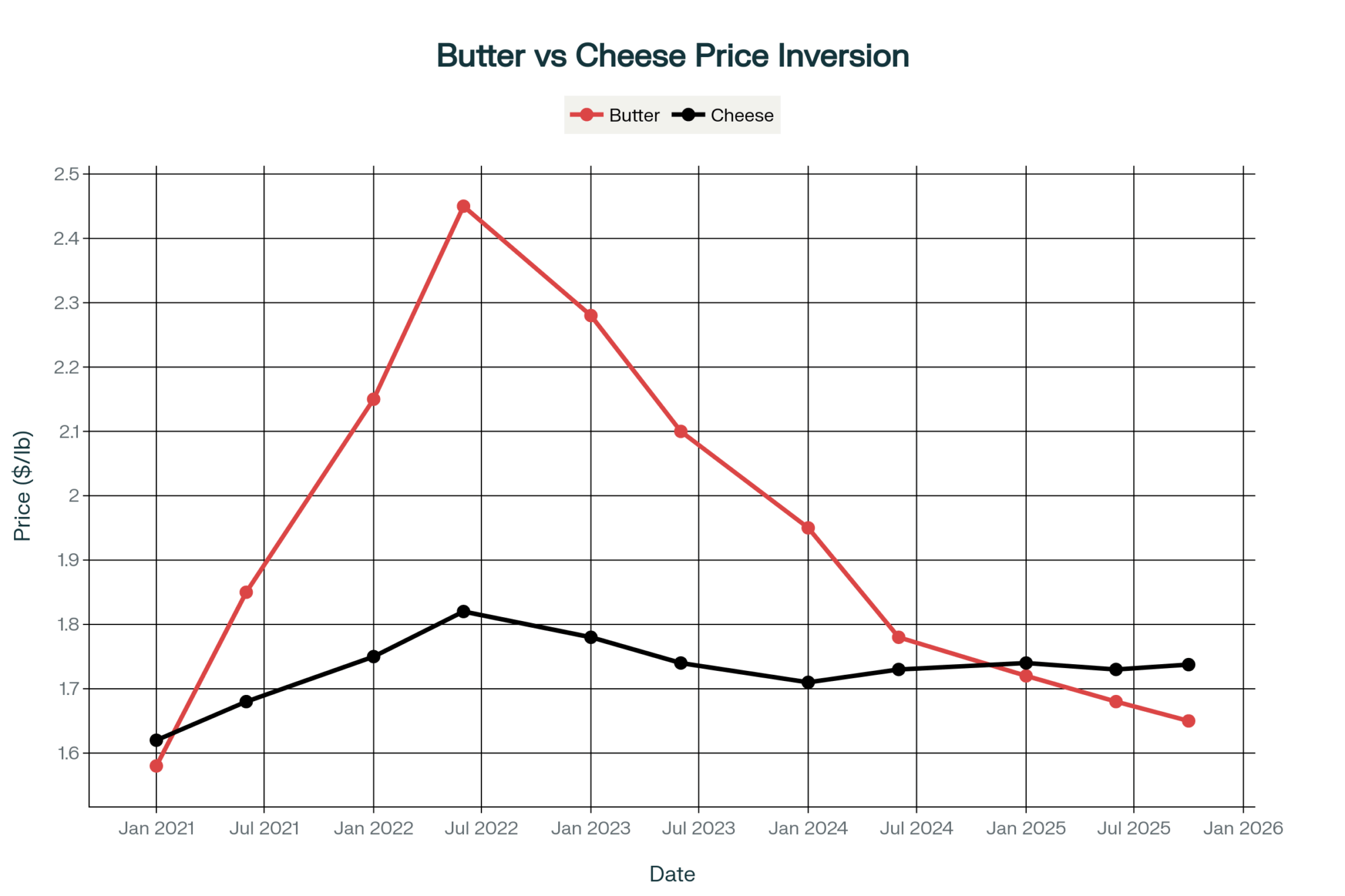
Let me share what’s happening with the Class III-IV spread—it hit $4.78 per hundredweight this week. That’s the widest gap we’ve ever had in Federal Order history, based on the CME futures data from November 13th.
You probably already know this, but for a 1,000-cow operation averaging 75 pounds daily, that’s a $10,755 monthly difference in revenue. Just depends on whether your milk heads to cheese or butter-powder processing. We’re talking real money here.
What’s even more dramatic is the component breakdown. USDA’s weekly report from November 13th shows whey protein concentrate at 34% protein trading at $3.85 per pound. But WPC80 instant? That’s commanding $6.35 per pound, and whey protein isolate reaches $10.70. Meanwhile—and this is what gets me—CME spot butter closed Friday at just $1.58 per pound.
I’ve been around long enough to remember when these components traded pretty much at parity. This protein-to-fat value ratio of about 2.44:1… that’s not your normal market fluctuation. It’s fundamentally different.
Here’s what the dairy market’s showing us right now:
- Class III futures sitting at $16.07-16.84/cwt through Q1 2026
- Class IV futures stuck in the mid-$14s
- That record $4.78/cwt Class III-IV spread
- Whey products are at historically high premiums
- Butter near multi-year lows, even with strong exports
The Processing Puzzle: Creating Opportunities
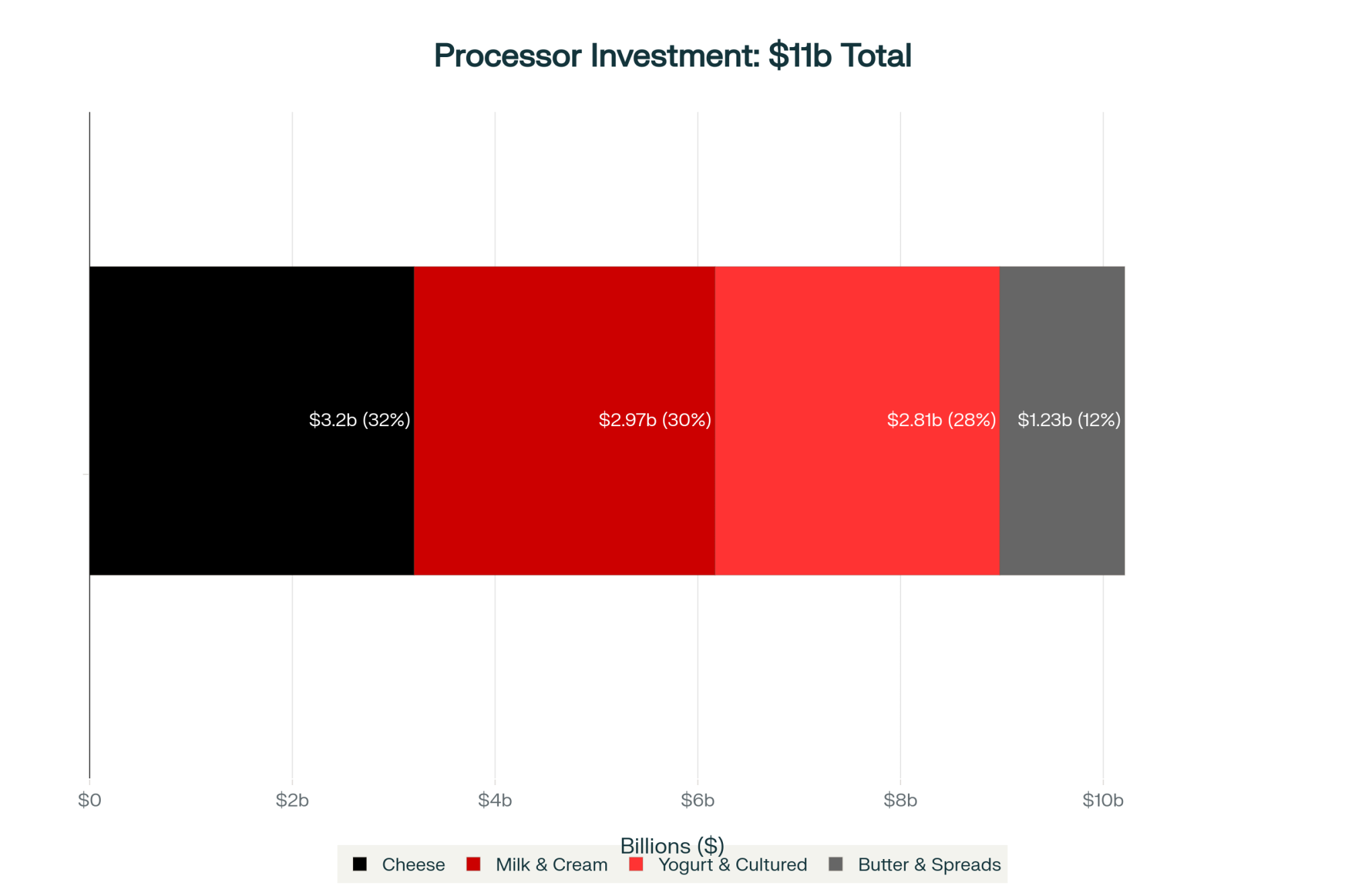
What’s interesting here is that between 2023 and 2025, processors committed somewhere around $10-11 billion to new milk processing capacity across the country—the International Dairy Foods Association has been tracking all this. We’re seeing major investments: Leprino Foods and Hilmar Cheese each building facilities to handle 8 million pounds daily, Chobani’s $1.2 billion Rome, NY plant, which they announced in 2023, plus that $650 million ultrafiltered dairy beverage facility Fairlife and Coca-Cola broke ground on in Webster, NY, last year.
Now, these plants were all engineered with specific assumptions about milk composition. The equipment manufacturers—Tetra Pak, GEA, those folks—they design systems expecting milk with 3.8-4.0% butterfat and 3.3-3.5% protein. That’s what everything was sized for.
But what’s actually showing up at the dock? Federal Order test data from September shows milk testing 4.40% butterfat but only 3.25% protein. That 17% deviation from design specs creates all sorts of operational headaches.
You see, cheese yields suffer because the casein networks can’t trap all that excess butterfat during coagulation—there’s been good research on this in the dairy science journals. One Midwest plant manager I spoke with—he couldn’t go on record, company policy—but he mentioned they’re dealing with reprocessing costs running $150,000-200,000 monthly, depending on facility size.
The result? According to USDA Foreign Agricultural Service trade data from July, U.S. imports of skim milk powder jumped 419% year-over-year through the first seven months of 2025. Processors are literally importing milk protein concentrate at $4.50-6.50 per pound—paying premium prices for components that domestic milk isn’t providing in the right concentrations.

The GLP-1 Factor Nobody Saw Coming
Looking at Medicare’s new GLP-1 coverage expansion, they enrolled 4.2 million patients in just two weeks after announcing medication prices would drop from around $1,000 monthly to $245 for Medicare Part D participants. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services released those enrollment numbers on November 14th.
These medications—Ozempic, Wegovy—they dramatically change what people can tolerate eating. Consumer tracking research shows cheese consumption drops around 7% in GLP-1 households, butter falls nearly 6%, but yogurt consumption? It runs three times higher than the typical American rate. These patients, they can’t physically handle high-fat foods the way they used to.
The nutritional requirements are pretty specific, too. Bariatric surgery guidelines recommend patients get 1.0-1.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight daily to preserve muscle mass during weight loss. For someone weighing 200 pounds, that’s 91-136 grams of protein every day.
With potentially 6.7 million Medicare beneficiaries eligible, according to Congressional Budget Office projections, we’re looking at roughly 38 million pounds of additional whey protein demand annually. And that’s just from this one demographic.
What’s Working for Farms Right Now
Quick Wins (Next 60 Days)
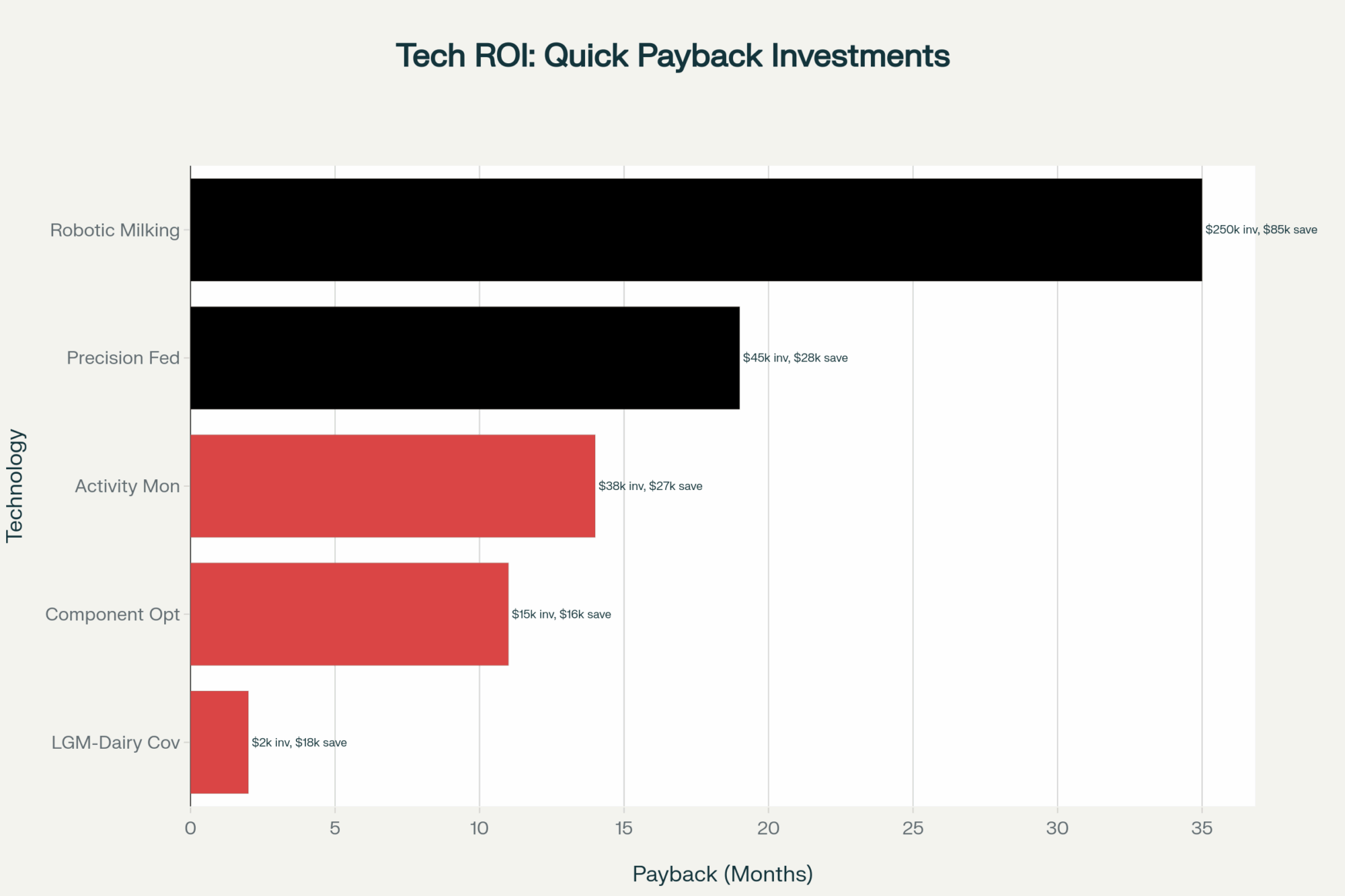
What I’m seeing with precision amino acid balancing is really encouraging. Dr. Charles Schwab from the University of New Hampshire has been recommending targeting lysine at 7.2-7.5% of metabolizable protein and methionine at 2.4-2.5%. Farms implementing this are seeing 0.10-0.15% protein gains within 60-75 days—that’s based on DHI testing data from operations in Wisconsin and New York.
For your typical 200-cow herd in the Upper Midwest or Northeast, that translates to about $2,618-3,435 monthly in improved component values at current Federal Order prices. Plus, you avoid those Federal Order deductions when the 3.3% protein minimum kicks in on December 1st.
The cost? It costs about $900-1,500 per month for rumen-protected amino acids from suppliers like Kemin, Adisseo, or Evonik. Pretty straightforward return on investment if you ask me.
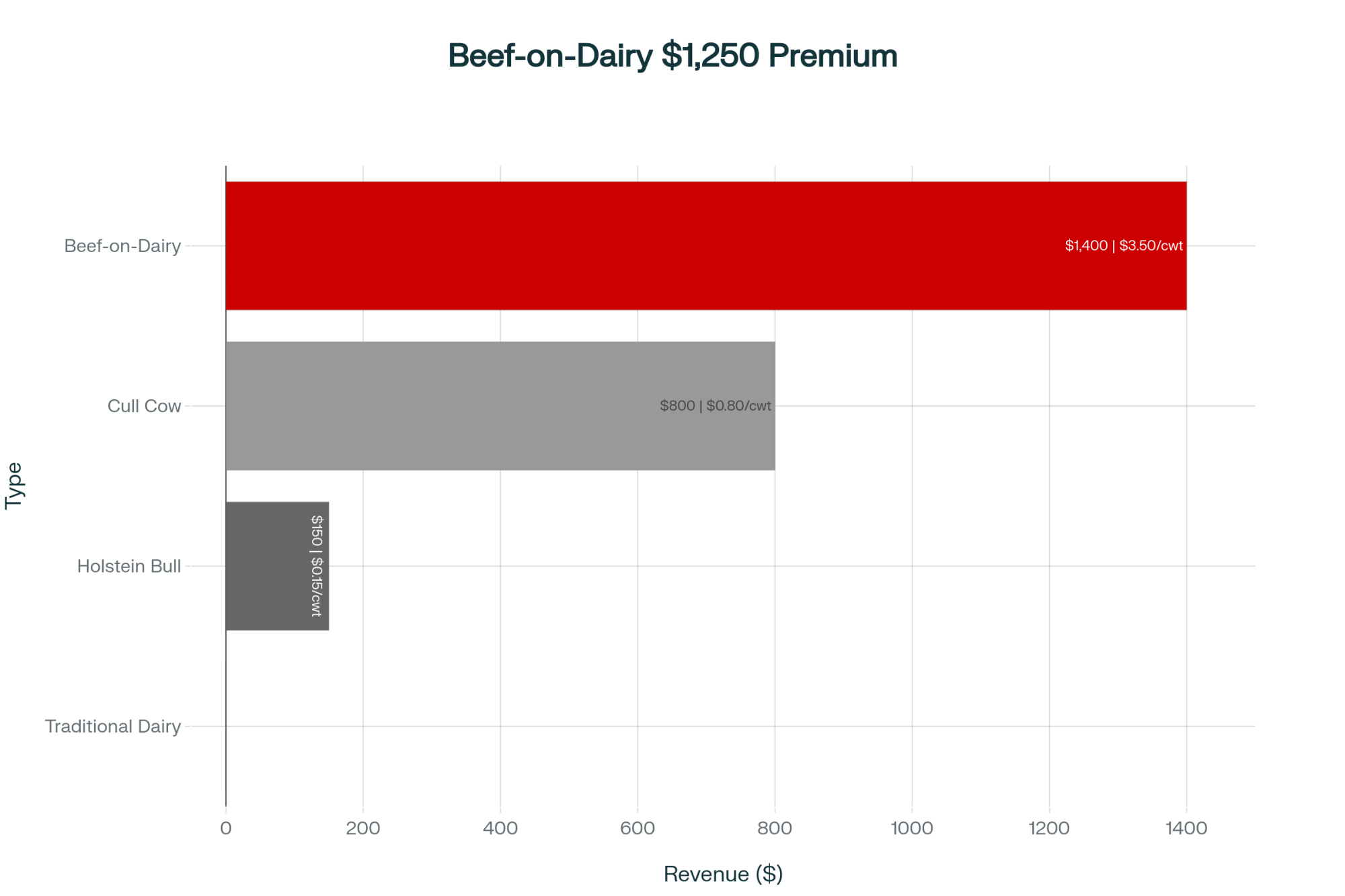
On the calf side, beef-on-dairy’s generating immediate cash. The Agricultural Marketing Service reported on November 11th that crossbred calves are averaging $1,400 at auction while Holstein bulls bring $350-450. So a 200-cow operation breeding their bottom 35%—that’s 70 cows—captures an additional $70,000 annually.
Several producers I know in Kansas and Texas are forward-selling spring 2026 calves at $1,150-$1,200, with locked prices. That provides working capital for other investments, which is crucial right now.
Strategic Medium-Term Moves
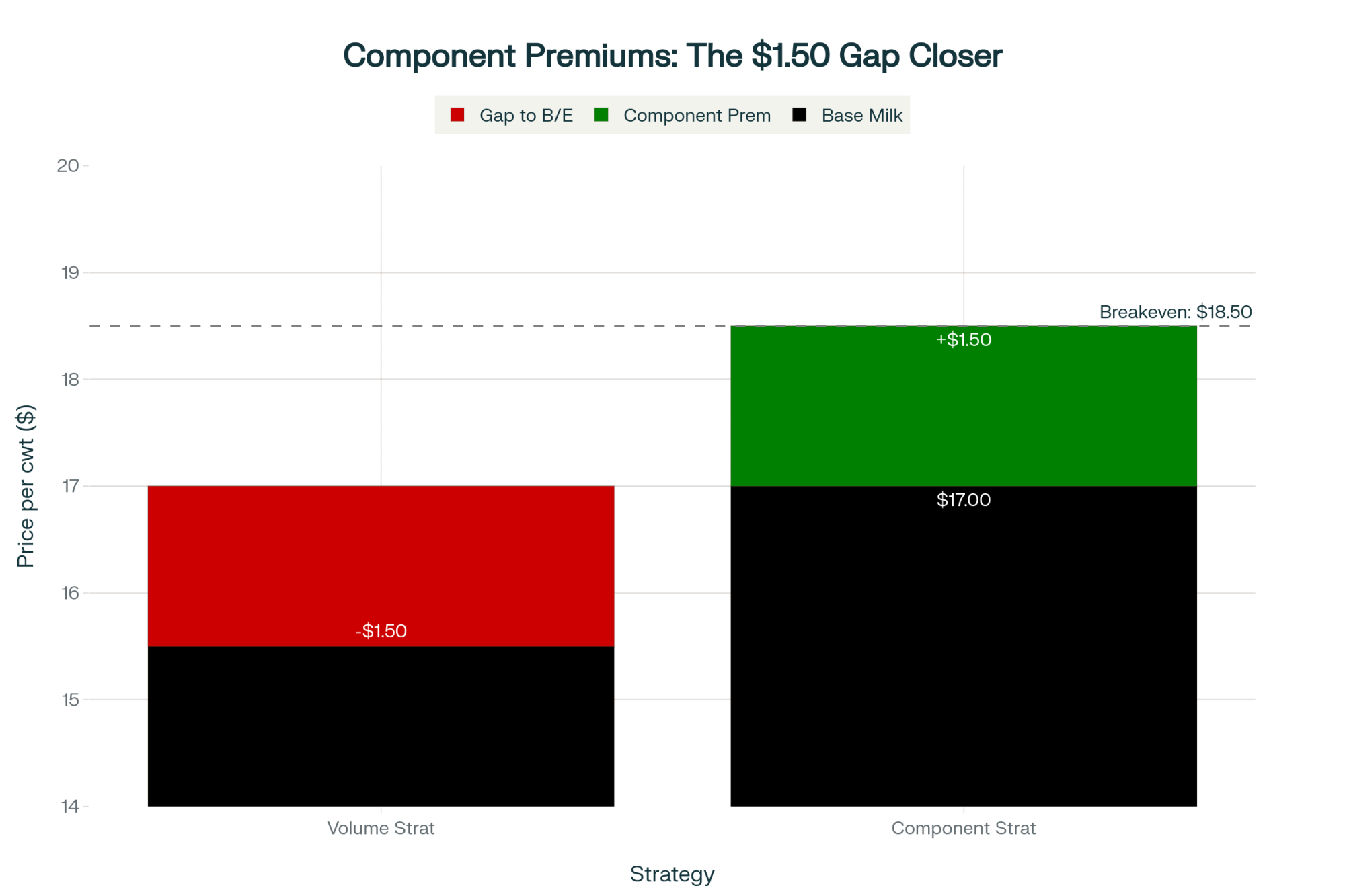
What’s proving interesting is how some farms approach processors directly rather than waiting for co-op negotiations. I know several operations in Vermont and upstate New York that secured $18.50-20.00/cwt contracts for milk testing above 3.35% protein. That’s a $3.00-5.50 premium over standard Federal Order pricing.
The genetics side is evolving quickly, too. Select Sires’ August proof run data shows that farms using sexed semen from A2A2 bulls with strong protein profiles—+0.08 to +0.12%—are well positioned for the late-2027 market when these animals enter production. Bulls like 7HO14158 BRASS and 7HO14229 TAHITI combine A2A2 status with solid protein transmission according to Holstein Association genomic evaluations.
Out in New Mexico, one producer working with a regional yogurt processor mentioned they’re getting similar premiums for consistent 3.4% protein milk. “The processor needs reliability more than volume,” she told me. “They’re willing to pay for it.” That Southwest perspective shows these opportunities aren’t just limited to traditional dairy regions.
The Jersey Question
Now, I realize suggesting Jersey cattle to Holstein producers usually gets some eye rolls. But here’s what successful operations are doing—they’re not converting whole herds. They’re introducing 25-50 Jersey or Jersey-Holstein crosses as test groups.
One Vermont producer I talked with added 40 Jerseys last year and is seeing interesting results. These animals naturally produce 3.8-4.0% protein milk and carry 60-92% A2A2 beta-casein genetics according to Jersey breed association data.
Yes, Jerseys produce 20-25% less volume. But they also eat 25-30% less feed based on university feeding trials. When you run the full economic analysis—feed costs, milk volume, component premiums—several farms report net advantages of $1.90-3.30 per cow daily.
Of course, results vary by region. What works in Vermont might not pencil out in California’s Central Valley or Idaho. You’ve got to run your own numbers.
A central Wisconsin producer running 600 Holsteins told me last week: “I’ve got too much invested in facilities and equipment sized for Holsteins to start mixing in Jerseys. For my operation, focusing on amino acids and genetics within my Holstein herd makes more sense.” And that’s a valid perspective—it really does depend on your specific situation.
Down in Georgia, another producer with 350 cows mentioned they’re seeing entirely different dynamics. “Our heat stress issues mean Jerseys actually perform better than Holsteins during summer months,” she said. “The component premiums plus heat tolerance make them work for us.” Regional differences matter.
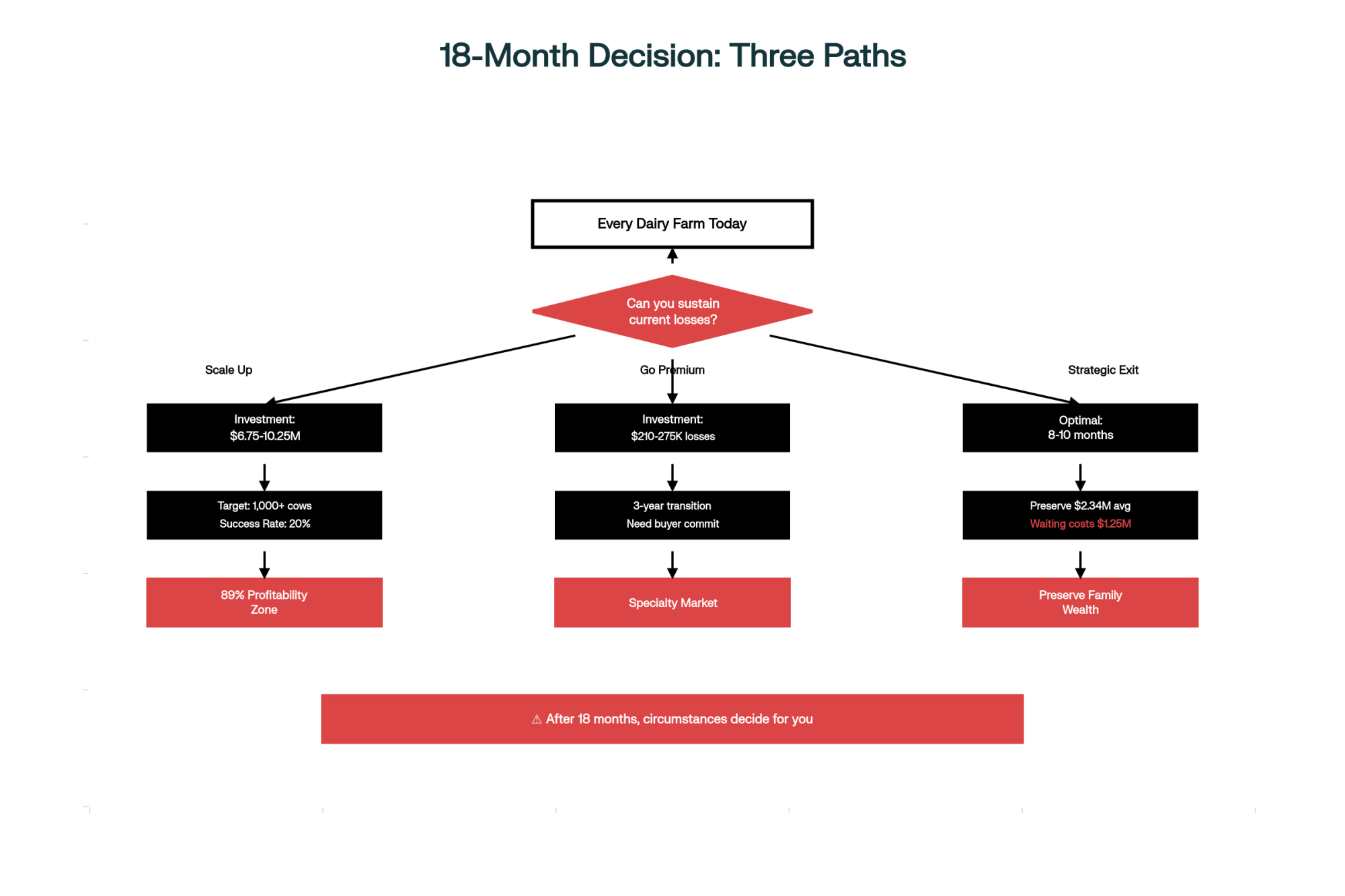
Timing the Market: When Windows Close

Beef-on-Dairy Reality Check
Here’s something to watch carefully. Patrick Linnell at CattleFax shared projections at their October outlook conference showing beef-on-dairy calf numbers reaching 5-6 million by 2026. That would be 15% of the entire fed cattle market, up from essentially zero in 2014.
October already gave us a warning when USDA-AMS reported that prices had dropped from $1,400 to $1,204 per head in just a few weeks. Linnell tells me the premium, averaging $1,050 per calf, will likely shrink significantly as supply increases. His advice? Lock forward contracts now at $1,150-1,200 for 2026 calf crops. Once the market gets oversupplied, we could see prices settling at $900-1,050 by late 2026. Still better than Holstein bull prices, but not today’s windfall.
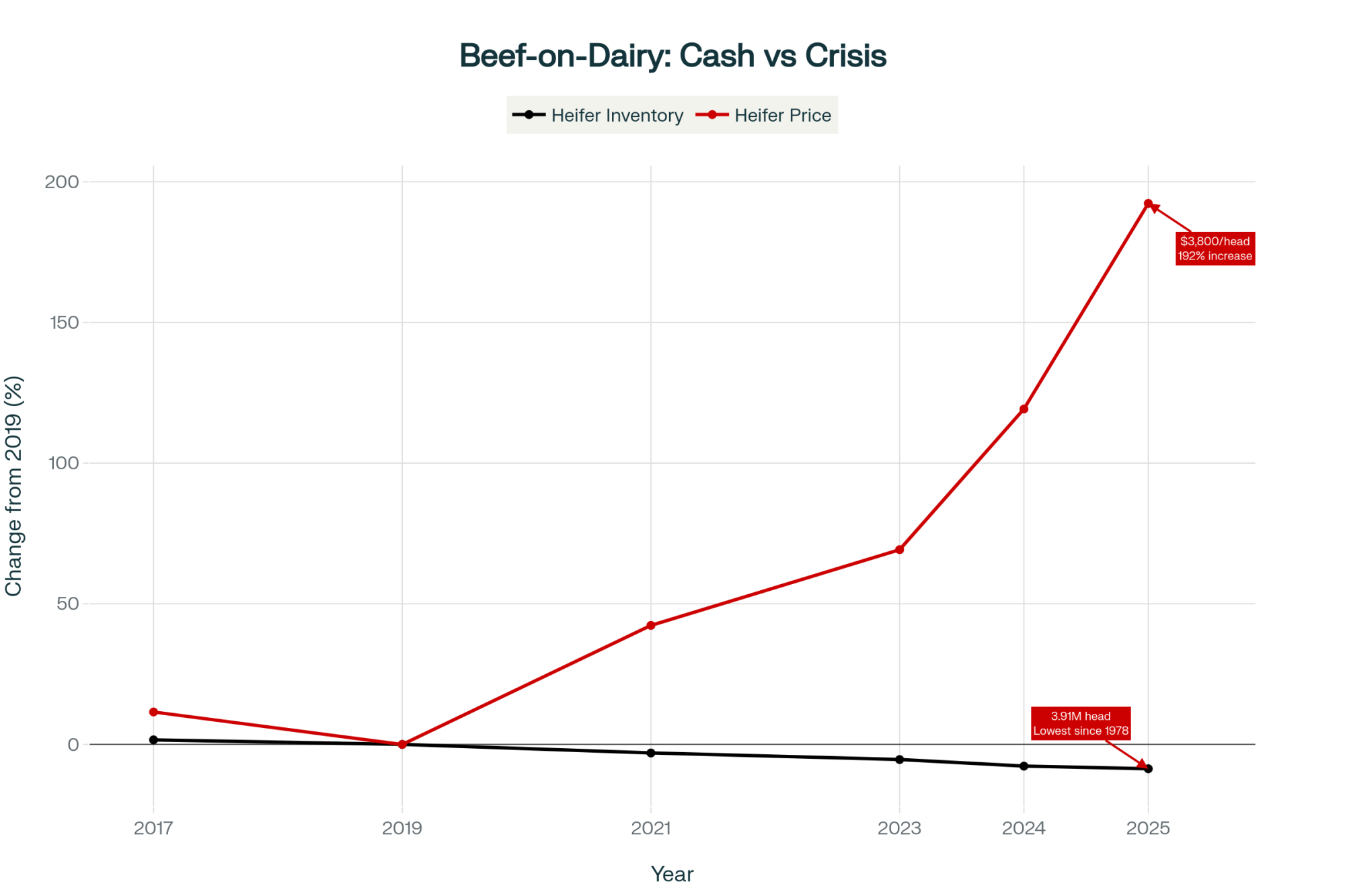
The Heifer Shortage Nobody’s Prepared For
Ben Laine, CoBank’s dairy economist, published some concerning modeling in their August 27th outlook. We’re looking at 796,334 fewer dairy replacement heifers through 2026 before any recovery begins in 2027.
This creates an interesting dynamic in which beef calves might be worth $900-1,050, while replacement heifers cost $3,500-4,000 or more. For a 200-cow operation needing 40 replacements annually, that’s $150,000 for heifers, while your beef calf revenue only brings in $136,500. That’s a $13,500 gap that really squeezes cash flow.
Farms implementing sexed semen programs now can produce their own replacements for $45,000-60,000 in raising costs, according to University of Wisconsin dairy management budgets. Those still buying heifers in 2027? They’ll be paying premium prices that could strain even healthy operations.
Why European Competition Isn’t the Threat
With European butter storage at 94% capacity according to EU Commission data from November, and global production up 3.8% per Rabobank’s Q4 report, you might wonder—why won’t cheap imports flood our market?
Well, USDA’s Foreign Agricultural Service analysis from October shows U.S. dairy tariffs add 10-15% to European MPC landed costs. Container freight from Europe runs $800-1,200 per 20-foot unit—that’s roughly $0.04-0.06 per pound based on the Freightos Baltic Index from November. When you add it up, European MPC lands here at $4.74-5.33 per pound. Not really undercutting domestic prices.
Plus, companies like Fonterra and Arla are pivoting toward Asian markets where they get better prices without tariff hassles. Fonterra announced in August that it’s selling its global consumer business to Lactalis for NZ$4.22 billion ($2.44 billion USD) to focus on B2B ingredients for Asian and Middle Eastern markets.
Though I should mention, one California dairyman running 800 cows pointed out that trade dynamics can shift quickly. What protects us today might not tomorrow. That’s a fair perspective worth monitoring.
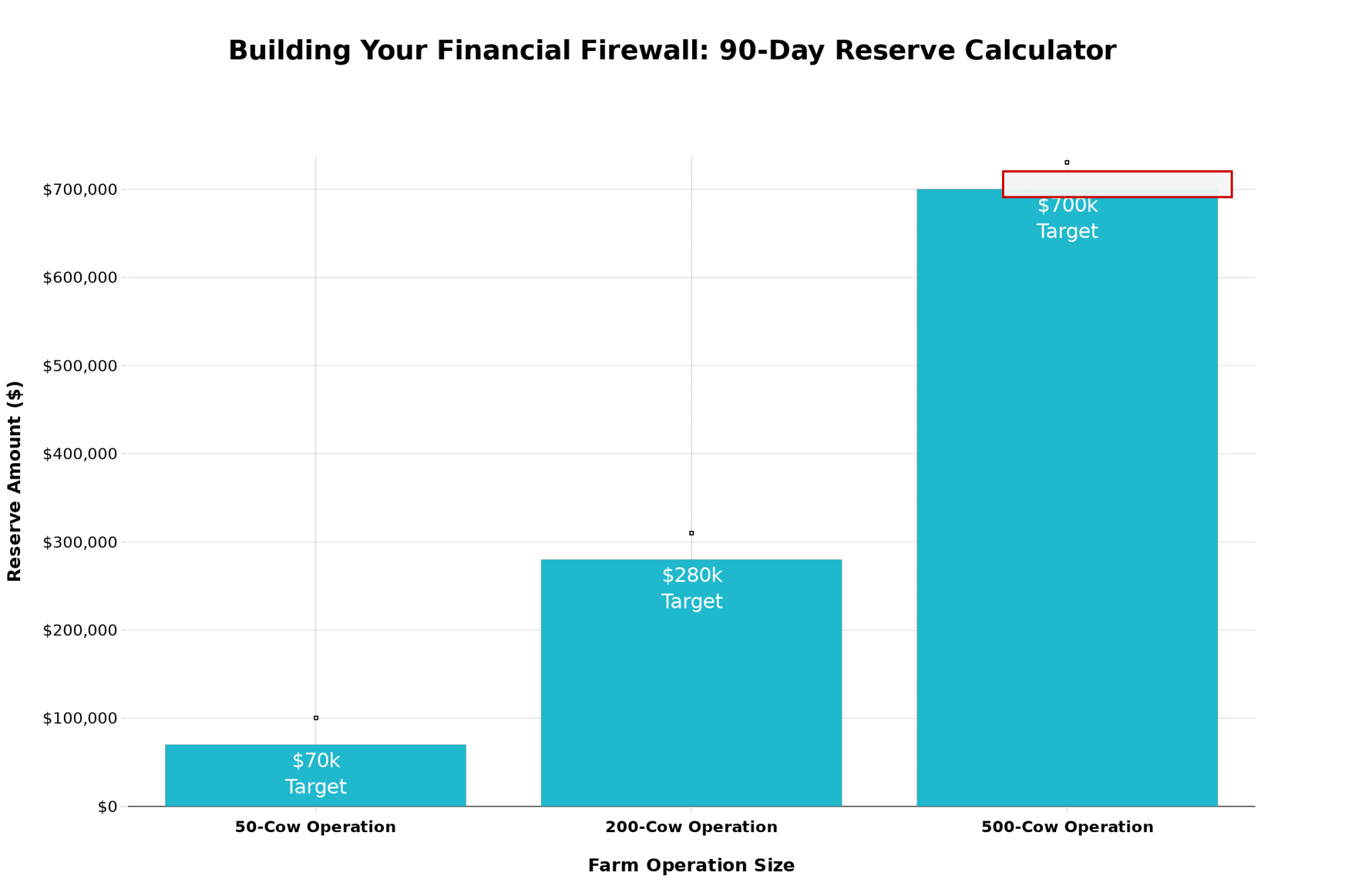
Surviving the Next 90 Days
With Class III futures at $16.07-16.84 according to CME closing prices from November 15th, and many operations facing breakeven costs of $13.50-15.00 based on October profitability analysis, margins are tight. Really tight.
Creative Financing That Works
FBN announced in November that they’re offering 0% interest through September 2026 on qualifying purchases—that includes amino acids and nutrition products. No cash upfront, payments due next March after your protein improvements show in milk checks. Farm Credit Canada offers similar programs with terms of 12-18 months, according to its 2025 program guidelines.
For beef-on-dairy, several feedlots are doing interesting things with forward contracts. One Kansas feedlot operator pre-sells 40-50 spring calves at $1,300 with a 50% advance payment. That generates $26,000-$32,500 in January working capital—enough for Jersey purchases or to cover operating expenses during tight months.
Some processors are even offering advances against future protein premiums. I’ve heard of deals—companies prefer not to be named—where they’ll provide $15,000-20,000 upfront against a 24-36 month high-protein supply agreement. The advance recovers through small deductions from premium payments.
Critical December Dates
Here’s what you need on your calendar:
December 1st: Federal Order 3.3% minimum protein requirement takes effect. If you’re testing below that, deductions start immediately.
December 20th: DMC enrollment deadline for 2026 coverage. Some states have earlier deadlines—check with your local FSA office this week.
December 31st: Last day to lock beef-on-dairy forward contracts for Q1 2026 delivery at most feedlots.
The One Decision That Can’t Wait: DMC Enrollment
If you take nothing else from this discussion, please hear this: enroll in Dairy Margin Coverage at $9.50/cwt before December 20th.
At $7,500 for 5 million pounds of Tier 1 coverage, DMC provides crucial protection. Mark Stephenson from the University of Wisconsin found that 13 of the last 15 years delivered positive net benefits at $9.50 coverage. With margins at $5.07-6.34/cwt based on current milk and feed prices, and production growing 4.2%, the odds of needing this protection in early 2026 are pretty high.
Think about it—if margins drop to $9.00/cwt with Class III at $15.50, you’d receive $25,000. Drop to $8.50/cwt? That generates a $50,000 payment according to the DMC calculator. When’s the last time $7,500 bought you that kind of downside protection?
Looking at the Bigger Picture
What we’re seeing here isn’t just another market cycle. Dr. Marin Bozic at the University of Minnesota characterizes these conditions as a significant structural shift—the kind that happens maybe once in a generation. You’ve got mismatched processing capacity, changing consumer preferences accelerated by weight-loss drugs, and genetics still catching up to new realities, all converging at once.
The arbitrage opportunities won’t last forever—that’s just how markets work. Current trajectories suggest beef-on-dairy saturates by mid-2026, protein premiums moderate by 2027, and heifer shortages resolve by 2028. But for producers acting strategically over the next 18-24 months, there’s a real opportunity to strengthen operations.
The November 10th production report showing 4.2% growth might seem like bad news at first glance. But understanding component economics and arbitrage opportunities actually illuminates a path forward. The math is compelling—it’s really about positioning yourself to take advantage.
Key Actions This Week
Looking at everything we’ve discussed, here’s what I’d prioritize:
This Week’s Must-Do List:
- Call your FSA office about DMC enrollment—deadline’s December 20th, but varies by state
- Get quotes on rumen-protected amino acids and ask about input financing terms
- Contact at least three feedlot buyers about spring 2026 calf contracts
- Schedule meetings with specialty processors within 50 miles
Planning Through 2026:
- Target 3.35-3.40% protein through nutrition management
- Consider sexed semen on your top 40% for A2A2 and protein traits
- Evaluate a small Jersey trial group if facilities and regional economics align
- Keep an eye on protein contract opportunities above $2.50/cwt
Risk Management Priorities:
- Watch beef calf forward pricing—below $1,150 means reassessing your breeding program
- Monitor heifer prices in your area—over $3,200 signals a serious shortage ahead
- Track processor premium offers—lock anything over $2.50/cwt
- Review component tests monthly and adjust accordingly
What other producers are telling me is that the farms coming out ahead won’t necessarily have perfect strategies. They’ll be the ones bridging the next 90 days through smart financing and risk management while these component markets sort themselves out.
DMC enrollment alone could make the difference between staying in business and having difficult conversations with your lender come February.
You know, this opportunity window is real, but it won’t stay open indefinitely. The clock’s ticking—DMC enrollment ends December 20th, and every day you wait on strategic decisions is a day your competition might be moving ahead. The question isn’t whether these opportunities exist… it’s whether you’re positioned to capture them.
And that’s something worth thinking about over your next cup of coffee.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- DMC by Dec 20 (Non-Negotiable): $7,500 premium buys $25,000-50,000 protection when Class III corrects—enrollment closes in 33 days
- Protein Boost Pays Fast: Amino acids cost $1,200/month, deliver 0.15% protein gain in 60 days, return $3,000+ monthly for 200 cows
- Beef-on-Dairy Has 12-Month Window: Today’s $1,400 calves drop to $900-1,050 by late 2026—lock $1,150+ contracts now
- Chase Processor Premiums: Direct contracts pay $3-5/cwt for 3.35%+ protein milk, but only through 2027 as capacity fills
- The Math Is Clear: $4.78 Class III-IV spread = $10,755/month extra at cheese plants. This historic gap closes within 18-24 months.
Complete references and supporting documentation are available upon request by contacting the editorial team at editor@thebullvine.com.
Learn More:
- Rumen-Protected Amino Acids: The Secret to Healthier Cows, Higher Profits, and a Sustainable Future – This guide details the tactical playbook for implementing the amino acid strategy mentioned in our main article, revealing how to balance lysine and methionine to achieve the 0.15% protein gains and immediate ROI outlined.
- Beyond the Milk Check: How Dairy Operations Are Building $300,000 in New Revenue Today – This strategic breakdown reveals how top operations are stacking revenue streams, detailing the real-world math behind maximizing beef-on-dairy profits and leveraging DMC as a high-return financial tool to survive margin compression.
- The GLP-1 Gold Rush: Why Dairy Protein is Pharma’s New Best Friend – Dives deeper into the “GLP-1 Factor,” showing how new consumer health trends are creating a massive protein market and why selecting for specific genetic traits like A2A2 and high protein deviation is the key to capturing premiums.
 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!
Join over 30,000 successful dairy professionals who rely on Bullvine Weekly for their competitive edge. Delivered directly to your inbox each week, our exclusive industry insights help you make smarter decisions while saving precious hours every week. Never miss critical updates on milk production trends, breakthrough technologies, and profit-boosting strategies that top producers are already implementing. Subscribe now to transform your dairy operation’s efficiency and profitability—your future success is just one click away.







 Join the Revolution!
Join the Revolution!